k8s
- 基础环境运维索引
- 安装docker
- 手工安装docker
- k8s常用命令
- 安装k8s-v1.20.15
- 安装k8s-v1.28.0
- k8s-v1.30.3&&rancher-v2.9.1
- 离线安装k8s-v1.20.15
- docker-keepalived
- 使用KUBE-VIP部署高可用k8s
- k8s单节点升级为高可用
- k3s证书过期&ks8证书过期&rancher 轮换证书
- rancher安装手册
- rancher2.8使用手册
- nfs网络共享
- rancher-2.5.15操作手册
- 使用nfs-storageClass
- calico-image-vp-whdev-v3.21.6
- 挂载磁盘&&分区
- 私有地址网段
- 运维常用排除方法
- k8s集群备份(迁移)工具velero
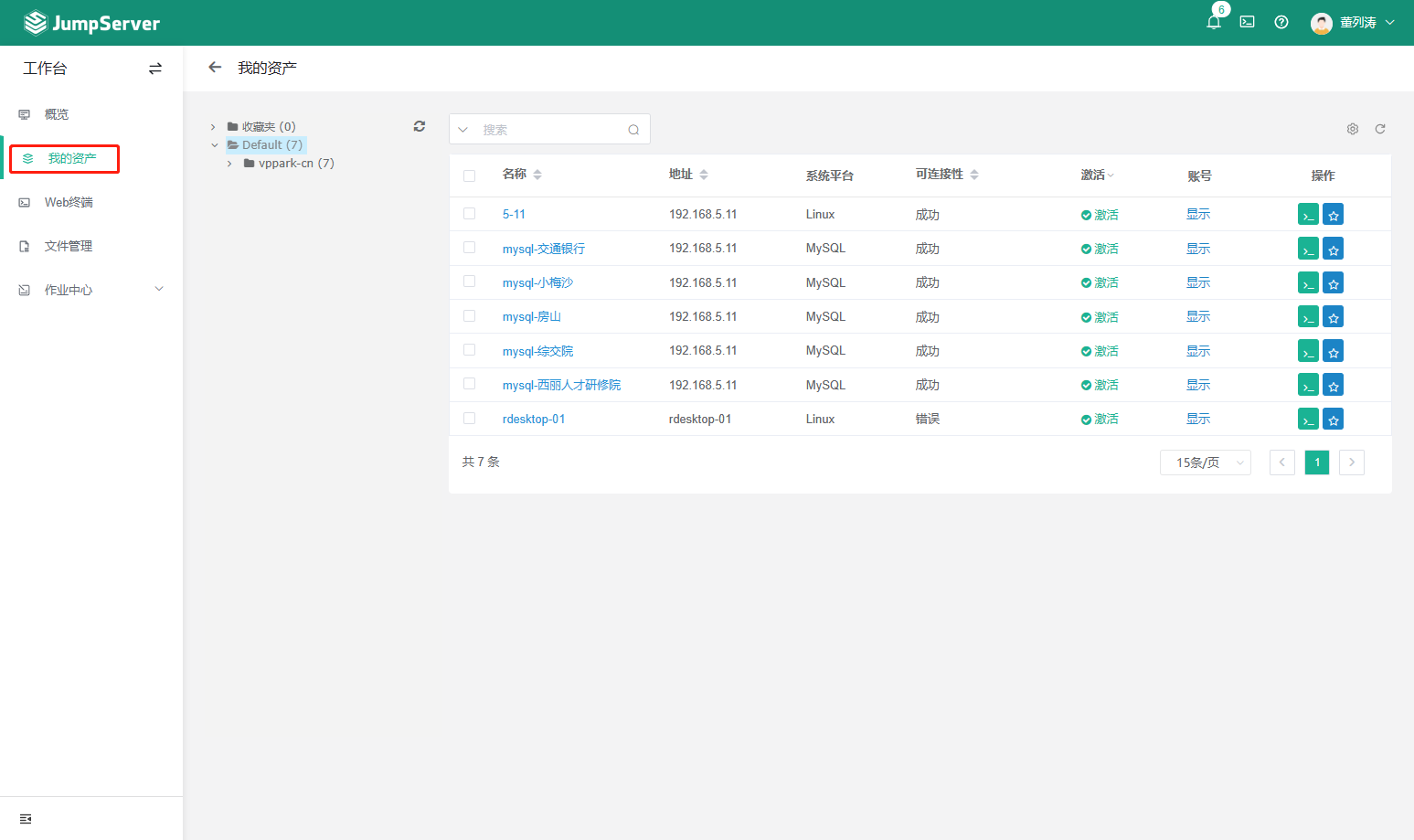
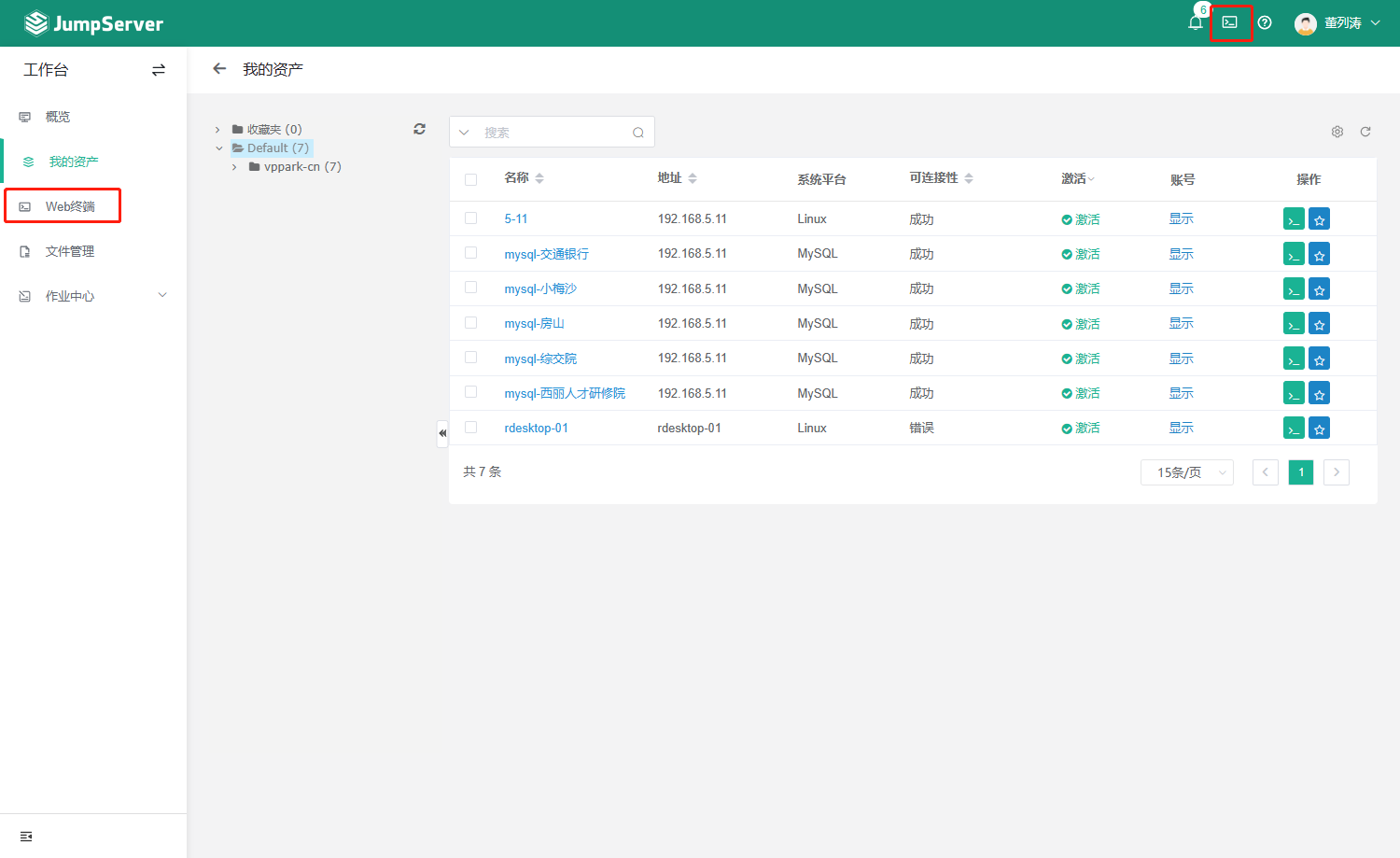
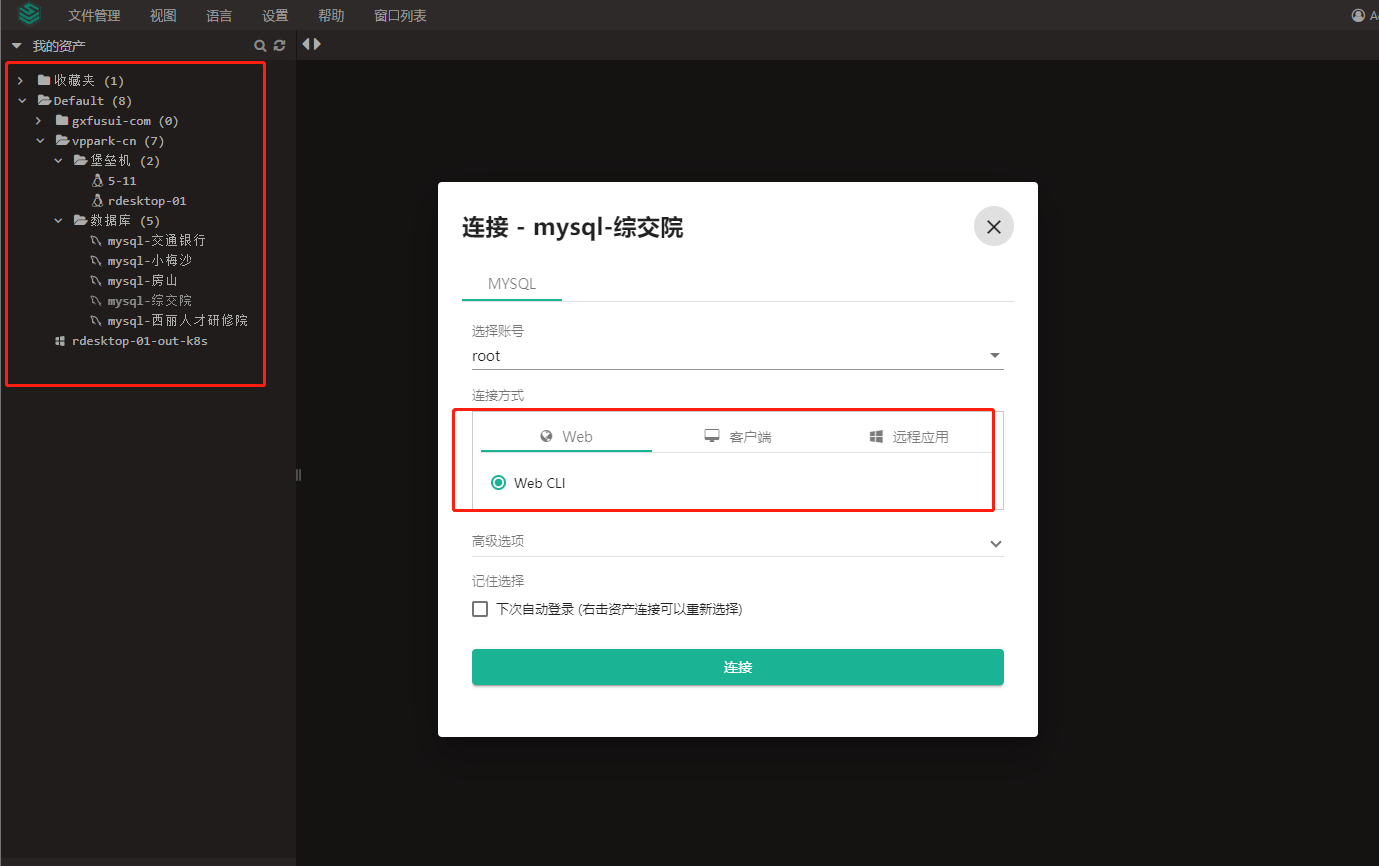
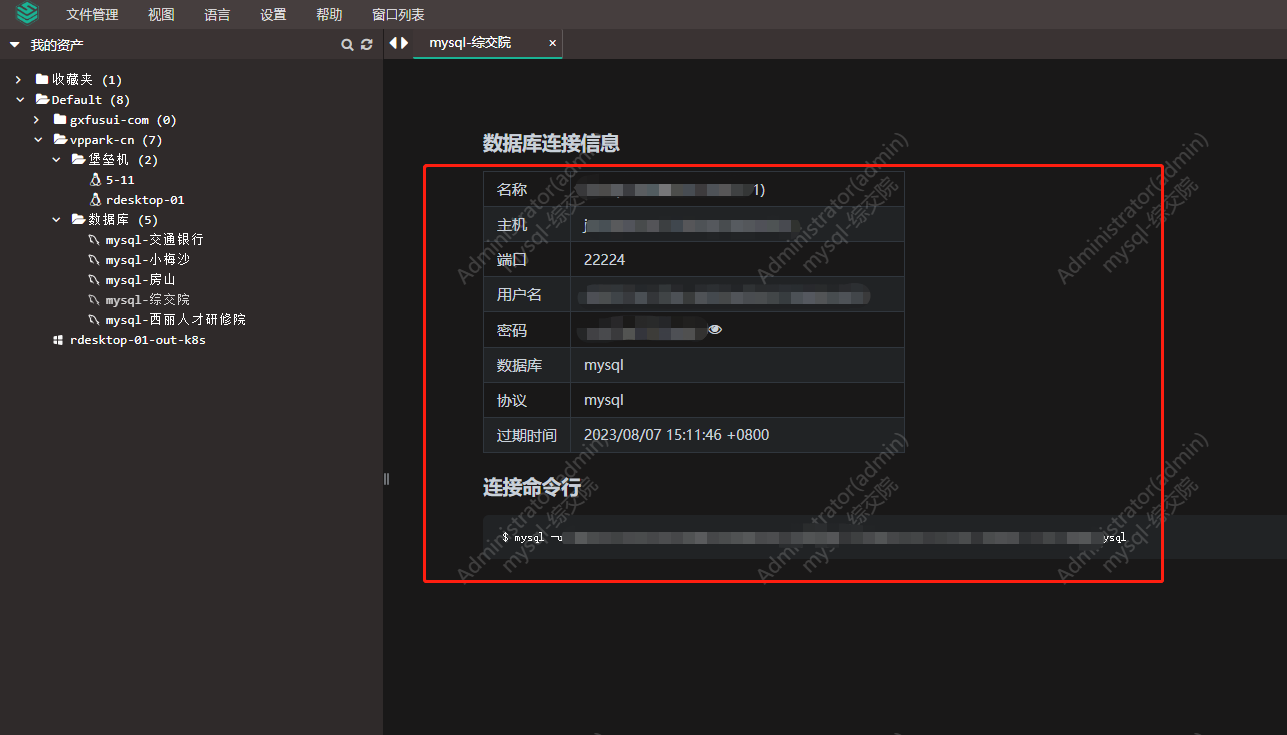
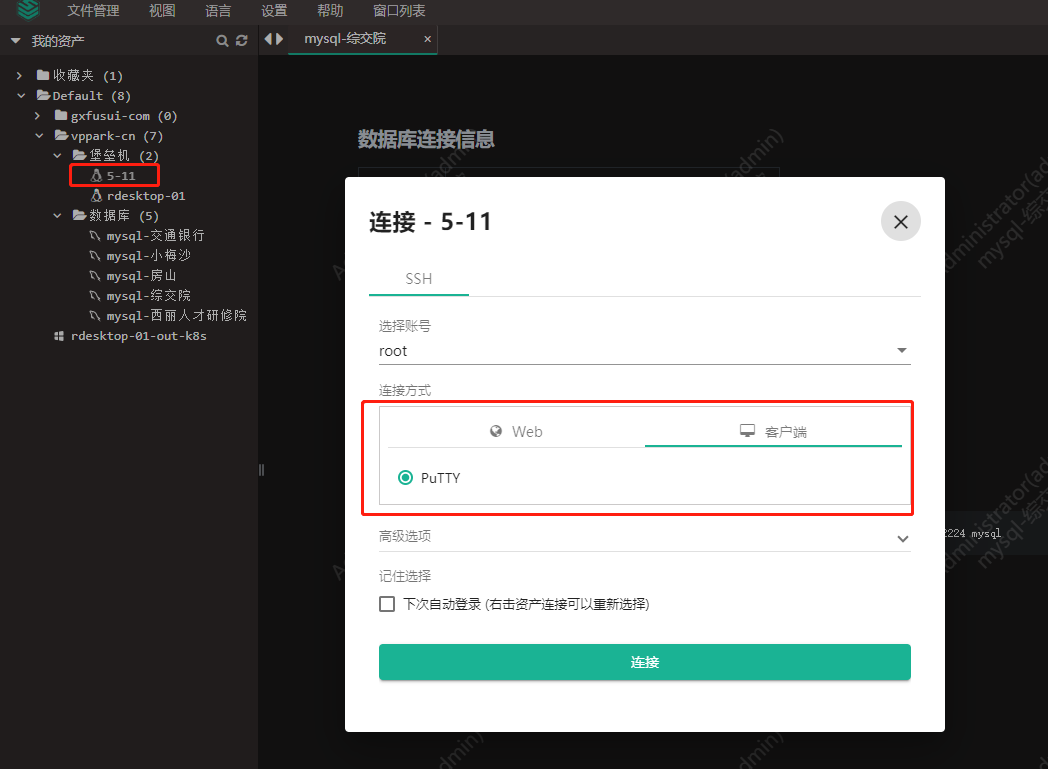
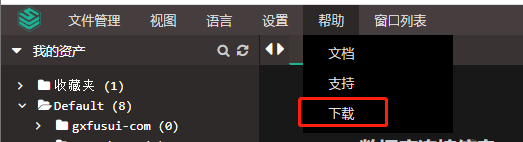
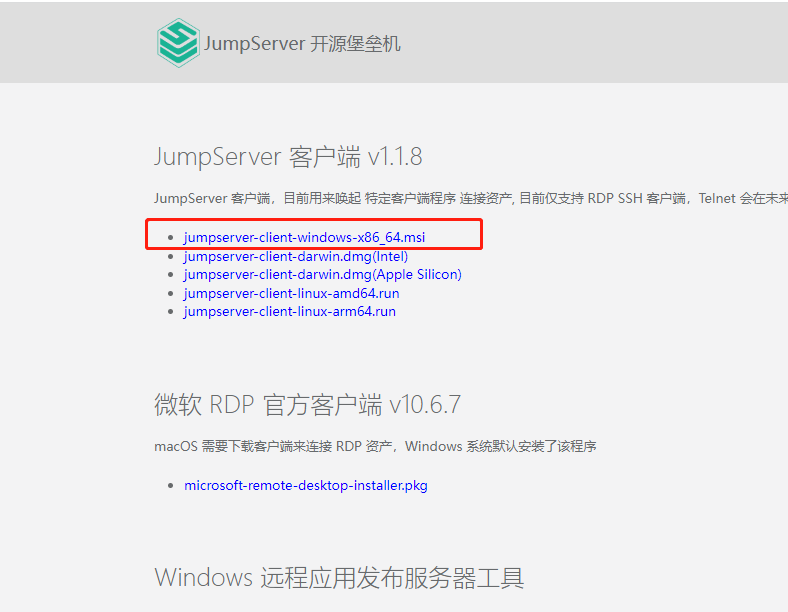
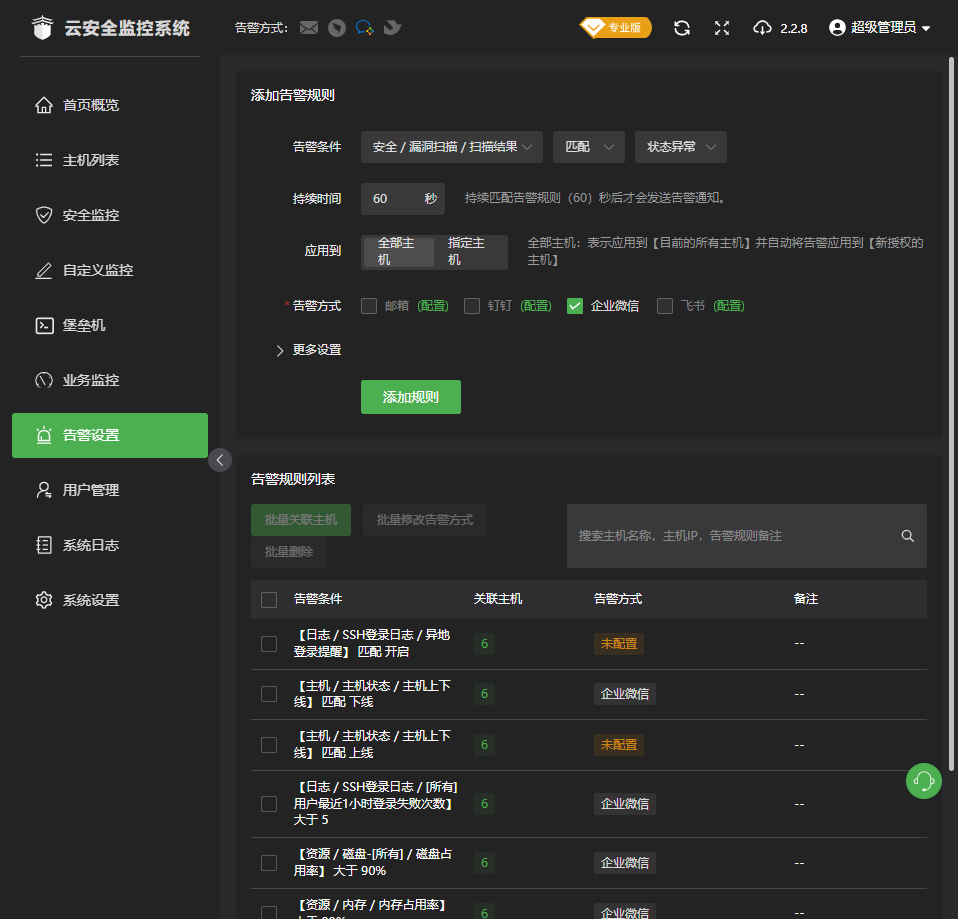
- 堡垒机jumpserver使用手册
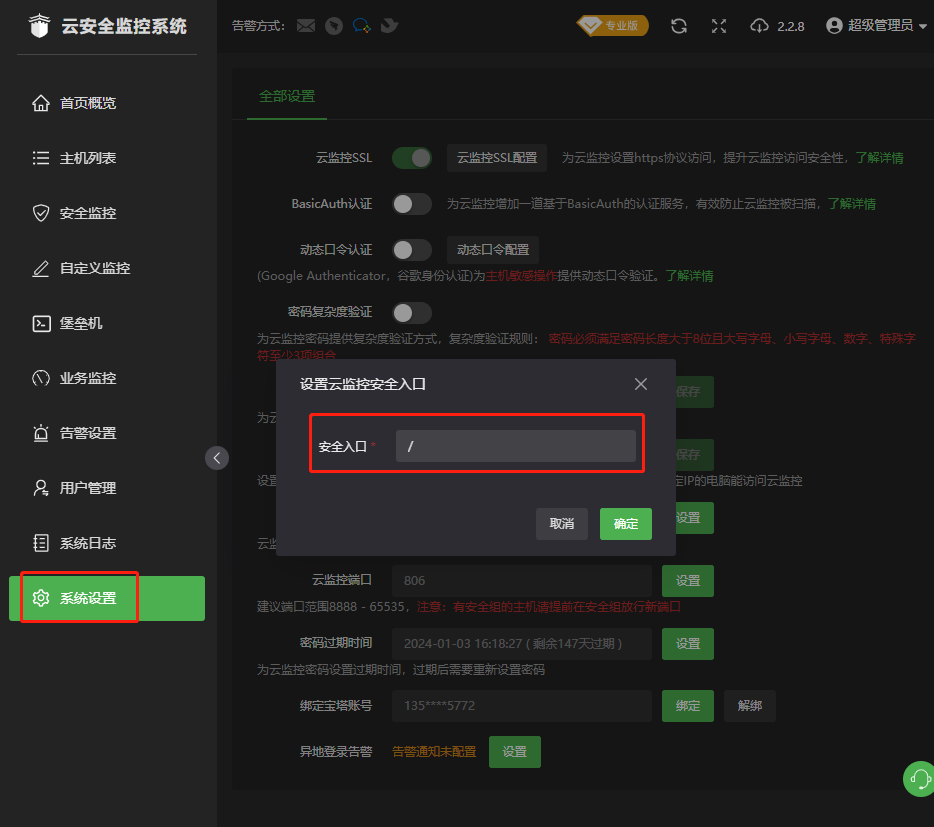
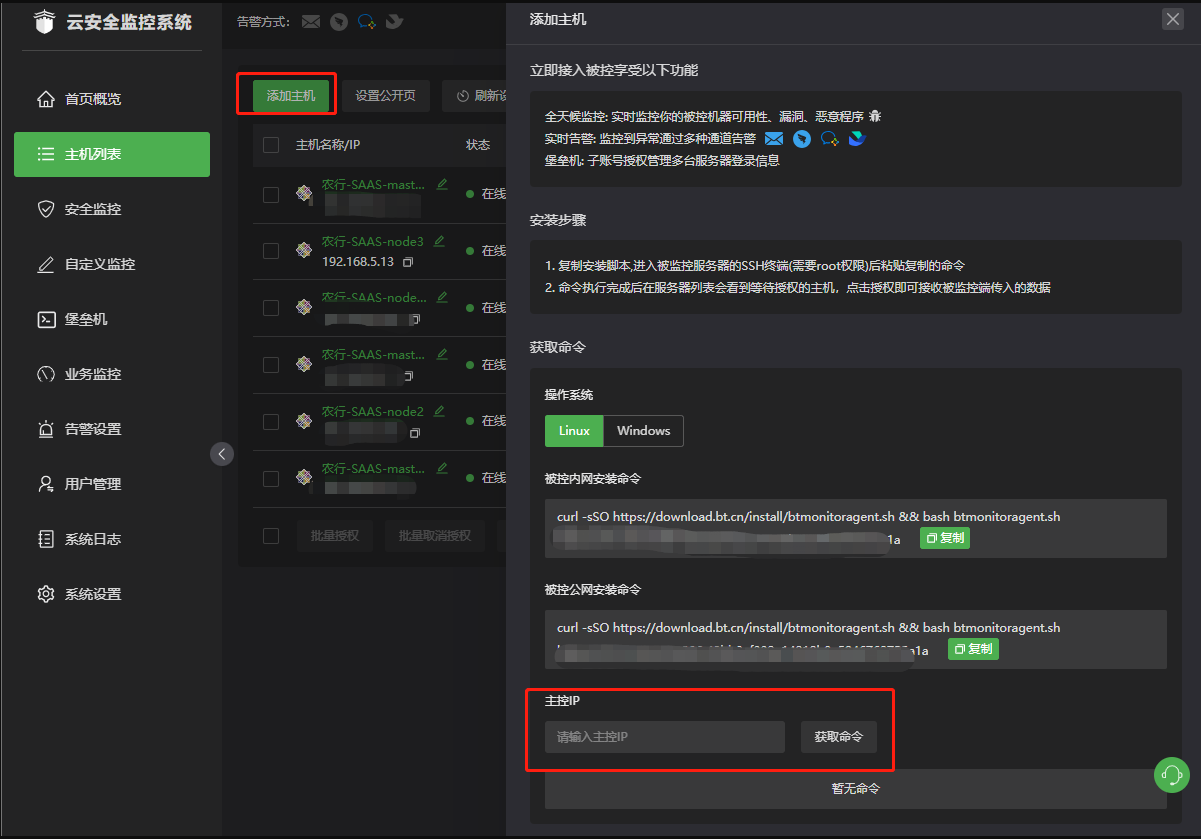
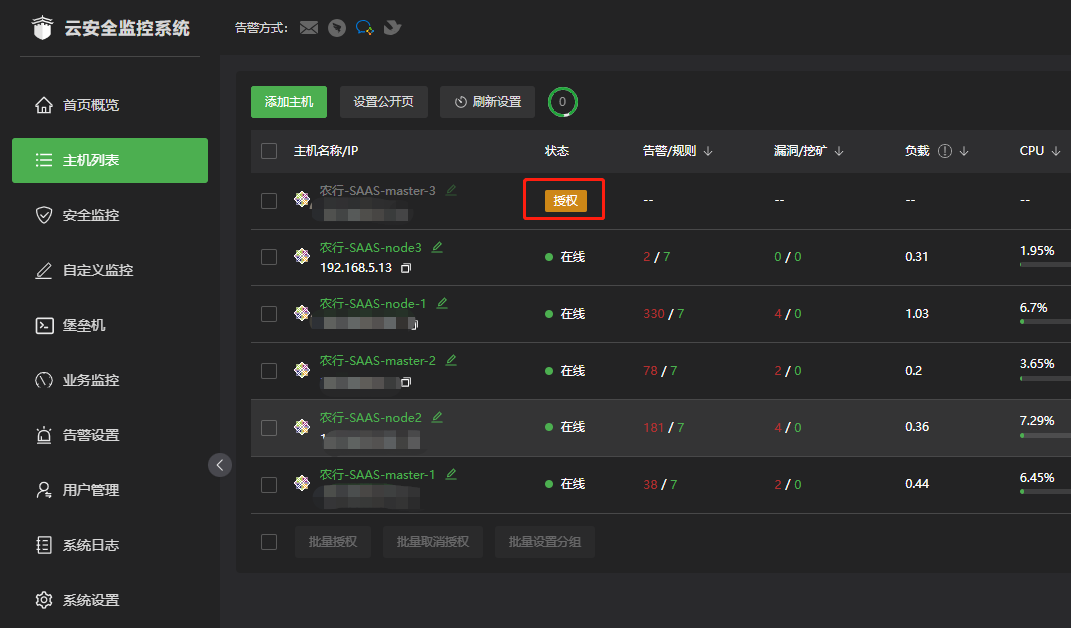
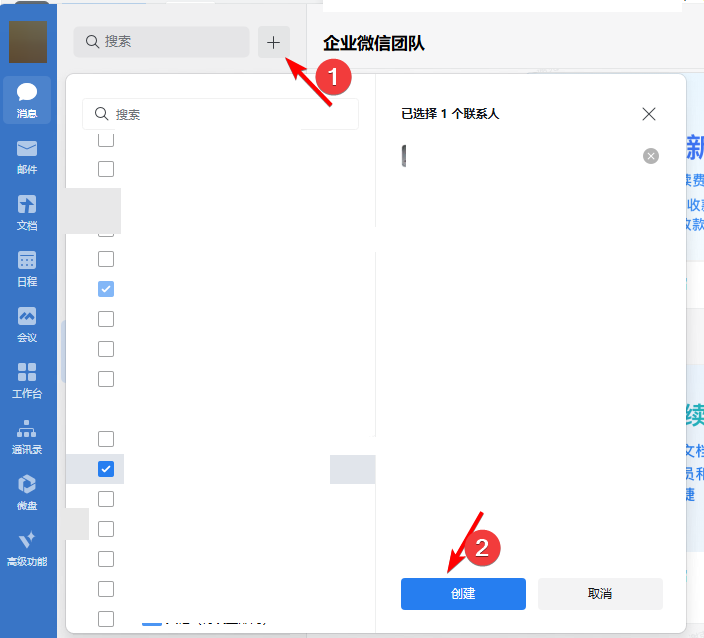
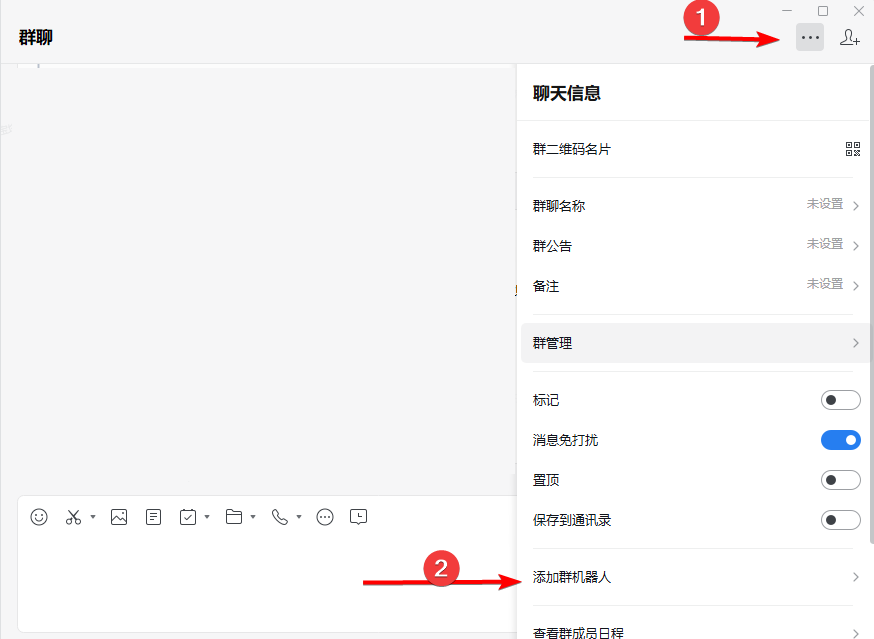
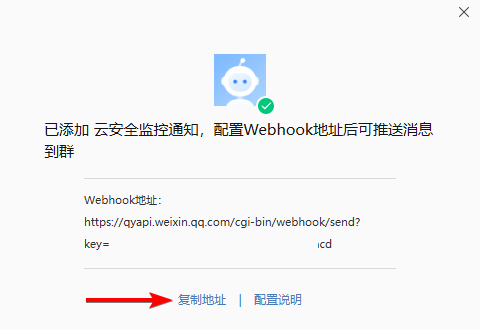
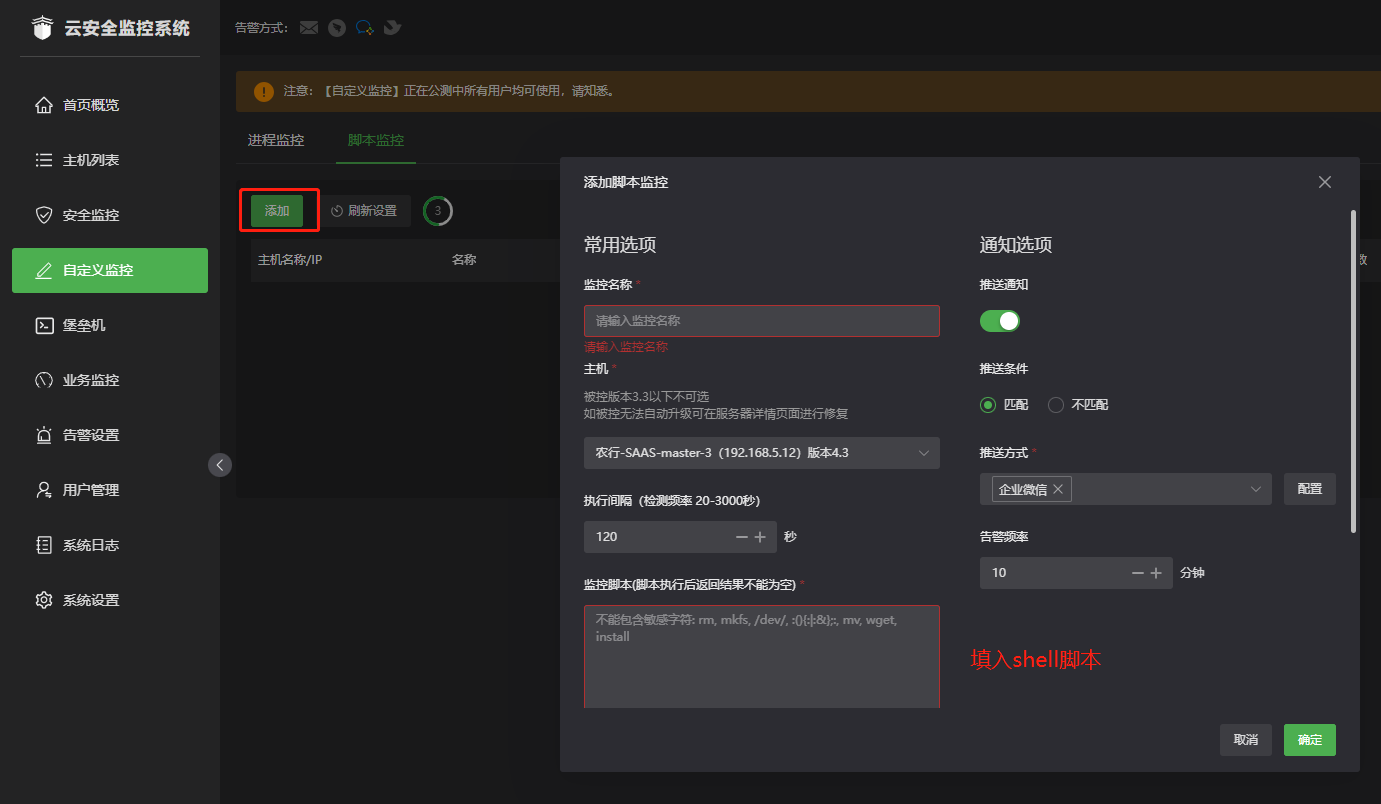
- 云监控bt-monitor
- k8s-etcdserver-no-space
- windows server 2019安装docker
- docker-compose
- nginx-ingress注释解释
- coredns增加全局解析
- traefik-ingress注解
- harbor&&docker代理&&docker被墙解决办法
- nginx&&nginx-ingress实现灰度发布
- 升级centos7内核
- centos7 阿里源
- ingress-nginx的几个小技巧
- 清除状态不正常的pod&&celanPods.sh
- k8s网络无法通讯一例
基础环境运维索引
容器概述
通过使用容器技术,将操作系统、应用程序全部打包为独立可执行镜像,镜像存储在镜像仓库,服务升级后,采取一个新的tag来标签区别镜像的版本。镜像包括了可以完整运行应用程序需要的操作系统环境、中间件环境,只需要一个脚本就启动一个应用程序,完美解决了应用程序微服务后,安装部署运维难的问题。借助容器编排技术,让基于脚本,可视化一键启动、关停一个、一组服务变得更简洁。通过流水线串联并驱动整个应用程序的开发周期,包括源代码的编译、镜像打包、自动部署和升级(开发环境、测试环境、生产环境)、自动化测试、以及运维阶段的告警、自动扩容。
下图为一个典型的安装部署架构,底层iaas提供vm虚拟化支持,通过基础容器平台与容器编排平台提供自动化部署,对一些标准的组件进行快速部署,对业务系统进行安装部署支持。
本文采用的容器引擎为docker,容器编排工具为k8s,编排可视化为rancher
安装部署docker
https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/docker
安装部署k8s
根据情况,选择最合适你的版本,本文推荐使用最新版,但是经过实践,v1.20.15为最稳定版本
v1.20.15版: https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/k8s-v12015
v1.28.0版:https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/k8s-v1280
k8s官方帮助:https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/setup/
安装容器编排可视化工具rancher
https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/rancher
rancher与k8s之间有版本匹配关系,对于v1.20.15版本的k8s,可以支持的rancher版本为v2.5.17,对于更新版本的k8s支持版本为v2.7.9
rancher与k8s的版本对应:https://www.suse.com/suse-rancher/support-matrix/all-supported-versions/rancher-v2-7-9/
rancher发布页:https://github.com/rancher/rancher/releases
rancher官方帮助:https://ranchermanager.docs.rancher.com/zh/
使用容器编排工具docker-compose
https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/docker-compose
安装nfs网络共享
https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/nfs
rancher使用手册
v2.5.17版本操作手册:https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/rancher-2515
v2.7.9版本操作手册:https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/rancher27
中间件自动化安装脚本
由于中间件需要持久化数据,对数据的一致性有比较高的要求,中间件不建议直接部署在k8s环境,而建议使用docker-compose运行。
-
minio:https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/miniodocker-compose
-
postgreSQL:https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/repmgrpostgresql
-
mongodb:https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/docker-composemogodb
-
nexus:https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/docker-compose-nexus
-
rabbitMQ:https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/docker-composerabbitmq
-
elasticsearch:https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/elasticsearch
其他实用性工具
-
在线文章发布网站应用:https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/bookstack
-
pritunl-vpn:pritunl-vpn
安装docker
# step 1
hostnamectl set-hostname 12.vpclub.io
yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
# step 2
yum install -y yum-utils \
device-mapper-persistent-data \
lvm2
# 更新包管理器
yum -y update
# step3 2024年11月22日,docker被墙了,可以使用阿里源
# yum-config-manager \
# --add-repo \
# https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# 使用阿里源
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# step 4
# yum install -y containerd.io docker-ce docker-ce-cli
# 20.10版可能不兼容
yum install -y docker-ce-19.03.13 docker-ce-cli-19.03.13 containerd.io
# step 5
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.25.3/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
mkdir -p /etc/docker
touch /etc/docker/daemon.json
vi /etc/docker/daemon.json
# 设置镜像加速和设置容器存储为外挂磁盘节约空间
{
"graph":"/data/docker",
"storage-driver": "overlay2",
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "300m",
"max-file": "10"
}
}
# 开启服务
systemctl enable docker
systemctl restart docker
如果安装的主机docker不能上网
# 如果机器不能上网,使用docker获取镜像
# 创建服务文件目录
mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d
touch /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf
# 编辑配置文件
vim /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf
[Service]
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:1080"
Environment="HTTPS_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:1080"
Environment= "NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1"
# 如果使用http代理,将上面的socks5修改为http
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
手工安装docker
2025年3月12日,在深圳市南山区政数局麒麟操作系统安装19.03时,containerd运行不起来,更新到24.0.9可以正常运行
安装建议:先直接运行dockerd,containerd , 将错误消除了在使用服务方式启动
- 2025年3月12日,深圳南山区政数局麒麟操作系统提示cni错误,增加下面的配置
# /etc/containerd/config.toml
version = 2
disabled_plugins = ["io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri"]
方法一
# 官网下载,建议版本19.03
https://download.docker.com/linux/static/stable/
# docker-compose下载
https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/
# 下载源文件(x86_64)
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/bin/docker-19.03.9.tgz
# 解压缩
tar -xvzf docker-19.03.9.tgz
# 赋予权限
chown root:root ./**
# 复制文件到/usr/bin目录
cp ./** /usr/bin
# 添加docker运行需要的用户组
# 注意,可能添加失败,提示组ID已经存在,可以修改一个组ID,但是一定要有dokcer组
# 注意,这个组的作用是启动docker.socket的,也可以修改docker.socket的SocketGroup=root
# 或者,不指定组id,直接使用groupadd docker 增加一个组
groupadd -g 994 docker
# 下载服务配置文件
curl -o /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/bin/docker.service
curl -o /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.socket qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/bin/docker.socket
curl -o /usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/bin/containerd.service
# 写入服务开机启动
方法二
# 下载rpm安装包
yumdownloader --resolve --downloadonly --downloaddir=/data/yum_download/docker docker-ce-19.03.13 docker-ce-cli-19.03.13 containerd.io
# 下载rpm安装包
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/containerd.io-1.6.33-3.1.el7.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/docker-ce-19.03.13-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/docker-ce-cli-19.03.13-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
yum install containerd.io-1.6.33-3.1.el7.x86_64.rpm docker-ce-19.03.13-3.el7.x86_64.rpm docker-ce-cli-19.03.13-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
# 其他可能需要的
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/conntrack-tools-1.4.4-7.el7.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/container-selinux-2.119.2-1.911c772.el7_8.noarch.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/libnetfilter_cthelper-1.0.0-11.el7.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/libnetfilter_cttimeout-1.0.0-7.el7.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/libnetfilter_queue-1.0.2-2.el7_2.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker/socat-1.7.3.2-2.el7.x86_64.rpm
k8s常用命令
常用命令行
# 查看master组件状态
kubectl get cs
# 查看集群节点
kubectl get nodes
# 查看pod信息
kubectl get pods
# 获取发布信息
kubectl get deployments
# 查看集群信息
kubectl cluster-info
# 删除节点
kubectl delete node node42.vpclub.io
# 删除 pod
kubectl delete pod nginx-3654852276-2dt73
# 删除deployment
kubectl delete deployment nginx
# 详细日志调试工具
kubectl describe pods
# 进入容器
kubectl exec -it <nginx-webapp-2067515279-1z0lb> /bin/bash
# 查看已经部署的yml配置信息
kubectl get deploy NAME -o yaml
# 强行删除
kubectl delete pod <pod名> --grace-period=0 --force
# 为node增加label
kubectl label nodes 190.vpclub.io <label>
# 删除node的label,既在label后面加 -
kubectl label nodes 190.vpclub.io <label>-
# 修改一个label ,需要增加参数 --overwrite
kubectl label nodes 190.vpclub.io role=apache --overwrite
# 节点不参与调度,同理,恢复标记为在 label后面加 -
# 节点不参与调度并立即驱离已经存在的POD
kubectl taint nodes 190.vpclub.io node-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoExecute
# 节点不参与调度,已经被调度的不受影响
kubectl taint nodes 190.vpclub.io node-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoSchedule
# 重新调度一组POD
kubectl get pod -n kube-system |grep kube-proxy |awk '{system("kubectl delete pod "$1" -n kube-system")}'
# 标记为维护
kubectl cordon 17.vpclub.io
# 取消维护状态
kubectl uncordon 5-16.vpclub.io
# 删除nginx-ingress后的报错
kubectl delete -A ValidatingWebhookConfiguration ingress-nginx-admission
# 获取不正常的POD
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces| grep "Terminating\|OutOfpods\|CrashLoopBackOff\|Evicted\|ContainerStatusUnknown\|Error"
# 强制删除全部不正常的POD
kubectl get pods -n trade | grep "Terminating\|OutOfpods\|CrashLoopBackOff\|Evicted\|ContainerStatusUnknown\|Error" | awk '{print $1}' | xargs kubectl delete pod -n trade --force --grace-period=0
# 使用环境变量删除所有不正常的PO
_opns=kube-system && kubectl get pods -n ${_opns} | grep "Terminating\|OutOfpods\|CrashLoopBackOff\|Evicted\|ContainerStatusUnknown\|Error" | awk '{print $1}' | xargs kubectl delete pod -n ${_opns} --force --grace-period=0
# 缩放实例
kubectl scale -n devops-default --replicas=0 deployment/devops-admin-api
# 把某个NS下面的部署全部缩放为0
kubectl scale deploy --replicas=0 --all -n park-zjy
# 最近有活动d部署
kubectl get deploy --all-namespaces --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp
# 查看节点cpu内存使用情况,需要先安装metrics-server
kubectl top node --sort-by memory
# 查看pod内存使用情况,需要先安装metrics-server
#kubectl top pods --sort-by memory
删除master节点
# 先安装删除node节点的方式删除节点
kubectl delete node 01.vpclub.io
# 随便找一个etcd容器,进入到容器内
kubectl exec -it etcd-00 sh -n kube-system
# 在Pod 中设置登录 ETCD 的命令(临时设置别名,退出后失效)
export ETCDCTL_API=3
alias etcdctl='etcdctl --endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 --cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt --key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key'
# 查看集群节点列表
etcdctl member list
# 示例:
669bc6472fb13679, started, master1, https://192.168.1.19:2380, https://192.168.1.19:2379, false
959c93e3261aadcb, started, master2, https://192.168.1.20:2380, https://192.168.1.20:2379, false
ca5f1f6f780545ba, started, master3, https://192.168.1.23:2380, https://192.168.1.23:2379, false
# 删除master3节点
etcdctl member remove ca5f1f6f780545ba
清除未使用的docker资源
# 清理所有未被使用的资源(包括镜像、容器、网络等)
# -a:清理所有未被使用的资源,包括镜像、容器、网络等。
# -f:强制执行清理操作,不进行确认提示。
docker system prune -af
# 清理未被使用的容器
docker volume prune
# 清理未被使用的网络
docker network prune
# 清理未被使用的卷
docker volume prune
# 清理未被使用的镜像
docker image prune
# 清理tag为空的镜像
docker rmi $(docker images -f "dangling=true" -q)
# 列出tag为空的镜像
docker images -f "dangling=true"
让pod可以运行在每一台不受污点影响
# 加在与volumes同级
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
将服务名解析到外部IP地址
# 服务定义
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mysql # 与端点名一致
spec:
clusterIP: None # headless
ports:
- name: default
protocol: TCP
port: 42
targetPort: 42
---
# 端点定义
apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
name: mysql # 与服务名一致
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: 192.168.0.46 # 外部地址
ports:
- name: default
port: 42
protocol: TCP
安装k8s-v1.20.15
选择高可用方案
- 使用kube-vip方案(简单):https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/kube-vipk8s
- 【推荐】 使用keepalived方案(独立可控):https://iovhm.com/book/books/42e7a/page/dockers-composekeepalived
kube-vip方案首先要求k8s集群是正常的,才能虚拟出虚拟IP,在集群出现故障后可能导致不好排除问题,优选keepalived方案
开始安装
# 修改主机名
hostnamectl set-hostname 5-10.vpclub.io
# 修改hosts文件,将所有节点加入,为了便于后续扩展,建议为master单独增加一个主机名:kube-api-server
vi /etc/hosts
192.168.5.10 5-10.vpclub.io
192.168.5.10 kube-api-server
# 下载 k8s 安装文件
# 查看k8s 最新版本 https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt
# 或者从google网站下载
# curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
# 三个主程序
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/kubeadm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/kubelet
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/kubectl
# docker-compose
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker-compose
# 服务配置文件
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/10-kubeadm.conf
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/kubelet.service
# 插件
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/calico.yaml
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/traefik-ingress.tar
# cni网络插件镜像加速
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/calico-image-vp-whdev.yaml
# 复制可执行文件到 /usr/local/bin 并给予执行权限
chmod 777 kubeadm kubelet kubectl docker-compose
cp kubeadm kubelet kubectl docker-compose /usr/local/bin
# 安装 socat conntrack 依赖软件
yum install -y socat
yum install -y conntrack
# 安装docker,修改docke运行方式
vi /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"graph":"/data/docker",
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
# 安装kubelet服务,开启服务自启动
# 需要注意 服务文件里面的执行路径,
cp kubelet.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service
mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d
cp 10-kubeadm.conf /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d
# 设置kubelet 开机启动服务
systemctl enable kubelet.service
systemctl status kubelet
多master安装(推荐,后期便于扩展多节点,前期也可以单节点使用)
# 使用kubeadm 安装
# 1.24.0 以前安装方法,会自动使用docker
# 为了便于扩展,建议apiserver使用主机名:kube-api-server:6443
kubeadm init --control-plane-endpoint "kube-api-server:6443" --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --upload-certs --kubernetes-version v1.20.15 --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16 --v 5
# 打印其他master加入节点命令
echo "$(kubeadm token create --print-join-command) --control-plane --certificate-key $(kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs | tail -1)"
# 打印node加入节点命令
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
单master安装(不推荐),单节点升级为高可用请参照 https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/k8s-ZsW
# 单机安装(不推荐)
kubeadm init --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --apiserver-advertise-address 192.168.5.10 --kubernetes-version v1.20.15 --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16 --v 5
# 重置重新安装
kubeadm reset
# 修改为ipvs模式
# 40行 , 有些是在54行,mode:"ipvs"
kubectl edit cm -n kube-system kube-proxy
# 安装cni网络插件
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml
安装ingress-controller
可以选择traefi-ingress或者nginx-ingress (推荐)
# 安装nginx-ingress
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/nginx-ingress/nginx-ingress.yaml
kubectl apply -f nginx-ingress.yaml
# 安装 traefik-controller
kubeclt apply -f 00-account.yaml -n kube-system
kubeclt apply -f 01-role.yaml -n kube-system
kubeclt apply -f 02-role-binding.yaml -n kube-system
kubeclt apply -f 03-traefik.yaml -n kube-system
kubeclt apply -f 04-traefik-services.yaml -n kube-system
kubeclt apply -f 05-traefik-default-tls.yaml -n kube-system
# 加入节点到集群
# 如果忘记了加入命令,可以再次打印
# kubeadm token create --print-join-command
k8s 证书过期重新续证书指南 https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/k3srancher
常用命令
https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/k8s-Si0
常见问题
# 某台主机太差,限制容器数量
# vi /var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env
# --max-pods=50
# pod之间ping不通
# kubectl edit cm -n kube-system kube-proxy
# 40行,mode:"ipvs"
# 这个设置应该在安装完成k8s后就处理
k8s容器内pod ping不通的情况下,需要修改kube-proxy模式为:ipvs模式,默认模式是iptables,然后重新启动kube-proxy
# 警告: 组件 controller-manager 不健康
# 警告: 组件 scheduler 不健康
# 编辑以下文件
vi /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml
vi /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-scheduler.yaml
# 两个文件,删除 --port=0
# calico-node 运行不起来提示 calico/node is not ready: BIRD is not ready: BGP not established
# calico-node 获取的网卡接口不对
# 增加环境变量,其中eth0是网络接口名称
IP_AUTODETECTION_METHOD = interface=eth0
# 如果网卡名称不固定,可以看IP是否可达来探测
IP_AUTODETECTION_METHO = can-reach=192.168.0.254
# traefik-ingress 状态一直显示初始化
# traefik 增加启动参数,ingressendpoint.hostname或者ingressendpoint.hostname两个都填或者只填一个
# 同时要看情况删除(需要多次测试) --providers.kubernetesingress.ingressendpoint.publishedService
--providers.kubernetesingress.ingressendpoint.hostname=park.vpclub.io
--providers.kubernetesingress.ingressendpoint.ip=0.0.0.0
# calico-kube-controllers 异常
# 提示Failed to write status error=open /status/status.json: permission denied
# 挂载一个一个数据卷
# 主机目录/var/run/calico/status 并给予权限 777映射容器目录 /status
# 看情况或者删除健康检查
# load balance L4 一直提示 pedding
# load balance 是收费功能。k8s没有包括这个组件。应该使用 nodeport 或者 hostport
# 可以把部署的traefik 重新克隆一个,修改为DaemonSet 并公布为 host端口模式
# 误删除kube-proxy或者coredns恢复
kubeadm init phase addon kube-proxy --kubeconfig ~/.kube/config --control-plane-endpoint "kube-api-server:6443" --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --kubernetes-version v1.28.0 --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16
安装k8s-v1.28.0
k8s 从1.24之后移除了dokcer直接支持,安装方式与1.24.0以前有不一样的地方
-
下载安装文件
# 三个主文件
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/kubectl
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/kubelet
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/kubeadm
# docker-compose
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker-compose
# 两个插件
# https://github.com/Mirantis/cri-dockerd
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/cri-dockerd-0.3.4-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
# https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cri-tools
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/crictl-v1.28.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# 服务配置文件
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/10-kubeadm.conf
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/kubelet.service
# 网络插件
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/calico.yaml
# 网络插件加速
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/calico-image-vp-whdev.yaml
# nginx-ingress
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/nginx-ingress.yaml
# traefik-ingress
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/traefik-ingress.tar
# nfs-storage
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.28.14/nfs-storage.tar
# 安装 socat conntrack 依赖软件
yum install -y socat
yum install -y conntrack
# 复制三个主文件到目录
cp kubectl kubelet kubeadm /usr/local/bin/
# 安装插件
yum install cri-dockerd-0.3.4-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
# 修改cri-docker服务配置
# vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/cri-docker.service
# 修改cri-docker配置文件,在后面增加参数,告诉告诉docker使用 pause镜像与版本
# --pod-infra-container-image=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.9
# 开启服务
systemctl enable cri-docker
systemctl restart cri-docker
# 复制crictl到目录
tar -xvzf crictl-v1.28.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
cp crictl /usr/local/bin
# 修改crictl配置文件(非必须)
# 因为crictl是一个统一的容器管理工具,管理多种容器,不修改如下配置也没事,只是看到一堆错误提示不友好
# vi /etc/crictl.yaml
# runtime-endpoint: unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
# 或者
echo "runtime-endpoint: unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock" >> /etc/crictl.yaml
# 安装kubelet服务,开启服务自启动
# 需要注意 服务文件里面的执行路径,
cp kubelet.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service
mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d
cp 10-kubeadm.conf /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d
# 安装docker,修改docke运行方式
vi /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"graph":"/data/docker",
"storage-driver": "overlay2",
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
# 设置kubelet 开机启动服务
# 此时会显示一堆错误,这是正常的
systemctl enable kubelet.service
systemctl status kubelet
-
使用keepalived方式高可用(推荐,独立可靠):
docker-keepalived:https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/docker-keepalived -
使用KUBE-VIP方式高可用(不推荐,简单易用)
kube-vip:https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/kube-vipk8s
# 部署KUBE-VIP 便于后期扩展,如果不想部署KUBE-VIP,可以直接使用主机名,强烈建议使用kube-api-server作为master主机名
docker run --network host --rm swr.cn-south-1.myhuaweicloud.com/vp-whdev/all-in-devops/kube-vip:v0.6.0 manifest pod --interface=eth0 --vip 192.168.0.200 --controlplane --services --arp --leaderElection | tee /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yaml
-
安装
# 初始化集群
kubeadm init --control-plane-endpoint "kube-api-server:6443" --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --upload-certs --kubernetes-version v1.28.14 --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16 --service-cidr=10.96.0.0/12 --cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock --v 5
# 如果服务器有多张网卡,kubeadm自动侦测的网卡地址不正确,需要加入参数
--apiserver-advertise-address 192.168.5.10
# 重新打印其他master加入命令
# 需要手工在后面加入 --cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock --v 5
echo "$(kubeadm token create --print-join-command) --control-plane --certificate-key $(kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs | tail -1)"
# 重新打印节点加入命令
# 需要手工在后面加入 --cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock --v 5
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
# 重置集群
kubeadm reset --cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
# 安装网络插件
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml
# 修改为ipvs模式
# 40行,mode:"ipvs"
kubectl edit cm -n kube-system kube-proxy
安装ingress-controller
推荐选择nginx-ingress
# 安装nginx-ingress
kubectl apply -f nginx-ingress.yaml
# 安装traefik-ingress
kubeclt apply -f 00-account.yaml -n kube-system \
-f 01-role.yaml -n kube-system \
-f 02-role-binding.yaml -n kube-system \
-f 03-traefik.yaml -n kube-system \
-f 04-traefik-services.yaml -n kube-system \
-f 05-traefik-default-tls.yaml -n kube-system
让pod运行在每一台机器不受污点限制
# 加在与volumes同级
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
k8s-v1.30.3&&rancher-v2.9.1
2024年9月23日,1.30.3与rancher兼容性非常差,暂停使用
rancher-v2.9.1对应的版本是k8s-v1.30.3
# 官网下载
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.30.3/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.30.3/bin/linux/amd64/kubeadm"
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.30.3/bin/linux/amd64/kubelet"
# 镜像加速下载
curl -LO https://qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/kubectl
curl -LO https://qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/kubeadm
curl -LO https://qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/kubelet
# docker-compose
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/docker-compose
# cri运行时
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/cri-dockerd-0.3.4-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/crictl-v1.28.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# 服务配置文件
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/10-kubeadm.conf
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/kubelet.service
# 网络组件
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/calico.yaml
# nginx-ingress
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/nginx-ingress.yaml
具体安装步骤与k8s-v1.28.0一致:https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/k8s-v1280
已知问题(不能开低于1024端口),其中nginx-ingress处理方法相同
# coredns提示 listen tcp :53: bind: permission denied
kubectl edit deploy coredns -n kube-system
allowPrivilegeEscalation: true
capabilities:
add:
- NET_BIND_SERVICE
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
已知问题,让pod在每一台机器执行,而不管节点是否有污点
# 加在与volumes同级
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
culr下载文件技巧
# 手动指定保存的文件名
curl -o kubectl https://qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/kubectl
# 直接使用远程文件的名称来保存文件
curl -O https://qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/kubectl
# 自动重定向
curl -LO https://qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.30.3/kubectl
离线安装k8s-v1.20.15
已经打包好的k8s基础镜像和calico镜像
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/google_containers.tar.gz
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/k8s/v1.20.15/calico.tar.gz
一、k8s镜像
1、获取k8s镜像
2、修改镜像名称
docker tag registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v1.20.15 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v1.20.15
docker tag registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.20.15 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.20.15
docker tag registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v1.20.15 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v1.20.15
docker tag registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-proxy:v1.20.15 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-proxy:v1.20.15
docker tag registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.2 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/pause:3.2
docker tag registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/etcd:3.4.13-0 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/etcd:3.4.13-0
docker tag registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns:1.7.0 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/coredns:1.7.0
3、保存镜像
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v1.20.15 > kube-apiserver:v1.20.15.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.20.15 > kube-controller-manager:v1.20.15.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v1.20.15 > kube-scheduler:v1.20.15.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-proxy:v1.20.15 > kube-proxy:v1.20.15.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/pause:3.2 > pause:3.2.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/etcd:3.4.13-0 > etcd:3.4.13-0.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/coredns:1.7.0 > coredns:1.7.0.tar
4、打包下载镜像
5、加载镜像
docker load < kube-apiserver:v1.20.15.tar
docker load < kube-controller-manager:v1.20.15.tar
docker load < kube-scheduler:v1.20.15.tar
docker load < kube-proxy:v1.20.15.tar
docker load < pause:3.2.tar
docker load < etcd:3.4.13-0.tar
docker load < coredns:1.7.0.tar
6、在harbor创建项目
curl -u "admin:Harbor12345" -X POST "http://your-harbor-domain/api/v2.0/projects" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"project_name": "google_containers","public": true}'
7、推送到新仓库
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v1.20.15
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.20.15
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v1.20.15
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/kube-proxy:v1.20.15
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/pause:3.2
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/etcd:3.4.13-0
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/google_containers/coredns:1.7.0
二、calico网络镜像
1、获取镜像
2、修改镜像名称
docker tag calico/kube-controllers:v3.21.6 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/kube-controllers:v3.21.6
docker tag calico/cni:v3.21.6 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/cni:v3.21.6
docker tag calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6
docker tag calico/node:v3.21.6 harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/node:v3.21.6
3、保存镜像
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/kube-controllers:v3.21.6 > kube-controllers:v3.21.6.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/cni:v3.21.6 > cni:v3.21.6.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6 > pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6.tar
docker save harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/node:v3.21.6 > node:v3.21.6.tar
4、打包下载镜像
5、加载镜像
docker load < kube-controllers:v3.21.6.tar
docker load < cni:v3.21.6.tar
docker load < pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6.tar
docker load < node:v3.21.6.tar
6、在harbor创建项目
curl -u "admin:Harbor12345" -X POST "http://your-harbor-domain/api/v2.0/projects" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"project_name": "hub","public": true}'
7、推送到新仓库
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/cni:v3.21.6
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6
docker push harbor.iovhm.com:5000/hub/calico/node:v3.21.6
docker-keepalived
keepalived是一个双活方案,是用arp伪造的方式,确定一个虚拟IP对应到多台主机的当前的实际主机,keepalived采用集群方式部署,节点之间互相通讯和选举,确定某一台机器可用,然后伪造出arp,以达到双活的目的。可以直接在主机安装,也可以使用docker安装
参考网址:https://github.com/osixia/docker-keepalived
当我们搭建高可用K8S时,可以选择kube-vip方案,也可以选择keepalived方案
version: '3'
services:
keepalived:
image: harbor.iovhm.com/hub/osixia/keepalived:2.0.20
restart: always
network_mode: host
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN
- NET_BROADCAST
- NET_RAW
environment:
- KEEPALIVED_INTERFACE=eth0 # 网络接口
# - KEEPALIVED_PASSWORD=d0cker # 密码
# - KEEPALIVED_PRIORITY=100 # 节点优先级
# - KEEPALIVED_ROUTER_ID=51 # 路由ID
- KEEPALIVED_UNICAST_PEERS="#PYTHON2BASH:['172.18.32.221','172.18.32.98','172.18.32.30']" # 主机列表
- KEEPALIVED_VIRTUAL_IPS=172.18.32.41/24 # 虚拟IP
使用KUBE-VIP部署高可用k8s
# 创建自动部署清单
docker run --network host --rm swr.cn-south-1.myhuaweicloud.com/vp-whdev/all-in-devops/kube-vip:v0.6.0 manifest pod --interface=eth0 --vip 172.18.41.242 --controlplane --services --arp --leaderElection | tee /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yaml
# 安装
kubeadm init --control-plane-endpoint "kube-api-server:6443" --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --upload-certs --kubernetes-version v1.20.15 --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16 --v 5
# 打印master加入节点命令
echo "$(kubeadm token create --print-join-command) --control-plane --certificate-key $(kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs | tail -1)"
# 打印node加入节点命令
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
# 复制kube-vip.yaml到每一台机器
cp kube-vip.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests
k8s单节点升级为高可用
参考网址:https://zahui.fan/posts/34d8fad0/
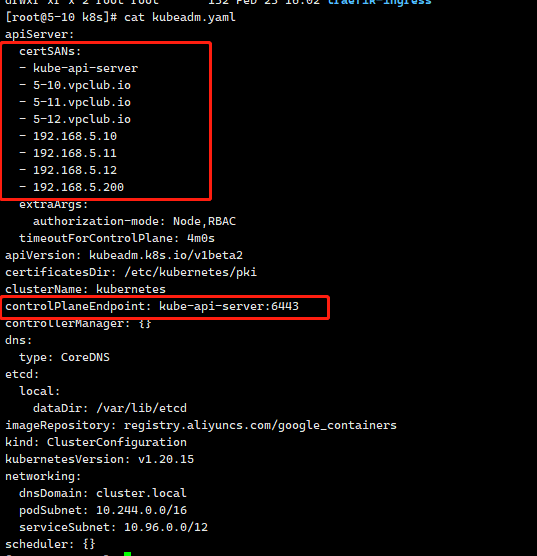
- 导出kubeadm配置
kubectl -n kube-system get configmap kubeadm-config -o jsonpath='{.data.ClusterConfiguration}' > kubeadm.yaml
- 添加证书SANs信息
certSANs到extraArgs中间的内容,既负载均衡地址,所有的master主机名,IP地址
controlPlaneEndpoint: kube-api-server:6443 修改成负载均衡的地址
如果没有则增加
apiServer:
certSANs:
# 这里需要包含负载均衡、所有master节点的hostname和ip
- kube-api-server
- 5-10.vpclub.io
- 5-11.vpclub.io
- 5-12.vpclub.io
- 192.168.5.10
- 192.168.5.11
- 192.168.5.12
- 192.168.5.200
extraArgs:
authorization-mode: Node,RBAC
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2
certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki
clusterName: kubernetes
controlPlaneEndpoint: kube-api-server:6443 # 修改成负载均衡的地址
controllerManager: {}
dns:
type: CoreDNS
etcd:
local:
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
imageRepository: registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: v1.20.15
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12
scheduler: {}
- 备份原kubernetes配置文件
mkdir -p /data/vpclub/kubernetes-bak/kubernetes-20240619
cp /etc/kubernetes/** /data/vpclub/kubernetes-bak/kubernetes-20240619 -rf
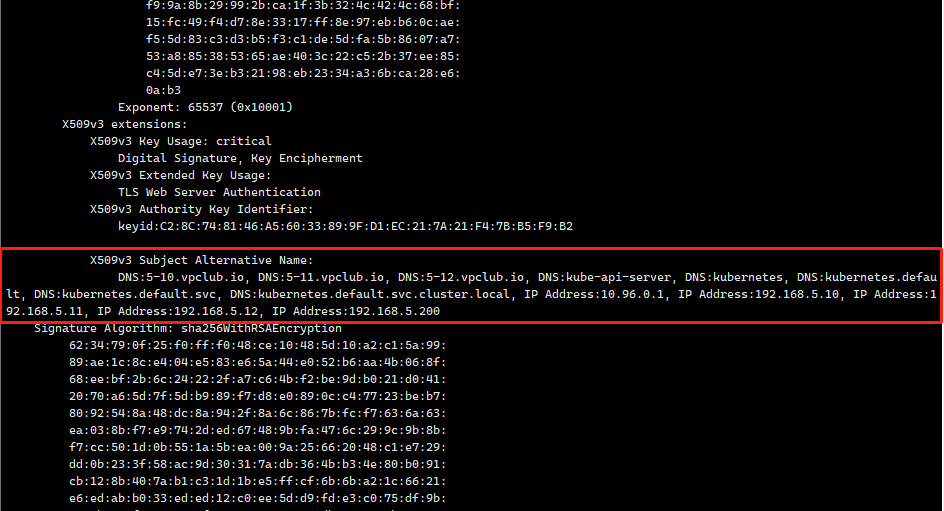
- 生成新的证书
# 删除旧的证书
rm /etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.key -rf
rm /etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.crt
# 生成新的配置
kubeadm init phase certs apiserver --config kubeadm.yaml
# 查看证书内容,应该要多出刚增加的那些主机和IP地址
openssl x509 -in /etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.crt -text
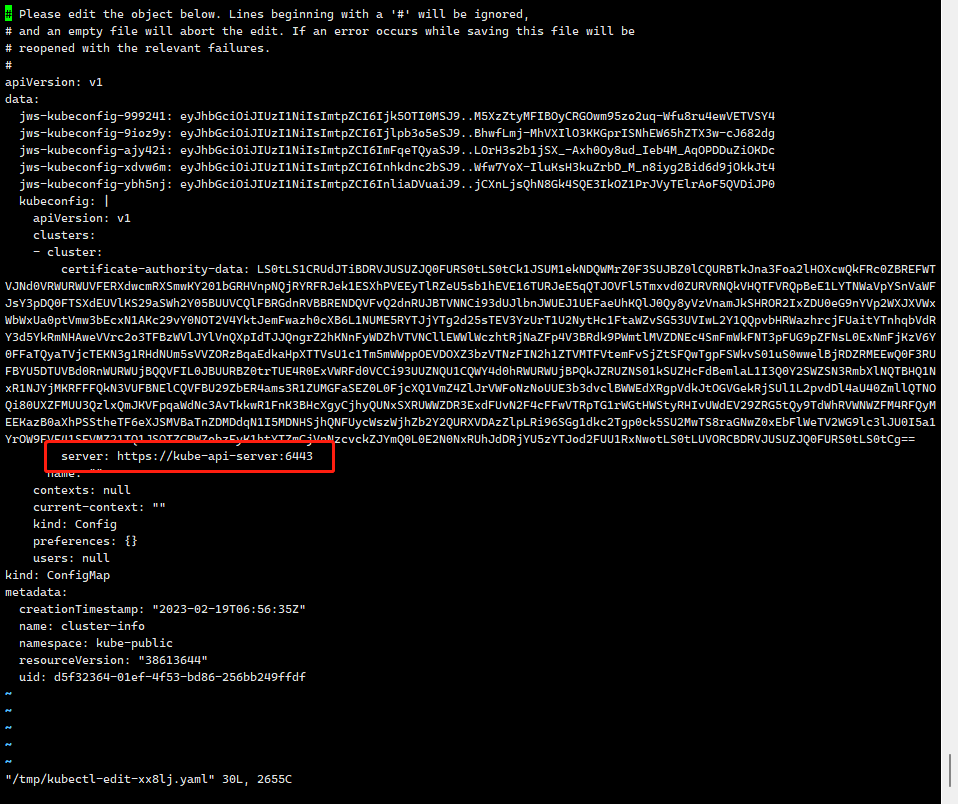
- 更新cluster-info配置
# server部分修改为负载均衡地址,本次使用的是 kube-api-server
kubectl -n kube-public edit cm cluster-info
- 将配置更新到集群
kubeadm init phase upload-config kubeadm --config kubeadm.yaml
# 再次查看配置是否已经生效,如果有不正确的地方需要修改过来
kubectl edit cm kubeadm-config -n kube-system
- 重启Apiserver
kubectl delete pod kube-apiserver-5-10.vpclub.io kube-controller-manager-5-10.vpclub.io -n kube-system
- 创建KUBE-VIP自动部署清单
# 注意命令行中的VIP地址,网卡名称
docker run --network host --rm swr.cn-south-1.myhuaweicloud.com/vp-whdev/all-in-devops/kube-vip:v0.6.0 manifest pod --interface=eth0 --vip 192.168.5.200 --controlplane --services --arp --leaderElection | tee /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yaml
# 测试一下VIP是否起效,到其他机器也ping一下
ping kube-api-server
ping 192.168.5.200
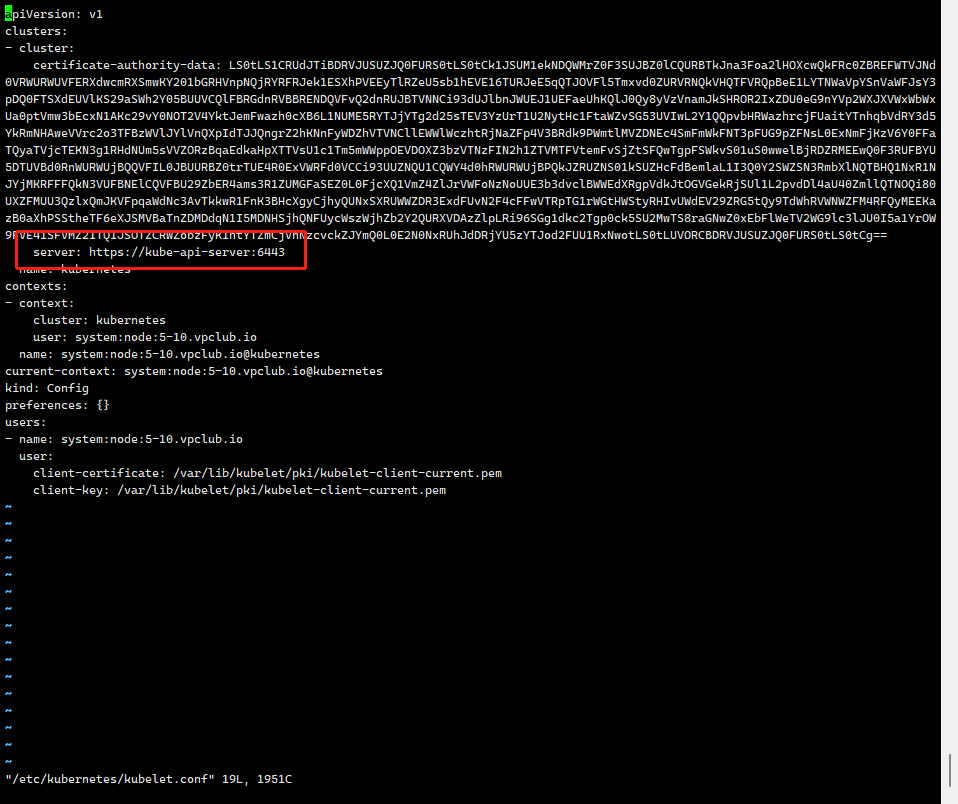
- 更新其他配置,将所有如下三个文件的server部分修改为负载均衡地址,本次使用的是 kube-api-server
vi /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf
# 不确定,默认情况下应该为主机IP
vi /etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf
# 不确定,默认情况下应该为主机IP
vi /etc/kubernetes/scheduler.conf
- 重启kubelet和容器
systemctl restart kubelet
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system kube-controller-manager-5-10.vpclub.io
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system kube-scheduler-5-10.vpclub.io
- 修改kube-proxy配置,将server 部分修改为负载均衡地址,本次使用的是 kube-api-server
kubectl edit configmap kube-proxy -n kube-system
# 重启 kube-proxy
kubectl rollout restart daemonset kube-proxy -n kube-system
- 修改kubectl 配置
vi ~/.kube/config
vi /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
# 查看集群信息
kubectl cluster-info
- 加入新master集群
echo "$(kubeadm token create --print-join-command) --control-plane --certificate-key $(kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs | tail -1)"
复制回显到新的master机器执行
- 加入node到集群
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
k3s证书过期&ks8证书过期&rancher 轮换证书
-
参考网址
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzkyNzM4Nzk1NQ==&mid=2247500723&idx=1&sn=64def8cd6ec7fd874440690f1f589a3a
- http://kingsd.top/2020/07/01/k3s-cert-rotary/
- https://www.cnblogs.com/databank/p/16334715.html
重要:本文提到要备份的地方,请老老实实的备份,否则集群损坏启动不了只能重装
【推荐】使用10年证书一键脚本
仅适用适用kubeadm安装的集群
相关脚本: https://github.com/yuyicai/update-kube-cert
# 查看证书过期情况
kubeadm certs check-expiration
# 赋予执行权限
chmod 777 update-kubeadm-cert.sh
# 一键更新所有证书
./update-kubeadm-cert.sh all
# 一键更新master证书(既排除etcd证书)
./update-kubeadm-cert.sh master
rancher证书过期
# 查看rancher证书是否过期状态
curl -Ikv https://ip:port
# 进入到容器
docker exec -it <rancher_server_id> /bin/bash
# 执行命令
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify -n kube-system delete secrets k3s-serving
kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify delete secret serving-cert -n cattle-system
# 删除或者移动备份证书目录
mv /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/tls /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/tls-20250507
rm -rf /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/tls
# 两次重启rancher,第一次为重新生成证书,第二次为加载证书
# 查看rancher-agent的集群代理容器状态
kubectl get po -n cattle-system
# 查看ranche agent容器状态,具体根据rancher版本查看对应的容器
docker ps -a|grep cattle
# 查看cattle-agent日志以获得更多信息
docker logs -f <cattle-agent-container-name>
-
集群不可用恢复
# 删除 agent,具体的名称要使用kubectl get ns
kubectl -n cattle-system delete daemonset.apps/cattle-node-agent deployment.apps/cattle-cluster-agent
# 更新集群,全局,系统设置,server-url;非必要步骤
# 设置环境变量
RANCHERURL="https://192.168.0.10:8000"
# 集群ID
CLUSTERID="c-8dlc7"
# 在当前登录用户菜单下创建新的toke,用户,api&&keys。把Bearer Token记录下来
# Token
TOKEN="token-8kdfz:f4kgn4ptrq92wxkmqlzjhf9wntbxc4jpnnwq6spnv6mlhm76259wl6"
# 安装jq
yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y jq
# 验证证书
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" "${RANCHERURL}/v3/clusterregistrationtokens?clusterId=${CLUSTERID}" | jq -r '.data[] | select(.name != "system") | .command'
# 此时返回新的导入连接
curl -s -k -H "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" "${RANCHERURL}/v3/clusterregistrationtokens?clusterId=${CLUSTERID}" | jq -r '.data[] | select(.name != "system") | .insecureCommand'
# 重新导入集群
curl --insecure -sfL https://192.168.0.10:8000/v3/import/sztcbkgpcffdvmrd8rn9qvd9flp595np5zcss6xljqk89jqkdx8rhf.yaml |k3s kubectl apply -f -
-
k3s证书过期
提示:k8s简化了安装过程,后续基础环境不在使用k3s而是已使用k8s
# 如果是k3s(k8s)提示证书过期,则先执行如下操作
# 如果集群证书没过期可以不用加 --insecure-skip-tls-verify=true 这个参数标识指不验证TLS
k3s kubectl --insecure-skip-tls-verify=true delete secret k3s-serving -n kube-system
# 删除k3s集群内的证书
kubectl delete secret k3s-serving -n kube-system
# 备份原文件
mkdir -p tlsbak
cp /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/tls/** ./tlsbak -rf
rm /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/tls/dynamic-cert.json
# 查看证书是否过期,或者直接从浏览器点击证书查看
openssl x509 -noout -dates -in server-ca.crt
# 重启k3s
systemctl restart k3s
手动续期k8s证书过期(很大几率导致集群无法启动,不推荐,有诸多排错过程)
# 备份配置文件
mkdir -p /data/vpclub/kubernetes-bak/kubernetes-20240620
cp /etc/kubernetes/** /data/vpclub/kubernetes-bak/kubernetes-20240620 -r
# 在主master执行,查看证书过期情况
kubeadm certs check-expiration
# 重新生成证书,如果你是单机,可以用这个命令
# 如果你是集群,不要用这个命令
# 如果你是集群,不要用这个命令
kubeadm certs renew all
# 如果你是集群,需要逐个更新证书,否则回导致ETCD集群不可用
kubeadm certs renew apiserver
kubeadm certs renew apiserver-etcd-client
kubeadm certs renew apiserver-kubelet-client
kubeadm certs renew etcd-healthcheck-client
kubeadm certs renew etcd-peer
kubeadm certs renew etcd-server
kubeadm certs renew front-proxy-client
kubeadm certs renew scheduler.conf
kubeadm certs renew admin.conf
# 在其他master另外的主机执行如上三步。
# 重启kubelet
systemctl restart kubelet
# 重启docker
systemctl restart docker
# 重新部署4个容器(删除POD即可)
# etcd 、 kube-apiserver 、 kube-scheduler 、 kube-controlle
网上有文章说是把主master的pki文件夹覆盖到其他机器,但是经过实践,有一定的概率导致etcd启动不了,etcd报tls错误。 这是因为etcd使用tls进行连接,每一个etcd实例都有单独的tls证书。如果因为复制覆盖了pki目录、而没有备份文件导致集群无法启动的情况下,此时需要重新生成新的证书
# 重新生成证书
kubeadm init phase certs all
# 将重新生成的pki目录中的etcd改名为etcd2
mv etcd/ etcd2/
# 复制主master证书pki目录的所有文件到目标主机
scp -r /etc/kubernetes/pki/** 172.18.41.4:/etc/kubernetes/pki/
# 将ectd2目录的 **peer.crt** **server.crt** 覆盖到etcd目录
cp etcd2/*peer.crt ./etcd/
cp etcd2/*server.crt ./etcd/
# 使用 kubeadm certs renew all 重新生成证书
-
K3S其他注意事项
- 更换机器后,主机名重复不能加入集群解决办法
# 在node主机
cat /etc/rancher/node/password
# 在 control panel (master)
cat /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/cred/node-passwd
# 将两边的密码保持一致,或者把某行删除
# 可能需要修改k3s.services的token
# 查看集群加入token
cat /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token
# 替换noded加入token
sed -i "s/<old-token>/<new-token>/g" /usr/lib/systemd/system/k3s.service
# 重新加载服务配置
systemctl daemon-reload
# 重启服务
systemctl restart k3s
rancher安装手册
rancher与K8S的对应关系
rancher与k8s之间有版本匹配关系,对于v1.20.15版本以下的k8s,可以支持的rancher版本为v2.5.17,对于更新版本的k8s支持版本为v2.7.9,请及时根据自己的K8S版本,升级到最稳定版本。
rancher与k8s的版本对应:https://ranchermanager.docs.rancher.com/versions
rancher发布页:https://github.com/rancher/rancher/releases
rancher官方帮助:https://ranchermanager.docs.rancher.com/zh/
2024年11月21日:当前最新文档版本,v2.8.5
docker-copose.yaml
version: "3"
services:
rancher-2.0:
image: rancher/rancher:v2.8.5
container_name: rancher-rancher
restart: always
privileged: true
ports:
- 8000:443
volumes:
- ./data:/var/lib/rancher/
- ./registries.yaml:/etc/rancher/k3s/registries.yaml
- ./auditlog:/var/log/auditlog
environment:
- AUDIT_LEVEL=1
- CATTLE_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_REGISTRY=harbor.iovhm.com/hub
- CATTLE_AGENT_IMAGE=harbor.iovhm.com/hub/rancher/rancher-agent:v2.8.5
# - HTTP_PROXY=socks5://192.168.0.10:1080
# - HTTPS_PROXY=socks5://192.168.0.10:1080
# - NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,0.0.0.0,10.0.0.0/8,cattle-system.svc,.svc,.cluster.local,10.101.25.0/24,.cn
mysql:
image: mysql:5.7 # 一定要写清楚版本号,不同版本之间会出现不兼容
privileged: true
restart: always # 自动重启
ports:
- 33306:3306
volumes:
- ./mysql:/var/lib/mysql # 文件存储
environment:
- TZ=Asia/Shanghai
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=<set your mysql root password> # root密码
使用https证书
# 准备证书文件
# ./ssl/cacerts.pem
# ./ssl/cert.pem
# ./ssl/key.pem
# 挂载
volumes:
- ./ssl:/etc/rancher/ssl
rancher2.8使用手册
一、进入安装部署环境
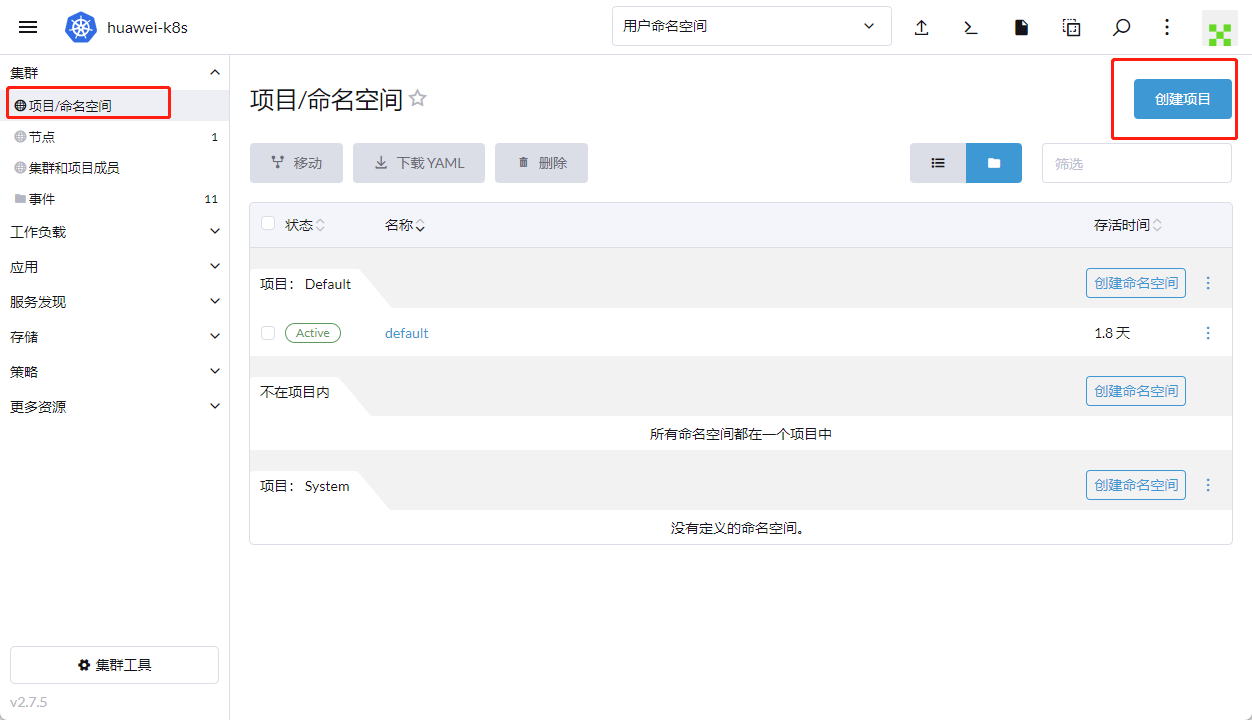
二、管理项目和命名空间
项目名称和命名空间要取的有意义
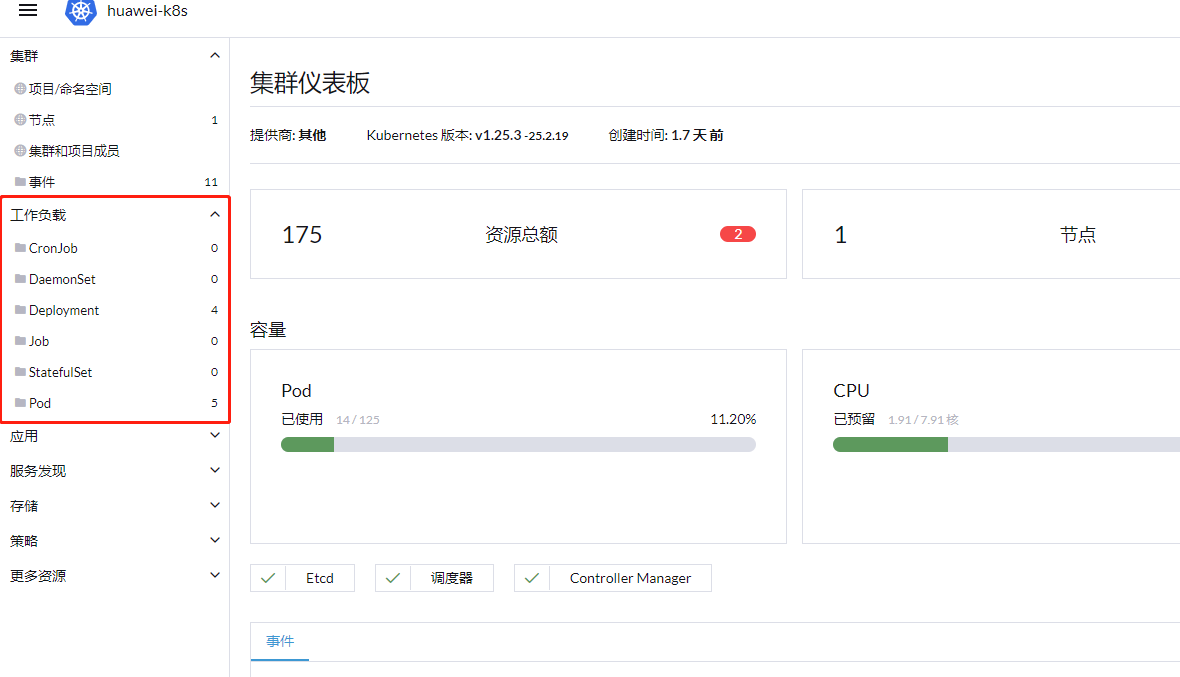
三、进入工作负载
- CronJob :定时任务,容器执行完成后退出
- DaemonSet:守护进程,每台主机安装部署一个
- Deploymen:普通部署,可以自己调整数量。默认使用
- Job:作业,一直跑
- StatefulSet:有状态服务
- Pod:暂时不清楚
四、筛选项目
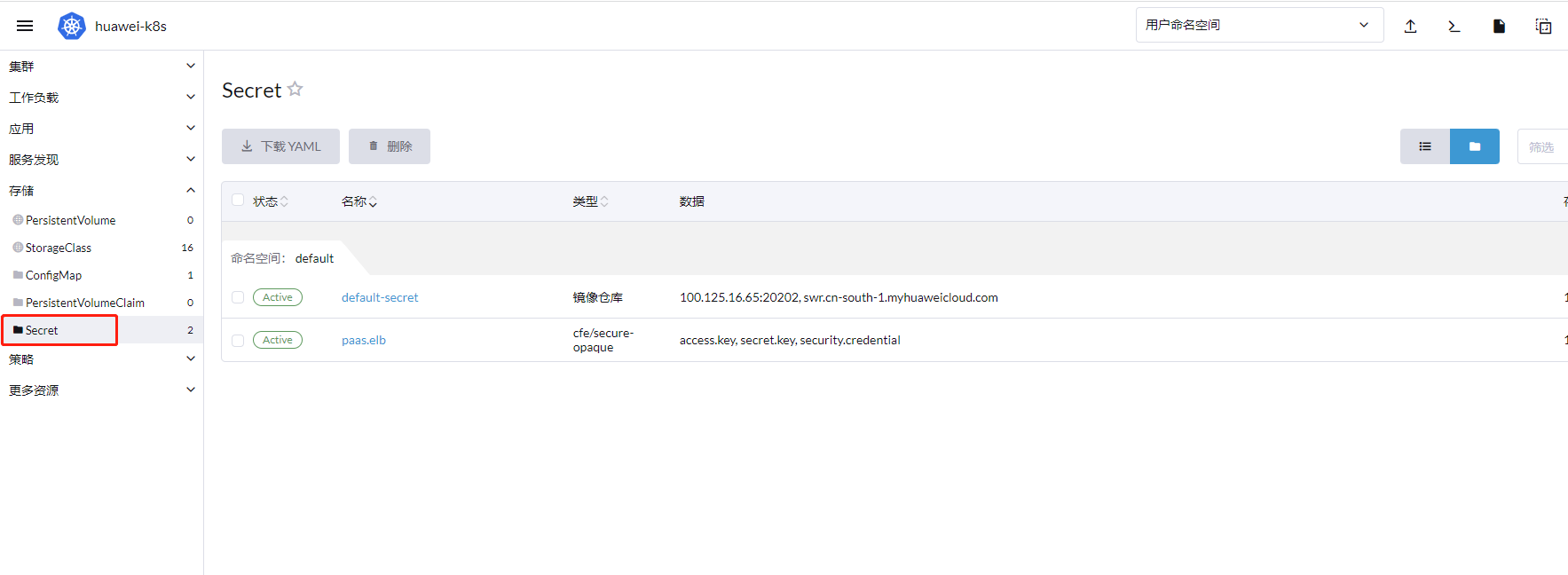
五、设置镜像仓库
选择secret标签页,点击右上角的创建按钮
选择创建一个镜像仓库凭据
输入你的镜像仓库凭据并保存
六、使用配置和密文
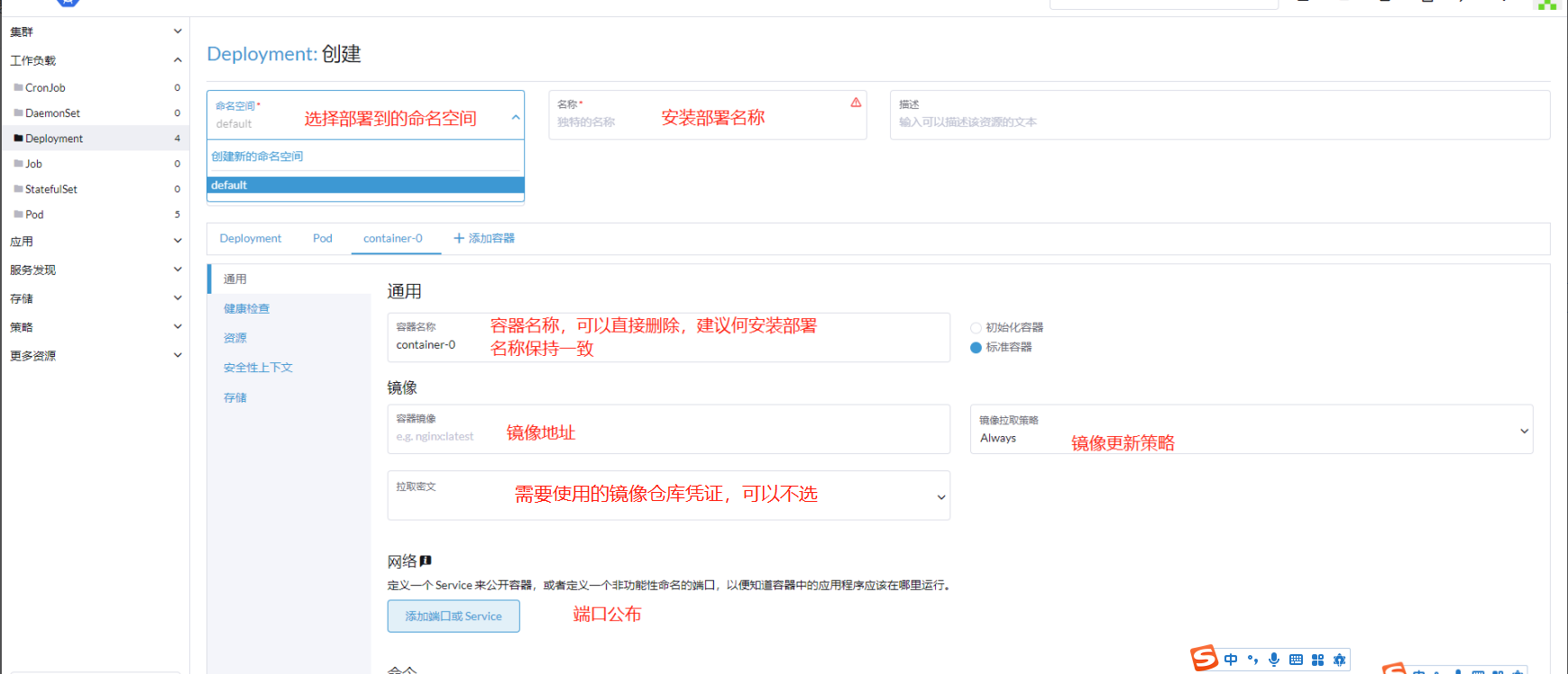
七、部署服务
选择deployment选项,点击创建,填入安装部署的基本参数
填入更多参数
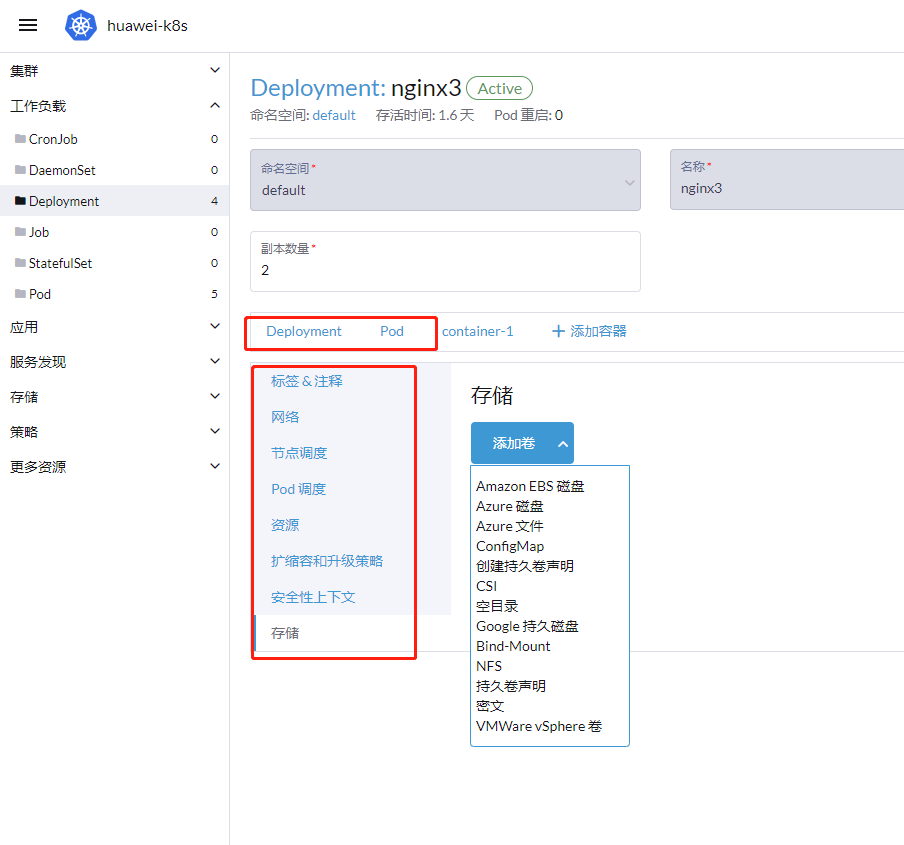
选择持久化存储类型
八、服务发现(服务间通讯)
正常情况下,当部署公布了端口,会自动进行服务公布。这一步不是必须的。
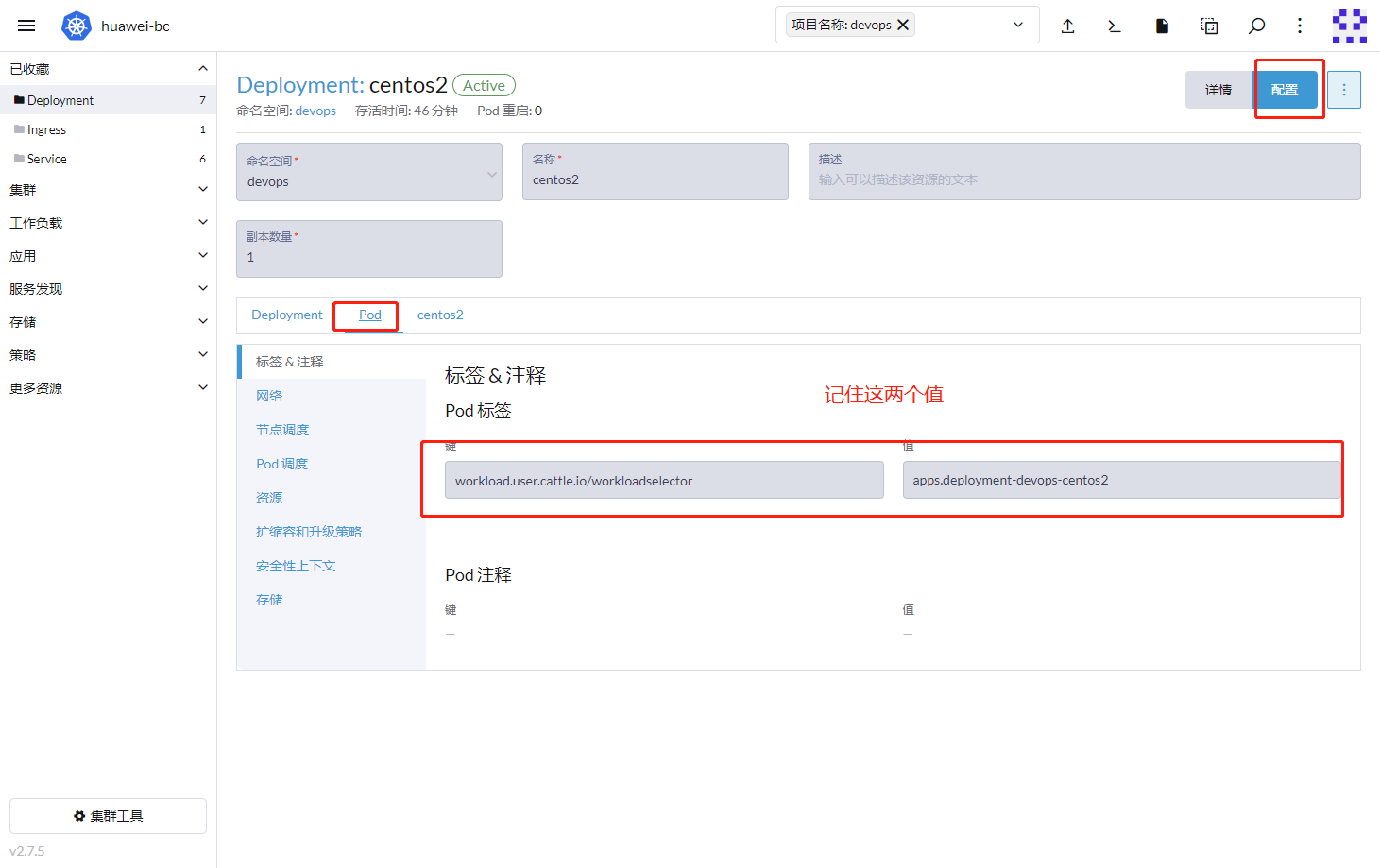
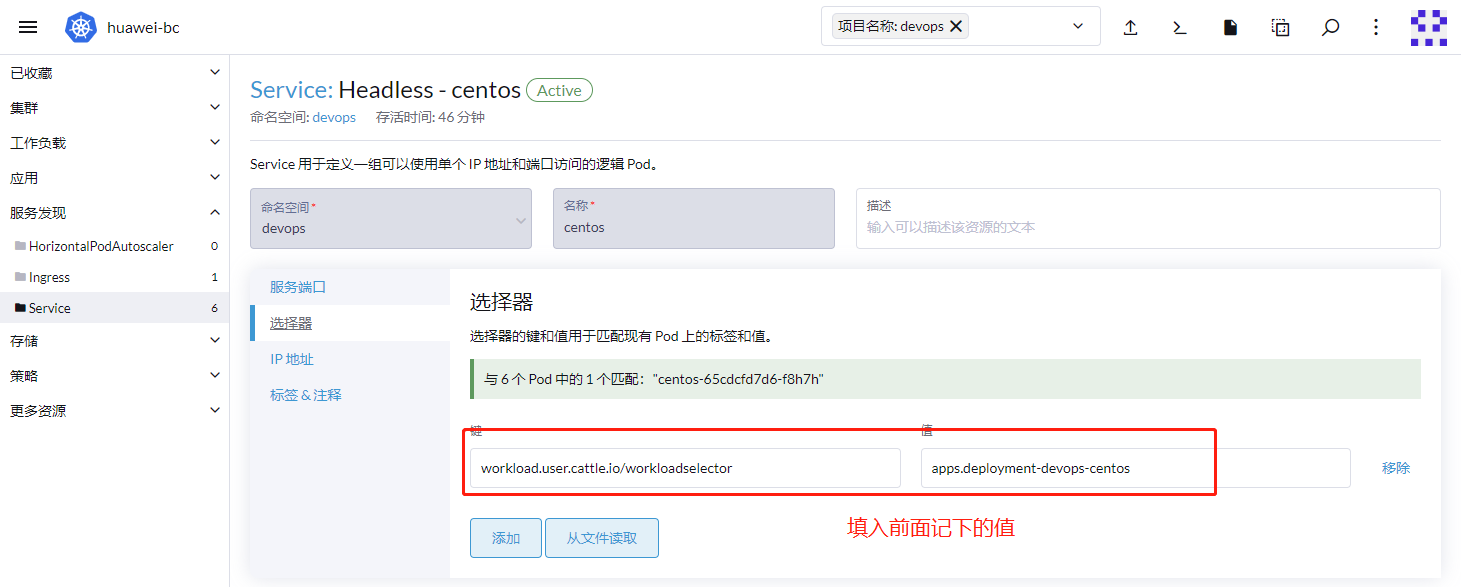
进入到deployment,记下部署的POD标签,如果没有,需要添加。
workload.user.cattle.io/workloadselector = apps.deployment-devops-bt-monitor-klipper-lb
# workload.user.cattle.io/workloadselector
# 旧版本ranher生成的,为了兼容,建议使用此值
# apps.deployment-devops-bt-monitor-klipper-lb
# 根据组成规则
# apps.deployment,这一段是固定值
# devops 是命名空间
# bt-monitor-klipper-lb 是部署的名称
-
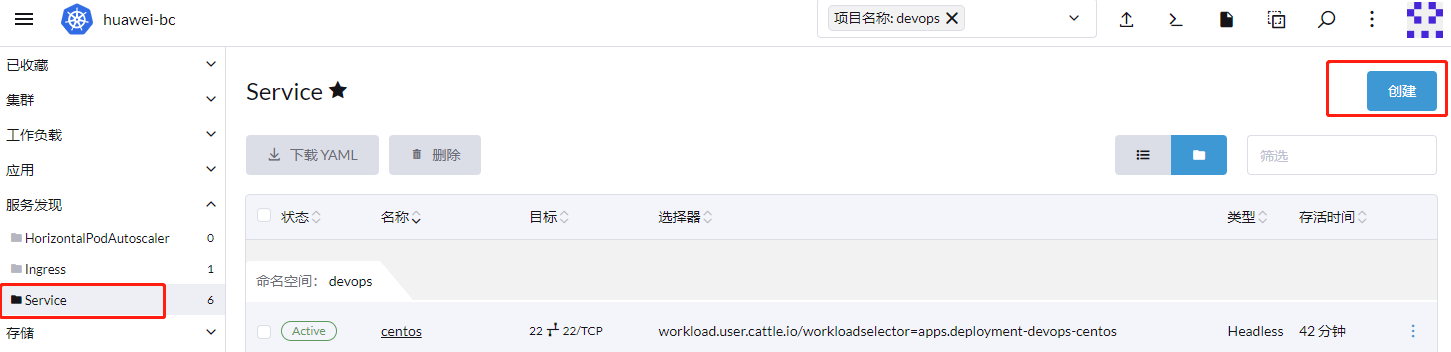
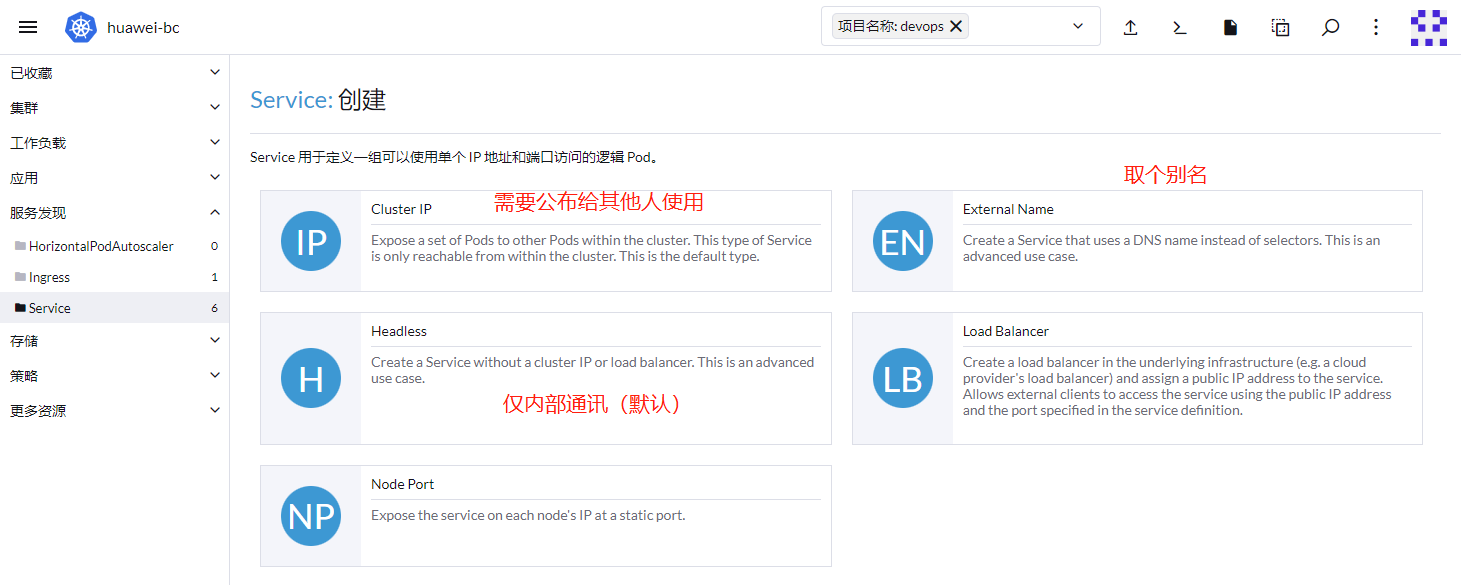
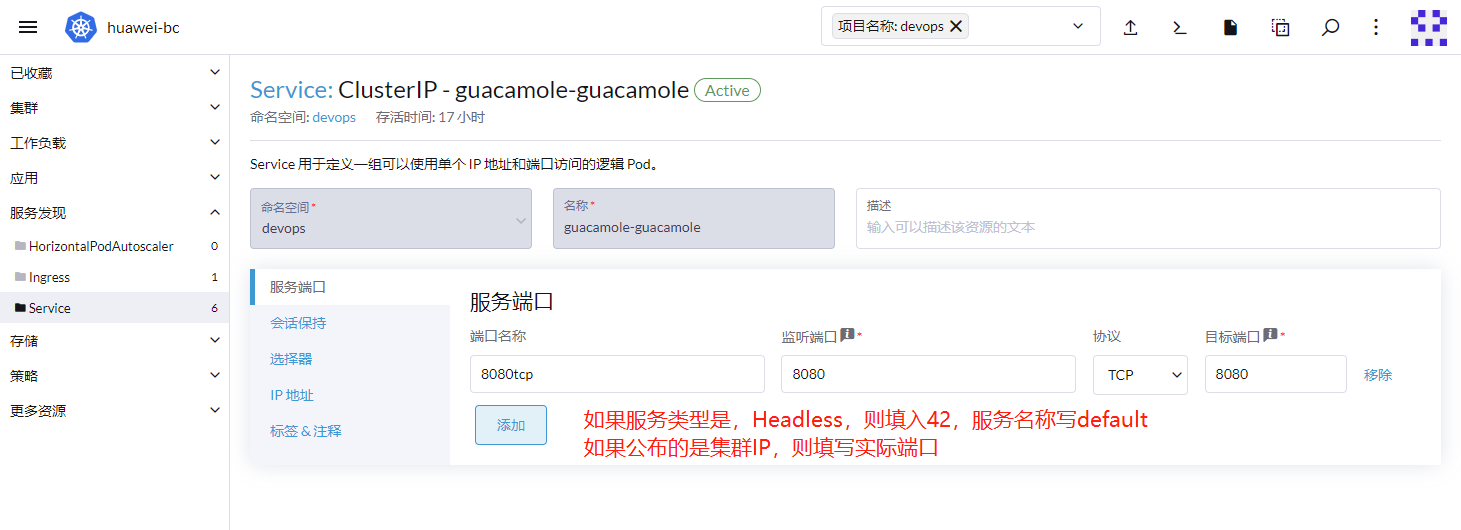
Headless:为服务发布一个名称,并且不会为服务公布IP,一般端口默认填写42端口,服务仅能在集群内部访问,集群内的其他服务,可以自由访问该服务的所有端口。非常方便。
-
ClusterIP:为服务分配一个集群IP,改端口可以在集群外部被访问。但是需要指定正确的端口。当服务确实需要公布给外面访问时使用。
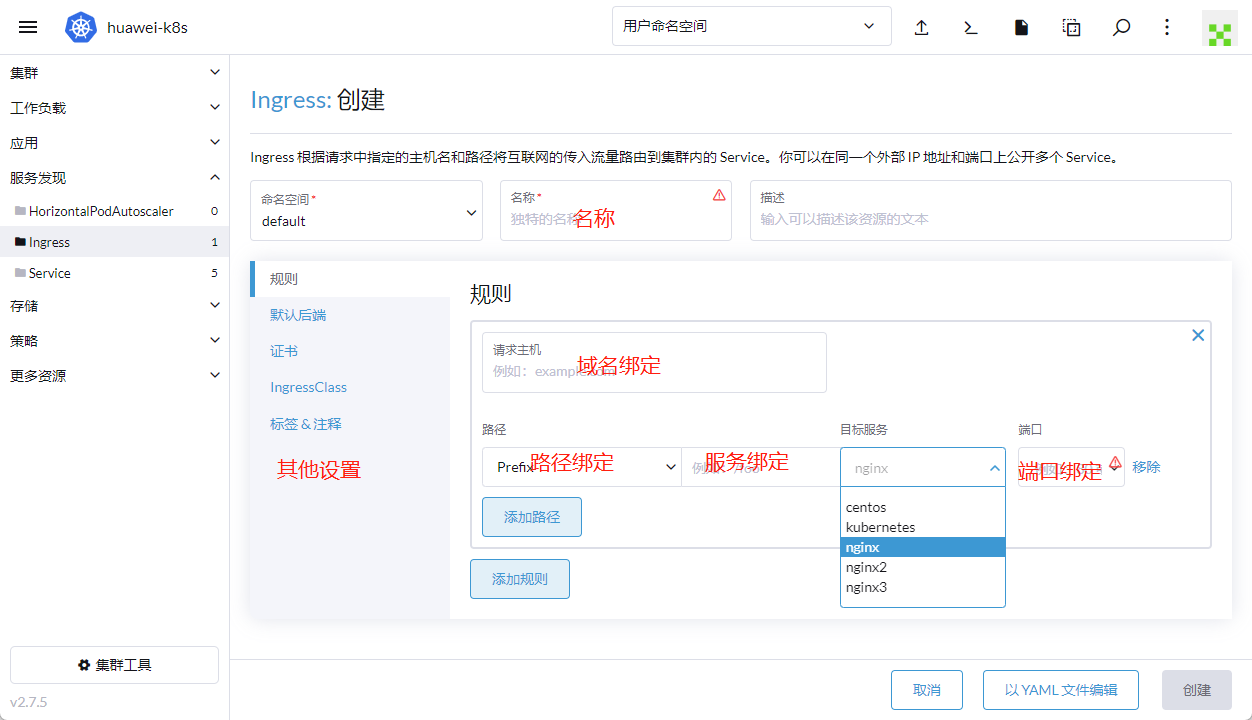
九、负载均衡和公布服务
选择ingress选项,增加一个ingress
对ingress进行配置
nfs网络共享
- 安装
# 查询是否有安装NFS,客户端只需要安装nfs-utils
rpm -qa nfs-utils rpcbind
# 如果没有安装,请安装,客户端只需要安装nfs-utils
yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind
# 查看服务启动状态
systemctl status rpcbind
# 如果rpc服务器没有启动请启动,只有服务器端需要启动
systemctl enable rpcbind
systemctl start rpcbind
# 查看prc注册情况
rpcinfo -p localhost
# 查看nfs服务状态
systemctl status nfs
# 启动NFS服务
systemctl enable nfs
systemctl start nfs
# 也可以是 systemctl start nfs-server
# 再次查看prc注册情况,应该会多了几个nfs相关的
rpcinfo -p localhost
- 服务器端
# 编写共享配置文件
vi /etc/exports
# 格式为: nfs共享目录 客户端地址(参数1,参数2)
# nfs共享目录要使用绝对路径
# 参数说明
# rw:目录读写
# sync:将数据同步写入内存缓冲区与磁盘中,效率低,但可以保证数据的一致性
# all_squash:将远程访问的所有普通用户及所属组都映射为匿名用户或用户组(nfsnobody)
# async 将数据先写入缓存,可以提高效率
# no_subtree_check 如果共享/usr/bin之类的子目录时,不检查父目录权限
# no_root_squash 当登录主机共享目录的使用者是root时,将其选项转换为nobody
/data/share *(rw,sync,all_squash,root_squash)
# 创建需要共享的文件夹
mkdir -p /data/share
# 修改文件夹权限
chown nfsnobody:nfsnobody /data/share
# 重新加载nfs配置
exportfs -rv
# 查看服务器挂载
showmount -e localhost
- 客户端
# 客户端不需要启动nfs和rpcbind,但是需要安装nfs-utils
yum install -y nfs-utils
systemctl disable nfs
systemctl disable rpcbind
# 创建文件夹
mkdir -p /data/nfs
# 挂载
mount -t nfs nfs-share.vpclub.io:/data/share /data/nfs
# 查看挂载
df -h
# 取消挂载
umount /mnt/home/vpclub/nfs
# 开机自动挂载
# vi /etc/fstab
# nfs-share.vpclub.io:/data/share /data/nfs nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0
echo "nfs-share.vpclub.io:/data/share /data/nfs nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0" >> /etc/fstab # 写入到开机自动挂载
rancher-2.5.15操作手册
-
访问集群管理界面
rancher集群地址:https://IP:8000/ , 填入刚刚安装完成基础环境的RANCHER地址,使用你的用户名登录
-
导入集群
如果您已经导入过集群,可以忽略此步骤。
选择添加集群
选择导入已有集群
填写集群名称
复制导入命令到有kubectld那一台主机执行
-
新建项目
默认情况下,会出现2个集群,local集群为rancher自带的管理集群,无实际用途,切换到default集群(名称和您导入集群设置有关系),集群默认有2个项目,其中system项目为管理项目,一般情况下不需要操作。
点击项目/命名空间按钮,增加一个项目,随后在项目下面增加命名空间。项目为RANCHER隔离使用,命名空间为k8s用。如果你需要使用kubectl命令管理项目,应该使用命名空间而不是项目名称。
-
切换到项目
依次点击集群 -> default-> <<projectName>>切换到项目,根据您的权限,您看的的可能与本图不一致,如果没有发现项目,请找集群管理员添加权限。
-
添加镜像仓库凭证
依次点击资源->密文->镜像仓库列表,添加镜像仓库私库的访问密码
如果你不慎先部署了镜像,后添加的镜像仓库,会导致应用一直无法部署,具体操作步骤请参见后面的章节
在此页面的证书列表选项卡,还可以管理你的https证书,你也可以在此上传https证书以便于后面使用
-
部署工作负载
点击资源菜单,回到工作负载页面,点击右上角的部署服务按钮
- 1.名称:唯一,可应用于服务发现,例如前后分离的前台服务需要访问后台服务,可以使用此服务名称进行服务发现
- 2.镜像:docker镜像
- 3.端口映射:如果服务需要进行发布,需要公开端口,网络模式 选择 集群IP(集群内部访问),原则上只有对外发布的服务才需要端口映射,比如承载了前端页面的nginx,后台服务无需进行端口公开。
- 4.环境变量:例如java开发环境需要的spring.profiles.active等可以在此填写。
- 5.数据卷:需要持久化的容器挂载,建议选择 映射主机目录,主机路径填写/data/nfs/<<projectName>>/<dataDir> 其中的/data/nfs 目录已经做了nfs网络共享,可以在任意节点共享数据
如果你先部署了POD,后增加的镜像仓库凭证,无论如何升级项目都一直部署失败,此时需要回到负载列表,选择负载,查看/编辑YAML,找到YAML正文内容的 imagePullSecrets 区块,将其中的name更改为你现在添加的正确的镜像仓库凭证,
或者将该负载删除,重新部署一个应用。
-
配置负载均衡
负载均衡既服务发布,点击右上角的添加规则按钮
自定义域名:服务发布的域名,需要设置dns解析通配。 目标后端:应该删除默认的规则,重新添加一条服务规则,然后选择工作负载,端口,注意,此处可选择的端口为你前面部署工作负载时公开的端口。可以添加多个服务,有点类似nginx的location
-
服务发现
即外部需要进行DNS解析的配置,例如您的数据库为外部地址,192.168.0.10,可以在此增加为一个服务发现,既您可以在你的工作应用程序使用 mysql:友好域名来访问外部服务。
- 1.外部IP:友好域名到外部IP地址
- 2.外部域名:友好域名到外部域名
- 3.服务别名:由于实际需要,需要将某一个部署的工作负载映射为另外一个名称既可以使用此项。
使用nfs-storageClass
-
storageClass (存储类)
k8s持久化存储有多种方式,当我们没有条件使用ceph时候,NFS存储则是理想的选择;通常的的作法有两种,但是两种方法都明显的弊端:
-
在每一台node上挂载主机nfs,然后在容器上映射到主机目录
每一台主机的挂载路径必须完全一致;由于对用到主机磁盘路径完全依靠手工填写,需要每个容器、至少是namespace级别统一规划好路径,否则很容易发生文件夹冲突。
-
使用PV/PVC;先创建PV,映射到NFS,在创建PVC,将PVC绑定到PV
项目或者POD数量较多时候,先创建PV、再创建PVC、然后附加数据卷步骤繁多,操作麻烦。特别是在rancher界面操作时,页面切换转来转去。
storageClass则是为了解决这个问题而诞生,他能够根据一组配置,自动生成PV/PVC
-
安装
- 00-nfs-storage-rabc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
# 替换为你的namespace
name: nfs-storage
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
# 替换为你的namespace
namespace: nfs-storage
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
# 替换为你的namespace
namespace: nfs-storage
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
# 替换为你的namespace
namespace: nfs-storage
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
# 替换为你的namespace
namespace: nfs-storage
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
# 替换为你的namespace
namespace: nfs-storage
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 01-nfs-storage-provisioner.yaml
这其实是一个容器,他会进行一些列的API监视,然后根据给定的参数创建PV/PVC并进行绑定。
需要设置的参数:
# env:
# - PROVISIONER_NAME:名称,这个地方在后面创建storageClass时候会用到
# - NFS_SERVER:nfs服务器地址
# - NFS_PATH: nfs路径
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
# image: registry.k8s.io/sig-storage/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2
image: k8s.dockerproxy.com/sig-storage/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
- name: NFS_SERVER
# value: <YOUR NFS SERVER HOSTNAME>
value: nfs-share.vpclub.io
- name: NFS_PATH
# value: /var/nfs
value: /data/share
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
# server: <YOUR NFS SERVER HOSTNAME>
server: nfs-share.vpclub.io
path: /data/share
# 因为PV创建以后不可以修改,非常麻烦,建议nfs主机使用域名方式
# 需要在每台主机增加hosts
# echo "192.168.5.10 nfs-share.vpclub.io" >> /etct/hosts
- 02-nfs-storage-class.yaml
provisioner参数需要和PROVISIONER_NAME参数对应
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: nfs-client-root-ns-pvname
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
parameters:
# 此处也可以使用各种规则构造nfs中真实目录名称
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.name}"
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.name}"
# 删除PVC时候的策略,delete :删除目录,retain保留目录
onDelete: retain
# 回收策略 Retain – 手动回收,Recycle – 需要擦除后才能再次使用,Delete – 当用户删除对应的 PVC 时,动态配置的 volume 将被自动删除。默认为 Delete
reclaimPolicy: Retain
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: nfs-client-root-ns-customer
# or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
# 替换为 provisioner pod 的 环境变量 PROVISIONER_NAME
provisioner: "k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner"
parameters:
# 此处也可以使用各种规则构造nfs中真实目录名称
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.name}"
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
# 删除PVC时候的策略,delete :删除目录,retain保留目录
onDelete: retain
# 删除PVC时候的策略,如果存在本项,且值为false,删除目录;如果存在 onDelete 设置,则以 onDelete 设置为准,既本配置项可以不需要
archiveOnDelete: "false"
# 回收策略 Retain – 手动回收,Recycle – 需要擦除后才能再次使用,Delete – 当用户删除对应的 PVC 时,动态配置的 volume 将被自动删除。默认为 Delete
reclaimPolicy: Retain
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: nfs-client-root-ns
# or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
# 替换为 provisioner pod 的 环境变量 PROVISIONER_NAME
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
parameters:
# 此处也可以使用各种规则构造nfs中真实目录名称
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.name}"
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}"
# 删除PVC时候的策略,delete :删除目录,retain保留目录
onDelete: retain
# 回收策略 Retain – 手动回收,Recycle – 需要擦除后才能再次使用,Delete – 当用户删除对应的 PVC 时,动态配置的 volume 将被自动删除。默认为 Delete
reclaimPolicy: Retain
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: nfs-client-root
# or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
# 替换为 provisioner pod 的 环境变量 PROVISIONER_NAME
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
parameters:
# 此处也可以使用各种规则构造nfs中真实目录名称
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.name}"
# "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
pathPattern: "${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
# 删除PVC时候的策略,delete :删除目录,retain保留目录
onDelete: retain
# 回收策略 Retain – 手动回收,Recycle – 需要擦除后才能再次使用,Delete – 当用户删除对应的 PVC 时,动态配置的 volume 将被自动删除。默认为 Delete
reclaimPolicy: Retain
- 执行安装
kubectl apply -f 00-nfs-storage-rabc.yaml
kubectl apply -f 01-nfs-storage-provisioner.yaml
kubectl apply -f 02-nfs-storage-class.yaml
-
使用存储类
- 预创建PVC
-
快捷创建
也可以在创建POD的时候,在添加数据卷的时候直接使用或者新建PVC,存储类选择给定的storageClass,配置选项与预创建一致
-
存储驱动创建pvc规则
pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.name}"
自动生成与PVC名称对应的路径
路径示例:
/data/share/<namespace>/<pvname>对应存储类选择: nfs-client-root-ns-pvname
pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
项目内(namespace)生成自定义路径,需要填写注释
nfs.io/storage-path,由于rancher创建PVC时并不支持填写注释,且PVC创建后不可以给更改,需要使用导入YML方式创建,也可以不指定storage-path,则默认从namespace开始路径示例:
/data/share/<namespace>/<storage-path>对应存储类选择: nfs-client-root-ns-custom
pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}"
自动生产从当前项目(amespace)对应的路径
路径示例:
/data/share/<namespace>对应存储类选择: nfs-client-root-ns
pathPattern: "${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
全完使用自定义路径,从nfs根目录开始,需要填写注释
nfs.io/storage-path,由于rancher创建PVC时并不支持填写注释,且PVC创建后不可以给更改,需要使用导入YML方式创建,也可以不指定storage-path,则默认从根目录开始。路径示例:
/data/share/<storage-path>,如果storage-path不填写,则直接从nfs更目录开始。对应存储类选择: nfs-client-root
- 03-nfs-storage-custome.yaml
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pvc-park-nsdsj
# namespace: nfs-storage
annotations:
nfs.io/storage-path: "park-tianwei" # not required, depending on whether this annotation was shown in the storage class description
spec:
storageClassName: nfs-client-root
# storageClassName: nfs-client-root-ns-customer
# storageClassName: nfs-client-root-ns-pvname
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
# 非必要
# 因为前文的storage-class路径规则为 "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
# 由于rancher界面使用快捷创建、预创建PVC,不支持增加注释,需要复制到导入YAML进行执行,如果你想指定到不同的路径下,可以执行这个
# kubectl apply -f 03-nfs-storage-customer.yaml
-
其他注意事项
- pv创建后不支持修改nfs地址,对于nfs主机应该使用域名
- 如果PVC有项目在使用,则PVC不可以不删,可以用一个centos镜像,将需要用到的PVC生成并挂载,避免误删除,同时可以可以进入到该容器查看磁盘结构和文件信息
calico-image-vp-whdev-v3.21.6
此版本不支持k8s-v1.28.0,提示kind错误
此版本可以在k8s-v1.20.15运行
版本号:v3.21.6
calico有时候下载不来,使用自定义镜像,主要涉及到4个镜像,然后将镜像改名或者修改部署使用的镜像,或者使用如下yaml
docker pull harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/cni:v3.21.6
docker pull harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6
docker pull harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/node:v3.21.6
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-config.yaml
# This ConfigMap is used to configure a self-hosted Calico installation.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: calico-config
namespace: kube-system
data:
# Typha is disabled.
typha_service_name: "none"
# Configure the backend to use.
calico_backend: "bird"
# Configure the MTU to use for workload interfaces and tunnels.
# By default, MTU is auto-detected, and explicitly setting this field should not be required.
# You can override auto-detection by providing a non-zero value.
veth_mtu: "0"
# The CNI network configuration to install on each node. The special
# values in this config will be automatically populated.
cni_network_config: |-
{
"name": "k8s-pod-network",
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "calico",
"log_level": "info",
"log_file_path": "/var/log/calico/cni/cni.log",
"datastore_type": "kubernetes",
"nodename": "__KUBERNETES_NODE_NAME__",
"mtu": __CNI_MTU__,
"ipam": {
"type": "calico-ipam"
},
"policy": {
"type": "k8s"
},
"kubernetes": {
"kubeconfig": "__KUBECONFIG_FILEPATH__"
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"snat": true,
"capabilities": {"portMappings": true}
},
{
"type": "bandwidth",
"capabilities": {"bandwidth": true}
}
]
}
---
# Source: calico/templates/kdd-crds.yaml
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: BGPConfiguration
listKind: BGPConfigurationList
plural: bgpconfigurations
singular: bgpconfiguration
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
description: BGPConfiguration contains the configuration for any BGP routing.
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: BGPConfigurationSpec contains the values of the BGP configuration.
properties:
asNumber:
description: 'ASNumber is the default AS number used by a node. [Default:
64512]'
format: int32
type: integer
communities:
description: Communities is a list of BGP community values and their
arbitrary names for tagging routes.
items:
description: Community contains standard or large community value
and its name.
properties:
name:
description: Name given to community value.
type: string
value:
description: Value must be of format `aa:nn` or `aa:nn:mm`.
For standard community use `aa:nn` format, where `aa` and
`nn` are 16 bit number. For large community use `aa:nn:mm`
format, where `aa`, `nn` and `mm` are 32 bit number. Where,
`aa` is an AS Number, `nn` and `mm` are per-AS identifier.
pattern: ^(\d+):(\d+)$|^(\d+):(\d+):(\d+)$
type: string
type: object
type: array
listenPort:
description: ListenPort is the port where BGP protocol should listen.
Defaults to 179
maximum: 65535
minimum: 1
type: integer
logSeverityScreen:
description: 'LogSeverityScreen is the log severity above which logs
are sent to the stdout. [Default: INFO]'
type: string
nodeToNodeMeshEnabled:
description: 'NodeToNodeMeshEnabled sets whether full node to node
BGP mesh is enabled. [Default: true]'
type: boolean
prefixAdvertisements:
description: PrefixAdvertisements contains per-prefix advertisement
configuration.
items:
description: PrefixAdvertisement configures advertisement properties
for the specified CIDR.
properties:
cidr:
description: CIDR for which properties should be advertised.
type: string
communities:
description: Communities can be list of either community names
already defined in `Specs.Communities` or community value
of format `aa:nn` or `aa:nn:mm`. For standard community use
`aa:nn` format, where `aa` and `nn` are 16 bit number. For
large community use `aa:nn:mm` format, where `aa`, `nn` and
`mm` are 32 bit number. Where,`aa` is an AS Number, `nn` and
`mm` are per-AS identifier.
items:
type: string
type: array
type: object
type: array
serviceClusterIPs:
description: ServiceClusterIPs are the CIDR blocks from which service
cluster IPs are allocated. If specified, Calico will advertise these
blocks, as well as any cluster IPs within them.
items:
description: ServiceClusterIPBlock represents a single allowed ClusterIP
CIDR block.
properties:
cidr:
type: string
type: object
type: array
serviceExternalIPs:
description: ServiceExternalIPs are the CIDR blocks for Kubernetes
Service External IPs. Kubernetes Service ExternalIPs will only be
advertised if they are within one of these blocks.
items:
description: ServiceExternalIPBlock represents a single allowed
External IP CIDR block.
properties:
cidr:
type: string
type: object
type: array
serviceLoadBalancerIPs:
description: ServiceLoadBalancerIPs are the CIDR blocks for Kubernetes
Service LoadBalancer IPs. Kubernetes Service status.LoadBalancer.Ingress
IPs will only be advertised if they are within one of these blocks.
items:
description: ServiceLoadBalancerIPBlock represents a single allowed
LoadBalancer IP CIDR block.
properties:
cidr:
type: string
type: object
type: array
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: BGPPeer
listKind: BGPPeerList
plural: bgppeers
singular: bgppeer
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: BGPPeerSpec contains the specification for a BGPPeer resource.
properties:
asNumber:
description: The AS Number of the peer.
format: int32
type: integer
keepOriginalNextHop:
description: Option to keep the original nexthop field when routes
are sent to a BGP Peer. Setting "true" configures the selected BGP
Peers node to use the "next hop keep;" instead of "next hop self;"(default)
in the specific branch of the Node on "bird.cfg".
type: boolean
maxRestartTime:
description: Time to allow for software restart. When specified,
this is configured as the graceful restart timeout. When not specified,
the BIRD default of 120s is used.
type: string
node:
description: The node name identifying the Calico node instance that
is targeted by this peer. If this is not set, and no nodeSelector
is specified, then this BGP peer selects all nodes in the cluster.
type: string
nodeSelector:
description: Selector for the nodes that should have this peering. When
this is set, the Node field must be empty.
type: string
password:
description: Optional BGP password for the peerings generated by this
BGPPeer resource.
properties:
secretKeyRef:
description: Selects a key of a secret in the node pod's namespace.
properties:
key:
description: The key of the secret to select from. Must be
a valid secret key.
type: string
name:
description: 'Name of the referent. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/names/#names
TODO: Add other useful fields. apiVersion, kind, uid?'
type: string
optional:
description: Specify whether the Secret or its key must be
defined
type: boolean
required:
- key
type: object
type: object
peerIP:
description: The IP address of the peer followed by an optional port
number to peer with. If port number is given, format should be `[<IPv6>]:port`
or `<IPv4>:<port>` for IPv4. If optional port number is not set,
and this peer IP and ASNumber belongs to a calico/node with ListenPort
set in BGPConfiguration, then we use that port to peer.
type: string
peerSelector:
description: Selector for the remote nodes to peer with. When this
is set, the PeerIP and ASNumber fields must be empty. For each
peering between the local node and selected remote nodes, we configure
an IPv4 peering if both ends have NodeBGPSpec.IPv4Address specified,
and an IPv6 peering if both ends have NodeBGPSpec.IPv6Address specified. The
remote AS number comes from the remote node's NodeBGPSpec.ASNumber,
or the global default if that is not set.
type: string
sourceAddress:
description: Specifies whether and how to configure a source address
for the peerings generated by this BGPPeer resource. Default value
"UseNodeIP" means to configure the node IP as the source address. "None"
means not to configure a source address.
type: string
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: BlockAffinity
listKind: BlockAffinityList
plural: blockaffinities
singular: blockaffinity
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: BlockAffinitySpec contains the specification for a BlockAffinity
resource.
properties:
cidr:
type: string
deleted:
description: Deleted indicates that this block affinity is being deleted.
This field is a string for compatibility with older releases that
mistakenly treat this field as a string.
type: string
node:
type: string
state:
type: string
required:
- cidr
- deleted
- node
- state
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
annotations:
controller-gen.kubebuilder.io/version: (devel)
creationTimestamp: null
name: caliconodestatuses.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: CalicoNodeStatus
listKind: CalicoNodeStatusList
plural: caliconodestatuses
singular: caliconodestatus
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: CalicoNodeStatusSpec contains the specification for a CalicoNodeStatus
resource.
properties:
classes:
description: Classes declares the types of information to monitor
for this calico/node, and allows for selective status reporting
about certain subsets of information.
items:
type: string
type: array
node:
description: The node name identifies the Calico node instance for
node status.
type: string
updatePeriodSeconds:
description: UpdatePeriodSeconds is the period at which CalicoNodeStatus
should be updated. Set to 0 to disable CalicoNodeStatus refresh.
Maximum update period is one day.
format: int32
type: integer
type: object
status:
description: CalicoNodeStatusStatus defines the observed state of CalicoNodeStatus.
No validation needed for status since it is updated by Calico.
properties:
agent:
description: Agent holds agent status on the node.
properties:
birdV4:
description: BIRDV4 represents the latest observed status of bird4.
properties:
lastBootTime:
description: LastBootTime holds the value of lastBootTime
from bird.ctl output.
type: string
lastReconfigurationTime:
description: LastReconfigurationTime holds the value of lastReconfigTime
from bird.ctl output.
type: string
routerID:
description: Router ID used by bird.
type: string
state:
description: The state of the BGP Daemon.
type: string
version:
description: Version of the BGP daemon
type: string
type: object
birdV6:
description: BIRDV6 represents the latest observed status of bird6.
properties:
lastBootTime:
description: LastBootTime holds the value of lastBootTime
from bird.ctl output.
type: string
lastReconfigurationTime:
description: LastReconfigurationTime holds the value of lastReconfigTime
from bird.ctl output.
type: string
routerID:
description: Router ID used by bird.
type: string
state:
description: The state of the BGP Daemon.
type: string
version:
description: Version of the BGP daemon
type: string
type: object
type: object
bgp:
description: BGP holds node BGP status.
properties:
numberEstablishedV4:
description: The total number of IPv4 established bgp sessions.
type: integer
numberEstablishedV6:
description: The total number of IPv6 established bgp sessions.
type: integer
numberNotEstablishedV4:
description: The total number of IPv4 non-established bgp sessions.
type: integer
numberNotEstablishedV6:
description: The total number of IPv6 non-established bgp sessions.
type: integer
peersV4:
description: PeersV4 represents IPv4 BGP peers status on the node.
items:
description: CalicoNodePeer contains the status of BGP peers
on the node.
properties:
peerIP:
description: IP address of the peer whose condition we are
reporting.
type: string
since:
description: Since the state or reason last changed.
type: string
state:
description: State is the BGP session state.
type: string
type:
description: Type indicates whether this peer is configured
via the node-to-node mesh, or via en explicit global or
per-node BGPPeer object.
type: string
type: object
type: array
peersV6:
description: PeersV6 represents IPv6 BGP peers status on the node.
items:
description: CalicoNodePeer contains the status of BGP peers
on the node.
properties:
peerIP:
description: IP address of the peer whose condition we are
reporting.
type: string
since:
description: Since the state or reason last changed.
type: string
state:
description: State is the BGP session state.
type: string
type:
description: Type indicates whether this peer is configured
via the node-to-node mesh, or via en explicit global or
per-node BGPPeer object.
type: string
type: object
type: array
required:
- numberEstablishedV4
- numberEstablishedV6
- numberNotEstablishedV4
- numberNotEstablishedV6
type: object
lastUpdated:
description: LastUpdated is a timestamp representing the server time
when CalicoNodeStatus object last updated. It is represented in
RFC3339 form and is in UTC.
format: date-time
nullable: true
type: string
routes:
description: Routes reports routes known to the Calico BGP daemon
on the node.
properties:
routesV4:
description: RoutesV4 represents IPv4 routes on the node.
items:
description: CalicoNodeRoute contains the status of BGP routes
on the node.
properties:
destination:
description: Destination of the route.
type: string
gateway:
description: Gateway for the destination.
type: string
interface:
description: Interface for the destination
type: string
learnedFrom:
description: LearnedFrom contains information regarding
where this route originated.
properties:
peerIP:
description: If sourceType is NodeMesh or BGPPeer, IP
address of the router that sent us this route.
type: string
sourceType:
description: Type of the source where a route is learned
from.
type: string
type: object
type:
description: Type indicates if the route is being used for
forwarding or not.
type: string
type: object
type: array
routesV6:
description: RoutesV6 represents IPv6 routes on the node.
items:
description: CalicoNodeRoute contains the status of BGP routes
on the node.
properties:
destination:
description: Destination of the route.
type: string
gateway:
description: Gateway for the destination.
type: string
interface:
description: Interface for the destination
type: string
learnedFrom:
description: LearnedFrom contains information regarding
where this route originated.
properties:
peerIP:
description: If sourceType is NodeMesh or BGPPeer, IP
address of the router that sent us this route.
type: string
sourceType:
description: Type of the source where a route is learned
from.
type: string
type: object
type:
description: Type indicates if the route is being used for
forwarding or not.
type: string
type: object
type: array
type: object
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: ClusterInformation
listKind: ClusterInformationList
plural: clusterinformations
singular: clusterinformation
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
description: ClusterInformation contains the cluster specific information.
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: ClusterInformationSpec contains the values of describing
the cluster.
properties:
calicoVersion:
description: CalicoVersion is the version of Calico that the cluster
is running
type: string
clusterGUID:
description: ClusterGUID is the GUID of the cluster
type: string
clusterType:
description: ClusterType describes the type of the cluster
type: string
datastoreReady:
description: DatastoreReady is used during significant datastore migrations
to signal to components such as Felix that it should wait before
accessing the datastore.
type: boolean
variant:
description: Variant declares which variant of Calico should be active.
type: string
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: FelixConfiguration
listKind: FelixConfigurationList
plural: felixconfigurations
singular: felixconfiguration
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
description: Felix Configuration contains the configuration for Felix.
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: FelixConfigurationSpec contains the values of the Felix configuration.
properties:
allowIPIPPacketsFromWorkloads:
description: 'AllowIPIPPacketsFromWorkloads controls whether Felix
will add a rule to drop IPIP encapsulated traffic from workloads
[Default: false]'
type: boolean
allowVXLANPacketsFromWorkloads:
description: 'AllowVXLANPacketsFromWorkloads controls whether Felix
will add a rule to drop VXLAN encapsulated traffic from workloads
[Default: false]'
type: boolean
awsSrcDstCheck:
description: 'Set source-destination-check on AWS EC2 instances. Accepted
value must be one of "DoNothing", "Enable" or "Disable". [Default:
DoNothing]'
enum:
- DoNothing
- Enable
- Disable
type: string
bpfConnectTimeLoadBalancingEnabled:
description: 'BPFConnectTimeLoadBalancingEnabled when in BPF mode,
controls whether Felix installs the connection-time load balancer. The
connect-time load balancer is required for the host to be able to
reach Kubernetes services and it improves the performance of pod-to-service
connections. The only reason to disable it is for debugging purposes. [Default:
true]'
type: boolean
bpfDataIfacePattern:
description: BPFDataIfacePattern is a regular expression that controls
which interfaces Felix should attach BPF programs to in order to
catch traffic to/from the network. This needs to match the interfaces
that Calico workload traffic flows over as well as any interfaces
that handle incoming traffic to nodeports and services from outside
the cluster. It should not match the workload interfaces (usually
named cali...).
type: string
bpfDisableUnprivileged:
description: 'BPFDisableUnprivileged, if enabled, Felix sets the kernel.unprivileged_bpf_disabled
sysctl to disable unprivileged use of BPF. This ensures that unprivileged
users cannot access Calico''s BPF maps and cannot insert their own
BPF programs to interfere with Calico''s. [Default: true]'
type: boolean
bpfEnabled:
description: 'BPFEnabled, if enabled Felix will use the BPF dataplane.
[Default: false]'
type: boolean
bpfExtToServiceConnmark:
description: 'BPFExtToServiceConnmark in BPF mode, control a 32bit
mark that is set on connections from an external client to a local
service. This mark allows us to control how packets of that connection
are routed within the host and how is routing intepreted by RPF
check. [Default: 0]'
type: integer
bpfExternalServiceMode:
description: 'BPFExternalServiceMode in BPF mode, controls how connections
from outside the cluster to services (node ports and cluster IPs)
are forwarded to remote workloads. If set to "Tunnel" then both
request and response traffic is tunneled to the remote node. If
set to "DSR", the request traffic is tunneled but the response traffic
is sent directly from the remote node. In "DSR" mode, the remote
node appears to use the IP of the ingress node; this requires a
permissive L2 network. [Default: Tunnel]'
type: string
bpfKubeProxyEndpointSlicesEnabled:
description: BPFKubeProxyEndpointSlicesEnabled in BPF mode, controls
whether Felix's embedded kube-proxy accepts EndpointSlices or not.
type: boolean
bpfKubeProxyIptablesCleanupEnabled:
description: 'BPFKubeProxyIptablesCleanupEnabled, if enabled in BPF
mode, Felix will proactively clean up the upstream Kubernetes kube-proxy''s
iptables chains. Should only be enabled if kube-proxy is not running. [Default:
true]'
type: boolean
bpfKubeProxyMinSyncPeriod:
description: 'BPFKubeProxyMinSyncPeriod, in BPF mode, controls the
minimum time between updates to the dataplane for Felix''s embedded
kube-proxy. Lower values give reduced set-up latency. Higher values
reduce Felix CPU usage by batching up more work. [Default: 1s]'
type: string
bpfLogLevel:
description: 'BPFLogLevel controls the log level of the BPF programs
when in BPF dataplane mode. One of "Off", "Info", or "Debug". The
logs are emitted to the BPF trace pipe, accessible with the command
`tc exec bpf debug`. [Default: Off].'
type: string
bpfPSNATPorts:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: 'BPFPSNATPorts sets the range from which we randomly
pick a port if there is a source port collision. This should be
within the ephemeral range as defined by RFC 6056 (1024–65535) and
preferably outside the ephemeral ranges used by common operating
systems. Linux uses 32768–60999, while others mostly use the IANA
defined range 49152–65535. It is not necessarily a problem if this
range overlaps with the operating systems. Both ends of the range
are inclusive. [Default: 20000:29999]'
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
chainInsertMode:
description: 'ChainInsertMode controls whether Felix hooks the kernel''s
top-level iptables chains by inserting a rule at the top of the
chain or by appending a rule at the bottom. insert is the safe default
since it prevents Calico''s rules from being bypassed. If you switch
to append mode, be sure that the other rules in the chains signal
acceptance by falling through to the Calico rules, otherwise the
Calico policy will be bypassed. [Default: insert]'
type: string
dataplaneDriver:
type: string
debugDisableLogDropping:
type: boolean
debugMemoryProfilePath:
type: string
debugSimulateCalcGraphHangAfter:
type: string
debugSimulateDataplaneHangAfter:
type: string
defaultEndpointToHostAction:
description: 'DefaultEndpointToHostAction controls what happens to
traffic that goes from a workload endpoint to the host itself (after
the traffic hits the endpoint egress policy). By default Calico
blocks traffic from workload endpoints to the host itself with an
iptables "DROP" action. If you want to allow some or all traffic
from endpoint to host, set this parameter to RETURN or ACCEPT. Use
RETURN if you have your own rules in the iptables "INPUT" chain;
Calico will insert its rules at the top of that chain, then "RETURN"
packets to the "INPUT" chain once it has completed processing workload
endpoint egress policy. Use ACCEPT to unconditionally accept packets
from workloads after processing workload endpoint egress policy.
[Default: Drop]'
type: string
deviceRouteProtocol:
description: This defines the route protocol added to programmed device
routes, by default this will be RTPROT_BOOT when left blank.
type: integer
deviceRouteSourceAddress:
description: This is the source address to use on programmed device
routes. By default the source address is left blank, leaving the
kernel to choose the source address used.
type: string
disableConntrackInvalidCheck:
type: boolean
endpointReportingDelay:
type: string
endpointReportingEnabled:
type: boolean
externalNodesList:
description: ExternalNodesCIDRList is a list of CIDR's of external-non-calico-nodes
which may source tunnel traffic and have the tunneled traffic be
accepted at calico nodes.
items:
type: string
type: array
failsafeInboundHostPorts:
description: 'FailsafeInboundHostPorts is a list of UDP/TCP ports
and CIDRs that Felix will allow incoming traffic to host endpoints
on irrespective of the security policy. This is useful to avoid
accidentally cutting off a host with incorrect configuration. For
back-compatibility, if the protocol is not specified, it defaults
to "tcp". If a CIDR is not specified, it will allow traffic from
all addresses. To disable all inbound host ports, use the value
none. The default value allows ssh access and DHCP. [Default: tcp:22,
udp:68, tcp:179, tcp:2379, tcp:2380, tcp:6443, tcp:6666, tcp:6667]'
items:
description: ProtoPort is combination of protocol, port, and CIDR.
Protocol and port must be specified.
properties:
net:
type: string
port:
type: integer
protocol:
type: string
required:
- port
- protocol
type: object
type: array
failsafeOutboundHostPorts:
description: 'FailsafeOutboundHostPorts is a list of UDP/TCP ports
and CIDRs that Felix will allow outgoing traffic from host endpoints
to irrespective of the security policy. This is useful to avoid
accidentally cutting off a host with incorrect configuration. For
back-compatibility, if the protocol is not specified, it defaults
to "tcp". If a CIDR is not specified, it will allow traffic from
all addresses. To disable all outbound host ports, use the value
none. The default value opens etcd''s standard ports to ensure that
Felix does not get cut off from etcd as well as allowing DHCP and
DNS. [Default: tcp:179, tcp:2379, tcp:2380, tcp:6443, tcp:6666,
tcp:6667, udp:53, udp:67]'
items:
description: ProtoPort is combination of protocol, port, and CIDR.
Protocol and port must be specified.
properties:
net:
type: string
port:
type: integer
protocol:
type: string
required:
- port
- protocol
type: object
type: array
featureDetectOverride:
description: FeatureDetectOverride is used to override the feature
detection. Values are specified in a comma separated list with no
spaces, example; "SNATFullyRandom=true,MASQFullyRandom=false,RestoreSupportsLock=".
"true" or "false" will force the feature, empty or omitted values
are auto-detected.
type: string
floatingIPs:
default: Disabled
description: FloatingIPs configures whether or not Felix will program
floating IP addresses.
enum:
- Enabled
- Disabled
type: string
genericXDPEnabled:
description: 'GenericXDPEnabled enables Generic XDP so network cards
that don''t support XDP offload or driver modes can use XDP. This
is not recommended since it doesn''t provide better performance
than iptables. [Default: false]'
type: boolean
healthEnabled:
type: boolean
healthHost:
type: string
healthPort:
type: integer
interfaceExclude:
description: 'InterfaceExclude is a comma-separated list of interfaces
that Felix should exclude when monitoring for host endpoints. The
default value ensures that Felix ignores Kubernetes'' IPVS dummy
interface, which is used internally by kube-proxy. If you want to
exclude multiple interface names using a single value, the list
supports regular expressions. For regular expressions you must wrap
the value with ''/''. For example having values ''/^kube/,veth1''
will exclude all interfaces that begin with ''kube'' and also the
interface ''veth1''. [Default: kube-ipvs0]'
type: string
interfacePrefix:
description: 'InterfacePrefix is the interface name prefix that identifies
workload endpoints and so distinguishes them from host endpoint
interfaces. Note: in environments other than bare metal, the orchestrators
configure this appropriately. For example our Kubernetes and Docker
integrations set the ''cali'' value, and our OpenStack integration
sets the ''tap'' value. [Default: cali]'
type: string
interfaceRefreshInterval:
description: InterfaceRefreshInterval is the period at which Felix
rescans local interfaces to verify their state. The rescan can be
disabled by setting the interval to 0.
type: string
ipipEnabled:
type: boolean
ipipMTU:
description: 'IPIPMTU is the MTU to set on the tunnel device. See
Configuring MTU [Default: 1440]'
type: integer
ipsetsRefreshInterval:
description: 'IpsetsRefreshInterval is the period at which Felix re-checks
all iptables state to ensure that no other process has accidentally
broken Calico''s rules. Set to 0 to disable iptables refresh. [Default:
90s]'
type: string
iptablesBackend:
description: IptablesBackend specifies which backend of iptables will
be used. The default is legacy.
type: string
iptablesFilterAllowAction:
type: string
iptablesLockFilePath:
description: 'IptablesLockFilePath is the location of the iptables
lock file. You may need to change this if the lock file is not in
its standard location (for example if you have mapped it into Felix''s
container at a different path). [Default: /run/xtables.lock]'
type: string
iptablesLockProbeInterval:
description: 'IptablesLockProbeInterval is the time that Felix will
wait between attempts to acquire the iptables lock if it is not
available. Lower values make Felix more responsive when the lock
is contended, but use more CPU. [Default: 50ms]'
type: string
iptablesLockTimeout:
description: 'IptablesLockTimeout is the time that Felix will wait
for the iptables lock, or 0, to disable. To use this feature, Felix
must share the iptables lock file with all other processes that
also take the lock. When running Felix inside a container, this
requires the /run directory of the host to be mounted into the calico/node
or calico/felix container. [Default: 0s disabled]'
type: string
iptablesMangleAllowAction:
type: string
iptablesMarkMask:
description: 'IptablesMarkMask is the mask that Felix selects its
IPTables Mark bits from. Should be a 32 bit hexadecimal number with
at least 8 bits set, none of which clash with any other mark bits
in use on the system. [Default: 0xff000000]'
format: int32
type: integer
iptablesNATOutgoingInterfaceFilter:
type: string
iptablesPostWriteCheckInterval:
description: 'IptablesPostWriteCheckInterval is the period after Felix
has done a write to the dataplane that it schedules an extra read
back in order to check the write was not clobbered by another process.
This should only occur if another application on the system doesn''t
respect the iptables lock. [Default: 1s]'
type: string
iptablesRefreshInterval:
description: 'IptablesRefreshInterval is the period at which Felix
re-checks the IP sets in the dataplane to ensure that no other process
has accidentally broken Calico''s rules. Set to 0 to disable IP
sets refresh. Note: the default for this value is lower than the
other refresh intervals as a workaround for a Linux kernel bug that
was fixed in kernel version 4.11. If you are using v4.11 or greater
you may want to set this to, a higher value to reduce Felix CPU
usage. [Default: 10s]'
type: string
ipv6Support:
type: boolean
kubeNodePortRanges:
description: 'KubeNodePortRanges holds list of port ranges used for
service node ports. Only used if felix detects kube-proxy running
in ipvs mode. Felix uses these ranges to separate host and workload
traffic. [Default: 30000:32767].'
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
logFilePath:
description: 'LogFilePath is the full path to the Felix log. Set to
none to disable file logging. [Default: /var/log/calico/felix.log]'
type: string
logPrefix:
description: 'LogPrefix is the log prefix that Felix uses when rendering
LOG rules. [Default: calico-packet]'
type: string
logSeverityFile:
description: 'LogSeverityFile is the log severity above which logs
are sent to the log file. [Default: Info]'
type: string
logSeverityScreen:
description: 'LogSeverityScreen is the log severity above which logs
are sent to the stdout. [Default: Info]'
type: string
logSeveritySys:
description: 'LogSeveritySys is the log severity above which logs
are sent to the syslog. Set to None for no logging to syslog. [Default:
Info]'
type: string
maxIpsetSize:
type: integer
metadataAddr:
description: 'MetadataAddr is the IP address or domain name of the
server that can answer VM queries for cloud-init metadata. In OpenStack,
this corresponds to the machine running nova-api (or in Ubuntu,
nova-api-metadata). A value of none (case insensitive) means that
Felix should not set up any NAT rule for the metadata path. [Default:
127.0.0.1]'
type: string
metadataPort:
description: 'MetadataPort is the port of the metadata server. This,
combined with global.MetadataAddr (if not ''None''), is used to
set up a NAT rule, from 169.254.169.254:80 to MetadataAddr:MetadataPort.
In most cases this should not need to be changed [Default: 8775].'
type: integer
mtuIfacePattern:
description: MTUIfacePattern is a regular expression that controls
which interfaces Felix should scan in order to calculate the host's
MTU. This should not match workload interfaces (usually named cali...).
type: string
natOutgoingAddress:
description: NATOutgoingAddress specifies an address to use when performing
source NAT for traffic in a natOutgoing pool that is leaving the
network. By default the address used is an address on the interface
the traffic is leaving on (ie it uses the iptables MASQUERADE target)
type: string
natPortRange:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: NATPortRange specifies the range of ports that is used
for port mapping when doing outgoing NAT. When unset the default
behavior of the network stack is used.
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
netlinkTimeout:
type: string
openstackRegion:
description: 'OpenstackRegion is the name of the region that a particular
Felix belongs to. In a multi-region Calico/OpenStack deployment,
this must be configured somehow for each Felix (here in the datamodel,
or in felix.cfg or the environment on each compute node), and must
match the [calico] openstack_region value configured in neutron.conf
on each node. [Default: Empty]'
type: string
policySyncPathPrefix:
description: 'PolicySyncPathPrefix is used to by Felix to communicate
policy changes to external services, like Application layer policy.
[Default: Empty]'
type: string
prometheusGoMetricsEnabled:
description: 'PrometheusGoMetricsEnabled disables Go runtime metrics
collection, which the Prometheus client does by default, when set
to false. This reduces the number of metrics reported, reducing
Prometheus load. [Default: true]'
type: boolean
prometheusMetricsEnabled:
description: 'PrometheusMetricsEnabled enables the Prometheus metrics
server in Felix if set to true. [Default: false]'
type: boolean
prometheusMetricsHost:
description: 'PrometheusMetricsHost is the host that the Prometheus
metrics server should bind to. [Default: empty]'
type: string
prometheusMetricsPort:
description: 'PrometheusMetricsPort is the TCP port that the Prometheus
metrics server should bind to. [Default: 9091]'
type: integer
prometheusProcessMetricsEnabled:
description: 'PrometheusProcessMetricsEnabled disables process metrics
collection, which the Prometheus client does by default, when set
to false. This reduces the number of metrics reported, reducing
Prometheus load. [Default: true]'
type: boolean
prometheusWireGuardMetricsEnabled:
description: 'PrometheusWireGuardMetricsEnabled disables wireguard
metrics collection, which the Prometheus client does by default,
when set to false. This reduces the number of metrics reported,
reducing Prometheus load. [Default: true]'
type: boolean
removeExternalRoutes:
description: Whether or not to remove device routes that have not
been programmed by Felix. Disabling this will allow external applications
to also add device routes. This is enabled by default which means
we will remove externally added routes.
type: boolean
reportingInterval:
description: 'ReportingInterval is the interval at which Felix reports
its status into the datastore or 0 to disable. Must be non-zero
in OpenStack deployments. [Default: 30s]'
type: string
reportingTTL:
description: 'ReportingTTL is the time-to-live setting for process-wide
status reports. [Default: 90s]'
type: string
routeRefreshInterval:
description: 'RouteRefreshInterval is the period at which Felix re-checks
the routes in the dataplane to ensure that no other process has
accidentally broken Calico''s rules. Set to 0 to disable route refresh.
[Default: 90s]'
type: string
routeSource:
description: 'RouteSource configures where Felix gets its routing
information. - WorkloadIPs: use workload endpoints to construct
routes. - CalicoIPAM: the default - use IPAM data to construct routes.'
type: string
routeTableRange:
description: Calico programs additional Linux route tables for various
purposes. RouteTableRange specifies the indices of the route tables
that Calico should use.
properties:
max:
type: integer
min:
type: integer
required:
- max
- min
type: object
serviceLoopPrevention:
description: 'When service IP advertisement is enabled, prevent routing
loops to service IPs that are not in use, by dropping or rejecting
packets that do not get DNAT''d by kube-proxy. Unless set to "Disabled",
in which case such routing loops continue to be allowed. [Default:
Drop]'
type: string
sidecarAccelerationEnabled:
description: 'SidecarAccelerationEnabled enables experimental sidecar
acceleration [Default: false]'
type: boolean
usageReportingEnabled:
description: 'UsageReportingEnabled reports anonymous Calico version
number and cluster size to projectcalico.org. Logs warnings returned
by the usage server. For example, if a significant security vulnerability
has been discovered in the version of Calico being used. [Default:
true]'
type: boolean
usageReportingInitialDelay:
description: 'UsageReportingInitialDelay controls the minimum delay
before Felix makes a report. [Default: 300s]'
type: string
usageReportingInterval:
description: 'UsageReportingInterval controls the interval at which
Felix makes reports. [Default: 86400s]'
type: string
useInternalDataplaneDriver:
type: boolean
vxlanEnabled:
type: boolean
vxlanMTU:
description: 'VXLANMTU is the MTU to set on the tunnel device. See
Configuring MTU [Default: 1440]'
type: integer
vxlanPort:
type: integer
vxlanVNI:
type: integer
wireguardEnabled:
description: 'WireguardEnabled controls whether Wireguard is enabled.
[Default: false]'
type: boolean
wireguardHostEncryptionEnabled:
description: 'WireguardHostEncryptionEnabled controls whether Wireguard
host-to-host encryption is enabled. [Default: false]'
type: boolean
wireguardInterfaceName:
description: 'WireguardInterfaceName specifies the name to use for
the Wireguard interface. [Default: wg.calico]'
type: string
wireguardListeningPort:
description: 'WireguardListeningPort controls the listening port used
by Wireguard. [Default: 51820]'
type: integer
wireguardMTU:
description: 'WireguardMTU controls the MTU on the Wireguard interface.
See Configuring MTU [Default: 1420]'
type: integer
wireguardRoutingRulePriority:
description: 'WireguardRoutingRulePriority controls the priority value
to use for the Wireguard routing rule. [Default: 99]'
type: integer
xdpEnabled:
description: 'XDPEnabled enables XDP acceleration for suitable untracked
incoming deny rules. [Default: true]'
type: boolean
xdpRefreshInterval:
description: 'XDPRefreshInterval is the period at which Felix re-checks
all XDP state to ensure that no other process has accidentally broken
Calico''s BPF maps or attached programs. Set to 0 to disable XDP
refresh. [Default: 90s]'
type: string
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: GlobalNetworkPolicy
listKind: GlobalNetworkPolicyList
plural: globalnetworkpolicies
singular: globalnetworkpolicy
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
properties:
applyOnForward:
description: ApplyOnForward indicates to apply the rules in this policy
on forward traffic.
type: boolean
doNotTrack:
description: DoNotTrack indicates whether packets matched by the rules
in this policy should go through the data plane's connection tracking,
such as Linux conntrack. If True, the rules in this policy are
applied before any data plane connection tracking, and packets allowed
by this policy are marked as not to be tracked.
type: boolean
egress:
description: The ordered set of egress rules. Each rule contains
a set of packet match criteria and a corresponding action to apply.
items:
description: "A Rule encapsulates a set of match criteria and an
action. Both selector-based security Policy and security Profiles
reference rules - separated out as a list of rules for both ingress
and egress packet matching. \n Each positive match criteria has
a negated version, prefixed with \"Not\". All the match criteria
within a rule must be satisfied for a packet to match. A single
rule can contain the positive and negative version of a match
and both must be satisfied for the rule to match."
properties:
action:
type: string
destination:
description: Destination contains the match criteria that apply
to destination entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
http:
description: HTTP contains match criteria that apply to HTTP
requests.
properties:
methods:
description: Methods is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply only to HTTP requests that use one of
the listed HTTP Methods (e.g. GET, PUT, etc.) Multiple
methods are OR'd together.
items:
type: string
type: array
paths:
description: 'Paths is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply to HTTP requests that use one of the
listed HTTP Paths. Multiple paths are OR''d together.
e.g: - exact: /foo - prefix: /bar NOTE: Each entry may
ONLY specify either a `exact` or a `prefix` match. The
validator will check for it.'
items:
description: 'HTTPPath specifies an HTTP path to match.
It may be either of the form: exact: <path>: which matches
the path exactly or prefix: <path-prefix>: which matches
the path prefix'
properties:
exact:
type: string
prefix:
type: string
type: object
type: array
type: object
icmp:
description: ICMP is an optional field that restricts the rule
to apply to a specific type and code of ICMP traffic. This
should only be specified if the Protocol field is set to "ICMP"
or "ICMPv6".
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
ipVersion:
description: IPVersion is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only match a specific IP version.
type: integer
metadata:
description: Metadata contains additional information for this
rule
properties:
annotations:
additionalProperties:
type: string
description: Annotations is a set of key value pairs that
give extra information about the rule
type: object
type: object
notICMP:
description: NotICMP is the negated version of the ICMP field.
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
notProtocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: NotProtocol is the negated version of the Protocol
field.
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
protocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: "Protocol is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic of a specific IP protocol. Required
if any of the EntityRules contain Ports (because ports only
apply to certain protocols). \n Must be one of these string
values: \"TCP\", \"UDP\", \"ICMP\", \"ICMPv6\", \"SCTP\",
\"UDPLite\" or an integer in the range 1-255."
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
source:
description: Source contains the match criteria that apply to
source entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
required:
- action
type: object
type: array
ingress:
description: The ordered set of ingress rules. Each rule contains
a set of packet match criteria and a corresponding action to apply.
items:
description: "A Rule encapsulates a set of match criteria and an
action. Both selector-based security Policy and security Profiles
reference rules - separated out as a list of rules for both ingress
and egress packet matching. \n Each positive match criteria has
a negated version, prefixed with \"Not\". All the match criteria
within a rule must be satisfied for a packet to match. A single
rule can contain the positive and negative version of a match
and both must be satisfied for the rule to match."
properties:
action:
type: string
destination:
description: Destination contains the match criteria that apply
to destination entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
http:
description: HTTP contains match criteria that apply to HTTP
requests.
properties:
methods:
description: Methods is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply only to HTTP requests that use one of
the listed HTTP Methods (e.g. GET, PUT, etc.) Multiple
methods are OR'd together.
items:
type: string
type: array
paths:
description: 'Paths is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply to HTTP requests that use one of the
listed HTTP Paths. Multiple paths are OR''d together.
e.g: - exact: /foo - prefix: /bar NOTE: Each entry may
ONLY specify either a `exact` or a `prefix` match. The
validator will check for it.'
items:
description: 'HTTPPath specifies an HTTP path to match.
It may be either of the form: exact: <path>: which matches
the path exactly or prefix: <path-prefix>: which matches
the path prefix'
properties:
exact:
type: string
prefix:
type: string
type: object
type: array
type: object
icmp:
description: ICMP is an optional field that restricts the rule
to apply to a specific type and code of ICMP traffic. This
should only be specified if the Protocol field is set to "ICMP"
or "ICMPv6".
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
ipVersion:
description: IPVersion is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only match a specific IP version.
type: integer
metadata:
description: Metadata contains additional information for this
rule
properties:
annotations:
additionalProperties:
type: string
description: Annotations is a set of key value pairs that
give extra information about the rule
type: object
type: object
notICMP:
description: NotICMP is the negated version of the ICMP field.
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
notProtocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: NotProtocol is the negated version of the Protocol
field.
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
protocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: "Protocol is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic of a specific IP protocol. Required
if any of the EntityRules contain Ports (because ports only
apply to certain protocols). \n Must be one of these string
values: \"TCP\", \"UDP\", \"ICMP\", \"ICMPv6\", \"SCTP\",
\"UDPLite\" or an integer in the range 1-255."
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
source:
description: Source contains the match criteria that apply to
source entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
required:
- action
type: object
type: array
namespaceSelector:
description: NamespaceSelector is an optional field for an expression
used to select a pod based on namespaces.
type: string
order:
description: Order is an optional field that specifies the order in
which the policy is applied. Policies with higher "order" are applied
after those with lower order. If the order is omitted, it may be
considered to be "infinite" - i.e. the policy will be applied last. Policies
with identical order will be applied in alphanumerical order based
on the Policy "Name".
type: number
preDNAT:
description: PreDNAT indicates to apply the rules in this policy before
any DNAT.
type: boolean
selector:
description: "The selector is an expression used to pick pick out
the endpoints that the policy should be applied to. \n Selector
expressions follow this syntax: \n \tlabel == \"string_literal\"
\ -> comparison, e.g. my_label == \"foo bar\" \tlabel != \"string_literal\"
\ -> not equal; also matches if label is not present \tlabel in
{ \"a\", \"b\", \"c\", ... } -> true if the value of label X is
one of \"a\", \"b\", \"c\" \tlabel not in { \"a\", \"b\", \"c\",
... } -> true if the value of label X is not one of \"a\", \"b\",
\"c\" \thas(label_name) -> True if that label is present \t! expr
-> negation of expr \texpr && expr -> Short-circuit and \texpr
|| expr -> Short-circuit or \t( expr ) -> parens for grouping \tall()
or the empty selector -> matches all endpoints. \n Label names are
allowed to contain alphanumerics, -, _ and /. String literals are
more permissive but they do not support escape characters. \n Examples
(with made-up labels): \n \ttype == \"webserver\" && deployment
== \"prod\" \ttype in {\"frontend\", \"backend\"} \tdeployment !=
\"dev\" \t! has(label_name)"
type: string
serviceAccountSelector:
description: ServiceAccountSelector is an optional field for an expression
used to select a pod based on service accounts.
type: string
types:
description: "Types indicates whether this policy applies to ingress,
or to egress, or to both. When not explicitly specified (and so
the value on creation is empty or nil), Calico defaults Types according
to what Ingress and Egress rules are present in the policy. The
default is: \n - [ PolicyTypeIngress ], if there are no Egress rules
(including the case where there are also no Ingress rules) \n
- [ PolicyTypeEgress ], if there are Egress rules but no Ingress
rules \n - [ PolicyTypeIngress, PolicyTypeEgress ], if there are
both Ingress and Egress rules. \n When the policy is read back again,
Types will always be one of these values, never empty or nil."
items:
description: PolicyType enumerates the possible values of the PolicySpec
Types field.
type: string
type: array
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: GlobalNetworkSet
listKind: GlobalNetworkSetList
plural: globalnetworksets
singular: globalnetworkset
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
description: GlobalNetworkSet contains a set of arbitrary IP sub-networks/CIDRs
that share labels to allow rules to refer to them via selectors. The labels
of GlobalNetworkSet are not namespaced.
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: GlobalNetworkSetSpec contains the specification for a NetworkSet
resource.
properties:
nets:
description: The list of IP networks that belong to this set.
items:
type: string
type: array
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: HostEndpoint
listKind: HostEndpointList
plural: hostendpoints
singular: hostendpoint
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: HostEndpointSpec contains the specification for a HostEndpoint
resource.
properties:
expectedIPs:
description: "The expected IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6) of the endpoint.
If \"InterfaceName\" is not present, Calico will look for an interface
matching any of the IPs in the list and apply policy to that. Note:
\tWhen using the selector match criteria in an ingress or egress
security Policy \tor Profile, Calico converts the selector into
a set of IP addresses. For host \tendpoints, the ExpectedIPs field
is used for that purpose. (If only the interface \tname is specified,
Calico does not learn the IPs of the interface for use in match
\tcriteria.)"
items:
type: string
type: array
interfaceName:
description: "Either \"*\", or the name of a specific Linux interface
to apply policy to; or empty. \"*\" indicates that this HostEndpoint
governs all traffic to, from or through the default network namespace
of the host named by the \"Node\" field; entering and leaving that
namespace via any interface, including those from/to non-host-networked
local workloads. \n If InterfaceName is not \"*\", this HostEndpoint
only governs traffic that enters or leaves the host through the
specific interface named by InterfaceName, or - when InterfaceName
is empty - through the specific interface that has one of the IPs
in ExpectedIPs. Therefore, when InterfaceName is empty, at least
one expected IP must be specified. Only external interfaces (such
as \"eth0\") are supported here; it isn't possible for a HostEndpoint
to protect traffic through a specific local workload interface.
\n Note: Only some kinds of policy are implemented for \"*\" HostEndpoints;
initially just pre-DNAT policy. Please check Calico documentation
for the latest position."
type: string
node:
description: The node name identifying the Calico node instance.
type: string
ports:
description: Ports contains the endpoint's named ports, which may
be referenced in security policy rules.
items:
properties:
name:
type: string
port:
type: integer
protocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
required:
- name
- port
- protocol
type: object
type: array
profiles:
description: A list of identifiers of security Profile objects that
apply to this endpoint. Each profile is applied in the order that
they appear in this list. Profile rules are applied after the selector-based
security policy.
items:
type: string
type: array
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: IPAMBlock
listKind: IPAMBlockList
plural: ipamblocks
singular: ipamblock
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: IPAMBlockSpec contains the specification for an IPAMBlock
resource.
properties:
affinity:
type: string
allocations:
items:
type: integer
# TODO: This nullable is manually added in. We should update controller-gen
# to handle []*int properly itself.
nullable: true
type: array
attributes:
items:
properties:
handle_id:
type: string
secondary:
additionalProperties:
type: string
type: object
type: object
type: array
cidr:
type: string
deleted:
type: boolean
strictAffinity:
type: boolean
unallocated:
items:
type: integer
type: array
required:
- allocations
- attributes
- cidr
- strictAffinity
- unallocated
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: IPAMConfig
listKind: IPAMConfigList
plural: ipamconfigs
singular: ipamconfig
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: IPAMConfigSpec contains the specification for an IPAMConfig
resource.
properties:
autoAllocateBlocks:
type: boolean
maxBlocksPerHost:
description: MaxBlocksPerHost, if non-zero, is the max number of blocks
that can be affine to each host.
type: integer
strictAffinity:
type: boolean
required:
- autoAllocateBlocks
- strictAffinity
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: IPAMHandle
listKind: IPAMHandleList
plural: ipamhandles
singular: ipamhandle
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: IPAMHandleSpec contains the specification for an IPAMHandle
resource.
properties:
block:
additionalProperties:
type: integer
type: object
deleted:
type: boolean
handleID:
type: string
required:
- block
- handleID
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ippools.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: IPPool
listKind: IPPoolList
plural: ippools
singular: ippool
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: IPPoolSpec contains the specification for an IPPool resource.
properties:
allowedUses:
description: AllowedUse controls what the IP pool will be used for. If
not specified or empty, defaults to ["Tunnel", "Workload"] for back-compatibility
items:
type: string
type: array
blockSize:
description: The block size to use for IP address assignments from
this pool. Defaults to 26 for IPv4 and 112 for IPv6.
type: integer
cidr:
description: The pool CIDR.
type: string
disableBGPExport:
description: 'Disable exporting routes from this IP Pool’s CIDR over
BGP. [Default: false]'
type: boolean
disabled:
description: When disabled is true, Calico IPAM will not assign addresses
from this pool.
type: boolean
ipip:
description: 'Deprecated: this field is only used for APIv1 backwards
compatibility. Setting this field is not allowed, this field is
for internal use only.'
properties:
enabled:
description: When enabled is true, ipip tunneling will be used
to deliver packets to destinations within this pool.
type: boolean
mode:
description: The IPIP mode. This can be one of "always" or "cross-subnet". A
mode of "always" will also use IPIP tunneling for routing to
destination IP addresses within this pool. A mode of "cross-subnet"
will only use IPIP tunneling when the destination node is on
a different subnet to the originating node. The default value
(if not specified) is "always".
type: string
type: object
ipipMode:
description: Contains configuration for IPIP tunneling for this pool.
If not specified, then this is defaulted to "Never" (i.e. IPIP tunneling
is disabled).
type: string
nat-outgoing:
description: 'Deprecated: this field is only used for APIv1 backwards
compatibility. Setting this field is not allowed, this field is
for internal use only.'
type: boolean
natOutgoing:
description: When nat-outgoing is true, packets sent from Calico networked
containers in this pool to destinations outside of this pool will
be masqueraded.
type: boolean
nodeSelector:
description: Allows IPPool to allocate for a specific node by label
selector.
type: string
vxlanMode:
description: Contains configuration for VXLAN tunneling for this pool.
If not specified, then this is defaulted to "Never" (i.e. VXLAN
tunneling is disabled).
type: string
required:
- cidr
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ipreservations.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: IPReservation
listKind: IPReservationList
plural: ipreservations
singular: ipreservation
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: IPReservationSpec contains the specification for an IPReservation
resource.
properties:
reservedCIDRs:
description: ReservedCIDRs is a list of CIDRs and/or IP addresses
that Calico IPAM will exclude from new allocations.
items:
type: string
type: array
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: kubecontrollersconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: KubeControllersConfiguration
listKind: KubeControllersConfigurationList
plural: kubecontrollersconfigurations
singular: kubecontrollersconfiguration
scope: Cluster
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: KubeControllersConfigurationSpec contains the values of the
Kubernetes controllers configuration.
properties:
controllers:
description: Controllers enables and configures individual Kubernetes
controllers
properties:
namespace:
description: Namespace enables and configures the namespace controller.
Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform reconciliation
with the Calico datastore. [Default: 5m]'
type: string
type: object
node:
description: Node enables and configures the node controller.
Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
hostEndpoint:
description: HostEndpoint controls syncing nodes to host endpoints.
Disabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
autoCreate:
description: 'AutoCreate enables automatic creation of
host endpoints for every node. [Default: Disabled]'
type: string
type: object
leakGracePeriod:
description: 'LeakGracePeriod is the period used by the controller
to determine if an IP address has been leaked. Set to 0
to disable IP garbage collection. [Default: 15m]'
type: string
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform reconciliation
with the Calico datastore. [Default: 5m]'
type: string
syncLabels:
description: 'SyncLabels controls whether to copy Kubernetes
node labels to Calico nodes. [Default: Enabled]'
type: string
type: object
policy:
description: Policy enables and configures the policy controller.
Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform reconciliation
with the Calico datastore. [Default: 5m]'
type: string
type: object
serviceAccount:
description: ServiceAccount enables and configures the service
account controller. Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform reconciliation
with the Calico datastore. [Default: 5m]'
type: string
type: object
workloadEndpoint:
description: WorkloadEndpoint enables and configures the workload
endpoint controller. Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform reconciliation
with the Calico datastore. [Default: 5m]'
type: string
type: object
type: object
etcdV3CompactionPeriod:
description: 'EtcdV3CompactionPeriod is the period between etcdv3
compaction requests. Set to 0 to disable. [Default: 10m]'
type: string
healthChecks:
description: 'HealthChecks enables or disables support for health
checks [Default: Enabled]'
type: string
logSeverityScreen:
description: 'LogSeverityScreen is the log severity above which logs
are sent to the stdout. [Default: Info]'
type: string
prometheusMetricsPort:
description: 'PrometheusMetricsPort is the TCP port that the Prometheus
metrics server should bind to. Set to 0 to disable. [Default: 9094]'
type: integer
required:
- controllers
type: object
status:
description: KubeControllersConfigurationStatus represents the status
of the configuration. It's useful for admins to be able to see the actual
config that was applied, which can be modified by environment variables
on the kube-controllers process.
properties:
environmentVars:
additionalProperties:
type: string
description: EnvironmentVars contains the environment variables on
the kube-controllers that influenced the RunningConfig.
type: object
runningConfig:
description: RunningConfig contains the effective config that is running
in the kube-controllers pod, after merging the API resource with
any environment variables.
properties:
controllers:
description: Controllers enables and configures individual Kubernetes
controllers
properties:
namespace:
description: Namespace enables and configures the namespace
controller. Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform
reconciliation with the Calico datastore. [Default:
5m]'
type: string
type: object
node:
description: Node enables and configures the node controller.
Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
hostEndpoint:
description: HostEndpoint controls syncing nodes to host
endpoints. Disabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
autoCreate:
description: 'AutoCreate enables automatic creation
of host endpoints for every node. [Default: Disabled]'
type: string
type: object
leakGracePeriod:
description: 'LeakGracePeriod is the period used by the
controller to determine if an IP address has been leaked.
Set to 0 to disable IP garbage collection. [Default:
15m]'
type: string
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform
reconciliation with the Calico datastore. [Default:
5m]'
type: string
syncLabels:
description: 'SyncLabels controls whether to copy Kubernetes
node labels to Calico nodes. [Default: Enabled]'
type: string
type: object
policy:
description: Policy enables and configures the policy controller.
Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform
reconciliation with the Calico datastore. [Default:
5m]'
type: string
type: object
serviceAccount:
description: ServiceAccount enables and configures the service
account controller. Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform
reconciliation with the Calico datastore. [Default:
5m]'
type: string
type: object
workloadEndpoint:
description: WorkloadEndpoint enables and configures the workload
endpoint controller. Enabled by default, set to nil to disable.
properties:
reconcilerPeriod:
description: 'ReconcilerPeriod is the period to perform
reconciliation with the Calico datastore. [Default:
5m]'
type: string
type: object
type: object
etcdV3CompactionPeriod:
description: 'EtcdV3CompactionPeriod is the period between etcdv3
compaction requests. Set to 0 to disable. [Default: 10m]'
type: string
healthChecks:
description: 'HealthChecks enables or disables support for health
checks [Default: Enabled]'
type: string
logSeverityScreen:
description: 'LogSeverityScreen is the log severity above which
logs are sent to the stdout. [Default: Info]'
type: string
prometheusMetricsPort:
description: 'PrometheusMetricsPort is the TCP port that the Prometheus
metrics server should bind to. Set to 0 to disable. [Default:
9094]'
type: integer
required:
- controllers
type: object
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: networkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: NetworkPolicy
listKind: NetworkPolicyList
plural: networkpolicies
singular: networkpolicy
scope: Namespaced
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
properties:
egress:
description: The ordered set of egress rules. Each rule contains
a set of packet match criteria and a corresponding action to apply.
items:
description: "A Rule encapsulates a set of match criteria and an
action. Both selector-based security Policy and security Profiles
reference rules - separated out as a list of rules for both ingress
and egress packet matching. \n Each positive match criteria has
a negated version, prefixed with \"Not\". All the match criteria
within a rule must be satisfied for a packet to match. A single
rule can contain the positive and negative version of a match
and both must be satisfied for the rule to match."
properties:
action:
type: string
destination:
description: Destination contains the match criteria that apply
to destination entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
http:
description: HTTP contains match criteria that apply to HTTP
requests.
properties:
methods:
description: Methods is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply only to HTTP requests that use one of
the listed HTTP Methods (e.g. GET, PUT, etc.) Multiple
methods are OR'd together.
items:
type: string
type: array
paths:
description: 'Paths is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply to HTTP requests that use one of the
listed HTTP Paths. Multiple paths are OR''d together.
e.g: - exact: /foo - prefix: /bar NOTE: Each entry may
ONLY specify either a `exact` or a `prefix` match. The
validator will check for it.'
items:
description: 'HTTPPath specifies an HTTP path to match.
It may be either of the form: exact: <path>: which matches
the path exactly or prefix: <path-prefix>: which matches
the path prefix'
properties:
exact:
type: string
prefix:
type: string
type: object
type: array
type: object
icmp:
description: ICMP is an optional field that restricts the rule
to apply to a specific type and code of ICMP traffic. This
should only be specified if the Protocol field is set to "ICMP"
or "ICMPv6".
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
ipVersion:
description: IPVersion is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only match a specific IP version.
type: integer
metadata:
description: Metadata contains additional information for this
rule
properties:
annotations:
additionalProperties:
type: string
description: Annotations is a set of key value pairs that
give extra information about the rule
type: object
type: object
notICMP:
description: NotICMP is the negated version of the ICMP field.
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
notProtocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: NotProtocol is the negated version of the Protocol
field.
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
protocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: "Protocol is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic of a specific IP protocol. Required
if any of the EntityRules contain Ports (because ports only
apply to certain protocols). \n Must be one of these string
values: \"TCP\", \"UDP\", \"ICMP\", \"ICMPv6\", \"SCTP\",
\"UDPLite\" or an integer in the range 1-255."
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
source:
description: Source contains the match criteria that apply to
source entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
required:
- action
type: object
type: array
ingress:
description: The ordered set of ingress rules. Each rule contains
a set of packet match criteria and a corresponding action to apply.
items:
description: "A Rule encapsulates a set of match criteria and an
action. Both selector-based security Policy and security Profiles
reference rules - separated out as a list of rules for both ingress
and egress packet matching. \n Each positive match criteria has
a negated version, prefixed with \"Not\". All the match criteria
within a rule must be satisfied for a packet to match. A single
rule can contain the positive and negative version of a match
and both must be satisfied for the rule to match."
properties:
action:
type: string
destination:
description: Destination contains the match criteria that apply
to destination entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
http:
description: HTTP contains match criteria that apply to HTTP
requests.
properties:
methods:
description: Methods is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply only to HTTP requests that use one of
the listed HTTP Methods (e.g. GET, PUT, etc.) Multiple
methods are OR'd together.
items:
type: string
type: array
paths:
description: 'Paths is an optional field that restricts
the rule to apply to HTTP requests that use one of the
listed HTTP Paths. Multiple paths are OR''d together.
e.g: - exact: /foo - prefix: /bar NOTE: Each entry may
ONLY specify either a `exact` or a `prefix` match. The
validator will check for it.'
items:
description: 'HTTPPath specifies an HTTP path to match.
It may be either of the form: exact: <path>: which matches
the path exactly or prefix: <path-prefix>: which matches
the path prefix'
properties:
exact:
type: string
prefix:
type: string
type: object
type: array
type: object
icmp:
description: ICMP is an optional field that restricts the rule
to apply to a specific type and code of ICMP traffic. This
should only be specified if the Protocol field is set to "ICMP"
or "ICMPv6".
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
ipVersion:
description: IPVersion is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only match a specific IP version.
type: integer
metadata:
description: Metadata contains additional information for this
rule
properties:
annotations:
additionalProperties:
type: string
description: Annotations is a set of key value pairs that
give extra information about the rule
type: object
type: object
notICMP:
description: NotICMP is the negated version of the ICMP field.
properties:
code:
description: Match on a specific ICMP code. If specified,
the Type value must also be specified. This is a technical
limitation imposed by the kernel's iptables firewall,
which Calico uses to enforce the rule.
type: integer
type:
description: Match on a specific ICMP type. For example
a value of 8 refers to ICMP Echo Request (i.e. pings).
type: integer
type: object
notProtocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: NotProtocol is the negated version of the Protocol
field.
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
protocol:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
description: "Protocol is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic of a specific IP protocol. Required
if any of the EntityRules contain Ports (because ports only
apply to certain protocols). \n Must be one of these string
values: \"TCP\", \"UDP\", \"ICMP\", \"ICMPv6\", \"SCTP\",
\"UDPLite\" or an integer in the range 1-255."
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
source:
description: Source contains the match criteria that apply to
source entity.
properties:
namespaceSelector:
description: "NamespaceSelector is an optional field that
contains a selector expression. Only traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) endpoints within the selected
namespaces will be matched. When both NamespaceSelector
and another selector are defined on the same rule, then
only workload endpoints that are matched by both selectors
will be selected by the rule. \n For NetworkPolicy, an
empty NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only workload endpoints in the same namespace
as the NetworkPolicy. \n For NetworkPolicy, `global()`
NamespaceSelector implies that the Selector is limited
to selecting only GlobalNetworkSet or HostEndpoint. \n
For GlobalNetworkPolicy, an empty NamespaceSelector implies
the Selector applies to workload endpoints across all
namespaces."
type: string
nets:
description: Nets is an optional field that restricts the
rule to only apply to traffic that originates from (or
terminates at) IP addresses in any of the given subnets.
items:
type: string
type: array
notNets:
description: NotNets is the negated version of the Nets
field.
items:
type: string
type: array
notPorts:
description: NotPorts is the negated version of the Ports
field. Since only some protocols have ports, if any ports
are specified it requires the Protocol match in the Rule
to be set to "TCP" or "UDP".
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
notSelector:
description: NotSelector is the negated version of the Selector
field. See Selector field for subtleties with negated
selectors.
type: string
ports:
description: "Ports is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that has a source (destination)
port that matches one of these ranges/values. This value
is a list of integers or strings that represent ranges
of ports. \n Since only some protocols have ports, if
any ports are specified it requires the Protocol match
in the Rule to be set to \"TCP\" or \"UDP\"."
items:
anyOf:
- type: integer
- type: string
pattern: ^.*
x-kubernetes-int-or-string: true
type: array
selector:
description: "Selector is an optional field that contains
a selector expression (see Policy for sample syntax).
\ Only traffic that originates from (terminates at) endpoints
matching the selector will be matched. \n Note that: in
addition to the negated version of the Selector (see NotSelector
below), the selector expression syntax itself supports
negation. The two types of negation are subtly different.
One negates the set of matched endpoints, the other negates
the whole match: \n \tSelector = \"!has(my_label)\" matches
packets that are from other Calico-controlled \tendpoints
that do not have the label \"my_label\". \n \tNotSelector
= \"has(my_label)\" matches packets that are not from
Calico-controlled \tendpoints that do have the label \"my_label\".
\n The effect is that the latter will accept packets from
non-Calico sources whereas the former is limited to packets
from Calico-controlled endpoints."
type: string
serviceAccounts:
description: ServiceAccounts is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates from
(or terminates at) a pod running as a matching service
account.
properties:
names:
description: Names is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account whose name is in the list.
items:
type: string
type: array
selector:
description: Selector is an optional field that restricts
the rule to only apply to traffic that originates
from (or terminates at) a pod running as a service
account that matches the given label selector. If
both Names and Selector are specified then they are
AND'ed.
type: string
type: object
services:
description: "Services is an optional field that contains
options for matching Kubernetes Services. If specified,
only traffic that originates from or terminates at endpoints
within the selected service(s) will be matched, and only
to/from each endpoint's port. \n Services cannot be specified
on the same rule as Selector, NotSelector, NamespaceSelector,
Nets, NotNets or ServiceAccounts. \n Ports and NotPorts
can only be specified with Services on ingress rules."
properties:
name:
description: Name specifies the name of a Kubernetes
Service to match.
type: string
namespace:
description: Namespace specifies the namespace of the
given Service. If left empty, the rule will match
within this policy's namespace.
type: string
type: object
type: object
required:
- action
type: object
type: array
order:
description: Order is an optional field that specifies the order in
which the policy is applied. Policies with higher "order" are applied
after those with lower order. If the order is omitted, it may be
considered to be "infinite" - i.e. the policy will be applied last. Policies
with identical order will be applied in alphanumerical order based
on the Policy "Name".
type: number
selector:
description: "The selector is an expression used to pick pick out
the endpoints that the policy should be applied to. \n Selector
expressions follow this syntax: \n \tlabel == \"string_literal\"
\ -> comparison, e.g. my_label == \"foo bar\" \tlabel != \"string_literal\"
\ -> not equal; also matches if label is not present \tlabel in
{ \"a\", \"b\", \"c\", ... } -> true if the value of label X is
one of \"a\", \"b\", \"c\" \tlabel not in { \"a\", \"b\", \"c\",
... } -> true if the value of label X is not one of \"a\", \"b\",
\"c\" \thas(label_name) -> True if that label is present \t! expr
-> negation of expr \texpr && expr -> Short-circuit and \texpr
|| expr -> Short-circuit or \t( expr ) -> parens for grouping \tall()
or the empty selector -> matches all endpoints. \n Label names are
allowed to contain alphanumerics, -, _ and /. String literals are
more permissive but they do not support escape characters. \n Examples
(with made-up labels): \n \ttype == \"webserver\" && deployment
== \"prod\" \ttype in {\"frontend\", \"backend\"} \tdeployment !=
\"dev\" \t! has(label_name)"
type: string
serviceAccountSelector:
description: ServiceAccountSelector is an optional field for an expression
used to select a pod based on service accounts.
type: string
types:
description: "Types indicates whether this policy applies to ingress,
or to egress, or to both. When not explicitly specified (and so
the value on creation is empty or nil), Calico defaults Types according
to what Ingress and Egress are present in the policy. The default
is: \n - [ PolicyTypeIngress ], if there are no Egress rules (including
the case where there are also no Ingress rules) \n - [ PolicyTypeEgress
], if there are Egress rules but no Ingress rules \n - [ PolicyTypeIngress,
PolicyTypeEgress ], if there are both Ingress and Egress rules.
\n When the policy is read back again, Types will always be one
of these values, never empty or nil."
items:
description: PolicyType enumerates the possible values of the PolicySpec
Types field.
type: string
type: array
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: networksets.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
group: crd.projectcalico.org
names:
kind: NetworkSet
listKind: NetworkSetList
plural: networksets
singular: networkset
scope: Namespaced
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
description: NetworkSet is the Namespaced-equivalent of the GlobalNetworkSet.
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: NetworkSetSpec contains the specification for a NetworkSet
resource.
properties:
nets:
description: The list of IP networks that belong to this set.
items:
type: string
type: array
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
---
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-kube-controllers-rbac.yaml
# Include a clusterrole for the kube-controllers component,
# and bind it to the calico-kube-controllers serviceaccount.
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
rules:
# Nodes are watched to monitor for deletions.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
# Pods are watched to check for existence as part of IPAM controller.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
# IPAM resources are manipulated when nodes are deleted.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- ippools
- ipreservations
verbs:
- list
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- blockaffinities
- ipamblocks
- ipamhandles
verbs:
- get
- list
- create
- update
- delete
- watch
# kube-controllers manages hostendpoints.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- hostendpoints
verbs:
- get
- list
- create
- update
- delete
# Needs access to update clusterinformations.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- clusterinformations
verbs:
- get
- create
- update
# KubeControllersConfiguration is where it gets its config
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- kubecontrollersconfigurations
verbs:
# read its own config
- get
# create a default if none exists
- create
# update status
- update
# watch for changes
- watch
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: calico-kube-controllers
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
---
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-node-rbac.yaml
# Include a clusterrole for the calico-node DaemonSet,
# and bind it to the calico-node serviceaccount.
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: calico-node
rules:
# The CNI plugin needs to get pods, nodes, and namespaces.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
# EndpointSlices are used for Service-based network policy rule
# enforcement.
- apiGroups: ["discovery.k8s.io"]
resources:
- endpointslices
verbs:
- watch
- list
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- endpoints
- services
verbs:
# Used to discover service IPs for advertisement.
- watch
- list
# Used to discover Typhas.
- get
# Pod CIDR auto-detection on kubeadm needs access to config maps.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- nodes/status
verbs:
# Needed for clearing NodeNetworkUnavailable flag.
- patch
# Calico stores some configuration information in node annotations.
- update
# Watch for changes to Kubernetes NetworkPolicies.
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- watch
- list
# Used by Calico for policy information.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- pods
- namespaces
- serviceaccounts
verbs:
- list
- watch
# The CNI plugin patches pods/status.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- pods/status
verbs:
- patch
# Calico monitors various CRDs for config.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- globalfelixconfigs
- felixconfigurations
- bgppeers
- globalbgpconfigs
- bgpconfigurations
- ippools
- ipreservations
- ipamblocks
- globalnetworkpolicies
- globalnetworksets
- networkpolicies
- networksets
- clusterinformations
- hostendpoints
- blockaffinities
- caliconodestatuses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
# Calico must create and update some CRDs on startup.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- ippools
- felixconfigurations
- clusterinformations
verbs:
- create
- update
# Calico must update some CRDs.
- apiGroups: [ "crd.projectcalico.org" ]
resources:
- caliconodestatuses
verbs:
- update
# Calico stores some configuration information on the node.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
# These permissions are only required for upgrade from v2.6, and can
# be removed after upgrade or on fresh installations.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- bgpconfigurations
- bgppeers
verbs:
- create
- update
# These permissions are required for Calico CNI to perform IPAM allocations.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- blockaffinities
- ipamblocks
- ipamhandles
verbs:
- get
- list
- create
- update
- delete
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- ipamconfigs
verbs:
- get
# Block affinities must also be watchable by confd for route aggregation.
- apiGroups: ["crd.projectcalico.org"]
resources:
- blockaffinities
verbs:
- watch
# The Calico IPAM migration needs to get daemonsets. These permissions can be
# removed if not upgrading from an installation using host-local IPAM.
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources:
- daemonsets
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: calico-node
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: calico-node
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: calico-node
namespace: kube-system
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-node.yaml
# This manifest installs the calico-node container, as well
# as the CNI plugins and network config on
# each master and worker node in a Kubernetes cluster.
kind: DaemonSet
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: calico-node
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: calico-node
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: calico-node
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: calico-node
spec:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
# Make sure calico-node gets scheduled on all nodes.
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
# Mark the pod as a critical add-on for rescheduling.
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
serviceAccountName: calico-node
# Minimize downtime during a rolling upgrade or deletion; tell Kubernetes to do a "force
# deletion": https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod/#termination-of-pods.
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
priorityClassName: system-node-critical
initContainers:
# This container performs upgrade from host-local IPAM to calico-ipam.
# It can be deleted if this is a fresh installation, or if you have already
# upgraded to use calico-ipam.
- name: upgrade-ipam
image: harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/cni:v3.21.6
command: ["/opt/cni/bin/calico-ipam", "-upgrade"]
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
# Allow KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST and KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT to be overridden for eBPF mode.
name: kubernetes-services-endpoint
optional: true
env:
- name: KUBERNETES_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: CALICO_NETWORKING_BACKEND
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: calico_backend
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/cni/networks
name: host-local-net-dir
- mountPath: /host/opt/cni/bin
name: cni-bin-dir
securityContext:
privileged: true
# This container installs the CNI binaries
# and CNI network config file on each node.
- name: install-cni
image: harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/cni:v3.21.6
command: ["/opt/cni/bin/install"]
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
# Allow KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST and KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT to be overridden for eBPF mode.
name: kubernetes-services-endpoint
optional: true
env:
# Name of the CNI config file to create.
- name: CNI_CONF_NAME
value: "10-calico.conflist"
# The CNI network config to install on each node.
- name: CNI_NETWORK_CONFIG
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: cni_network_config
# Set the hostname based on the k8s node name.
- name: KUBERNETES_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
# CNI MTU Config variable
- name: CNI_MTU
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: veth_mtu
# Prevents the container from sleeping forever.
- name: SLEEP
value: "false"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host/opt/cni/bin
name: cni-bin-dir
- mountPath: /host/etc/cni/net.d
name: cni-net-dir
securityContext:
privileged: true
# Adds a Flex Volume Driver that creates a per-pod Unix Domain Socket to allow Dikastes
# to communicate with Felix over the Policy Sync API.
- name: flexvol-driver
image: harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.21.6
volumeMounts:
- name: flexvol-driver-host
mountPath: /host/driver
securityContext:
privileged: true
containers:
# Runs calico-node container on each Kubernetes node. This
# container programs network policy and routes on each
# host.
- name: calico-node
image: harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/node:v3.21.6
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
# Allow KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST and KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT to be overridden for eBPF mode.
name: kubernetes-services-endpoint
optional: true
env:
# Use Kubernetes API as the backing datastore.
- name: DATASTORE_TYPE
value: "kubernetes"
# Wait for the datastore.
- name: WAIT_FOR_DATASTORE
value: "true"
# Set based on the k8s node name.
- name: NODENAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
# Choose the backend to use.
- name: CALICO_NETWORKING_BACKEND
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: calico_backend
# Cluster type to identify the deployment type
- name: CLUSTER_TYPE
value: "k8s,bgp"
# Auto-detect the BGP IP address.
- name: IP
value: "autodetect"
# Enable IPIP
- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_IPIP
value: "Always"
# Enable or Disable VXLAN on the default IP pool.
- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_VXLAN
value: "Never"
# Set MTU for tunnel device used if ipip is enabled
- name: FELIX_IPINIPMTU
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: veth_mtu
# Set MTU for the VXLAN tunnel device.
- name: FELIX_VXLANMTU
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: veth_mtu
# Set MTU for the Wireguard tunnel device.
- name: FELIX_WIREGUARDMTU
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: calico-config
key: veth_mtu
# The default IPv4 pool to create on startup if none exists. Pod IPs will be
# chosen from this range. Changing this value after installation will have
# no effect. This should fall within `--cluster-cidr`.
# - name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR
# value: "192.168.0.0/16"
# Disable file logging so `kubectl logs` works.
- name: CALICO_DISABLE_FILE_LOGGING
value: "true"
# Set Felix endpoint to host default action to ACCEPT.
- name: FELIX_DEFAULTENDPOINTTOHOSTACTION
value: "ACCEPT"
# Disable IPv6 on Kubernetes.
- name: FELIX_IPV6SUPPORT
value: "false"
- name: FELIX_HEALTHENABLED
value: "true"
securityContext:
privileged: true
resources:
requests:
cpu: 250m
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command:
- /bin/calico-node
- -shutdown
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/calico-node
- -felix-live
- -bird-live
periodSeconds: 10
initialDelaySeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 6
timeoutSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/calico-node
- -felix-ready
- -bird-ready
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 10
volumeMounts:
# For maintaining CNI plugin API credentials.
- mountPath: /host/etc/cni/net.d
name: cni-net-dir
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /lib/modules
name: lib-modules
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /run/xtables.lock
name: xtables-lock
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /var/run/calico
name: var-run-calico
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /var/lib/calico
name: var-lib-calico
readOnly: false
- name: policysync
mountPath: /var/run/nodeagent
# For eBPF mode, we need to be able to mount the BPF filesystem at /sys/fs/bpf so we mount in the
# parent directory.
- name: sysfs
mountPath: /sys/fs/
# Bidirectional means that, if we mount the BPF filesystem at /sys/fs/bpf it will propagate to the host.
# If the host is known to mount that filesystem already then Bidirectional can be omitted.
mountPropagation: Bidirectional
- name: cni-log-dir
mountPath: /var/log/calico/cni
readOnly: true
volumes:
# Used by calico-node.
- name: lib-modules
hostPath:
path: /lib/modules
- name: var-run-calico
hostPath:
path: /var/run/calico
- name: var-lib-calico
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/calico
- name: xtables-lock
hostPath:
path: /run/xtables.lock
type: FileOrCreate
- name: sysfs
hostPath:
path: /sys/fs/
type: DirectoryOrCreate
# Used to install CNI.
- name: cni-bin-dir
hostPath:
path: /opt/cni/bin
- name: cni-net-dir
hostPath:
path: /etc/cni/net.d
# Used to access CNI logs.
- name: cni-log-dir
hostPath:
path: /var/log/calico/cni
# Mount in the directory for host-local IPAM allocations. This is
# used when upgrading from host-local to calico-ipam, and can be removed
# if not using the upgrade-ipam init container.
- name: host-local-net-dir
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/cni/networks
# Used to create per-pod Unix Domain Sockets
- name: policysync
hostPath:
type: DirectoryOrCreate
path: /var/run/nodeagent
# Used to install Flex Volume Driver
- name: flexvol-driver-host
hostPath:
type: DirectoryOrCreate
path: /usr/libexec/kubernetes/kubelet-plugins/volume/exec/nodeagent~uds
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: calico-node
namespace: kube-system
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-kube-controllers.yaml
# See https://github.com/projectcalico/kube-controllers
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
spec:
# The controllers can only have a single active instance.
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
spec:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
tolerations:
# Mark the pod as a critical add-on for rescheduling.
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: calico-kube-controllers
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
containers:
- name: calico-kube-controllers
image: harbor.iovhm.com/hub/calico/kube-controllers:v3.21.6
env:
# Choose which controllers to run.
- name: ENABLED_CONTROLLERS
value: node
- name: DATASTORE_TYPE
value: kubernetes
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /usr/bin/check-status
- -l
periodSeconds: 10
initialDelaySeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 6
timeoutSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /usr/bin/check-status
- -r
periodSeconds: 10
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
---
# This manifest creates a Pod Disruption Budget for Controller to allow K8s Cluster Autoscaler to evict
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodDisruptionBudget
metadata:
name: calico-kube-controllers
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
spec:
maxUnavailable: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: calico-kube-controllers
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-etcd-secrets.yaml
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-typha.yaml
---
# Source: calico/templates/configure-canal.yaml
挂载磁盘&&分区
yum install -y yum-utils \
xfsprogs \
device-mapper-persistent-data \
lvm2
# 查看磁盘,找到磁盘路径
fdisk -l
# 创建物理卷
pvcreate /dev/vdb #就是找到的新磁盘
# 创建逻辑卷组
# vgcreate <vg_name> <pv_path>
vgcreate vg_vdb /dev/vdb
# 创建虚拟分区
# lvcreate -n <lv_name> -l <size> <vg_name>
# -l 100%VG VG的全部大小
# -L 200G 10240M
lvcreate -n lv0 -l 100%VG vg_vdb
# 创建格式
# mkfs.xfs <lv_path>
mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_vdb/lv0
mkdir -p /data
# 挂载
echo "/dev/vg_vdb/lv0 /data xfs defaults 1 1" >> /etc/fstab #挂载到data
mount -a
df -hT
du -h --max-depth=1
查看已经存在的VG
# 显示PV
pvdisplay
pvs
# 显示vg
vgdisplay
vgs
# 显示lv
lvdisplay
lvs
# 重装操作系统后挂载已经存在的vg
sudo vgchange -ay your_vg
查看分区文件格式
fdisk -l
Disk /dev/vda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000bcb4e
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vda1 * 2048 83886079 41942016 83 Linux
“system”为“Linux”表示分区形式为MBR。“system”为“GPT”表示分区形式为GPT。
# 查看文件系统格式
lsblk -f
NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT
sdb LVM2_member 5CZc4N-IkIX-L8Ht-ptS7-X260-yFcz-3uajVe
└─data-data xfs e97e47e4-ff6c-4707-b275-e74daeae8923 /data
sda
└─sda1 ext4 414df44a-36f4-4406-bfb0-8bebe6c31e49 /
# 扩展MBR分区
growpart /dev/vda 1
磁盘扩容
# 调整PV
pvresize /dev/vdb
# 调整LV
lvresize -L +80G /dev/vg_sdb/lv0
lvresize -L +100%FREE /dev/vg_sdb/lv0
# 调整文件系统xfs文件格式
xfs_growfs /dev/mapper/vg_sdb-lv0
# xfs_growfs /data
# ext2/ext3/ext4文件格式
# resize2fs /dev/mapper/vg_sdb-lv0
私有地址网段
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10.0.0.0/8 prefix)
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16.0.0/12 prefix)
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168.0.0/16 prefix)
子网计算器:https://www.sojson.com/convert/subnetmask.html
运维常用排除方法
主机运维
# 测试磁盘写入速度
dd if=/dev/zero of=/home/testfile bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct
# 测试磁盘读取速度
dd if=/home/testfile of=/dev/null bs=1G count=l iflag=direct
# 自定义主机名称与域名
cat /etc/hosts
# 查看DNS服务器
cat /etc/resolv.conf
# 网络与端口相关
# 使用curl 测试网络连通性
curl ip:port
# 使用ip地址连接时携带主机头
curl -H "host:www.iovhm.com" ip:port
# 显示详细http请求
curl -vvv ip:port
# 测试端口开放情况
telnet ip port
# 查看主机开放端口
netstat -antlp |grep <port>
#主机性能相关
# 磁盘查看
df -h
# 内存查看
free -h
K8S常见故障
更多命令: https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/k8s-v12015
# 确定kubelet、docker运行是否正常
systemctl status docker -l
systemctl kubelet docker -l
journalctl -xeu kubelet
# 确定master主机和节点状态
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get nodes
# 查看kube-system部署的容器是否正常,对应于rancher,既为system项目
kubectl get po -n kube-system
# 对显示异常的pod查看错误
kubectl describe po -n kube-system traefik-6fd8z
# kube-system命名空间(对应于rancher为system项目)POD解释
# 软件交换机,用于服务间的网络通信,服务不通大概会和他有关系
calico-node
# 内部NDS服务器,ping服务的时候提示找不到主机,那基本就是DNS坏了
coredns
# k8sd数据持久化
etcd
# k8s控制器
kube-controller-manager
# k8s代理程序
kube-proxy
# 入口网关
traefik
更多k8s命令
# 查看集群信息
kubectl cluster-info
# 查看集群节点
kubectl get nodes
# 删除节点
kubectl delete node node42.vpclub.io
# 查看所有的namespace(对应于rancher,既为项目项目下面的明明空间)
kubectl get ns
# 查看pod信息
kubectl get pods -n your-ns-name
# 删除 pod
kubectl delete pod nginx-3654852276-2dt73 -n your-ns-name
# 获取发布部署
kubectl get deployments -n your-ns-name
# 删除deployment
kubectl delete deployment nginx -n your-ns-name
# 详细日志调试工具
kubectl describe pods podname -n your-ns-name
# 进入容器
kubectl exec -it <nginx-webapp-2067515279-1z0lb> /bin/bash -n your-ns-name
# 查看已经部署的yml配置信息
kubectl get deploy NAME -o yaml your-ns-name
# 强行删除
kubectl delete pod <pod名> --grace-period=0 --force your-ns-name
# 为node增加label
kubectl label nodes 190.vpclub.io <label>
# 删除node的label,既在label后面加 -
kubectl label nodes 190.vpclub.io <label>-
# 修改一个label ,需要增加参数 --overwrite
kubectl label nodes 190.vpclub.io role=apache --overwrite
# 节点不参与调度,同理,删除污点为在后面加 -
# 节点不参与调度并立即驱离已经存在的POD
kubectl taint nodes 190.vpclub.io node-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoExecute
# 节点不参与调度,已经被调度的不受影响
kubectl taint nodes 190.vpclub.io node-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoSchedule
# 尽可能不调度到
kubectl taint nodes 190.vpclub.io node-role.kubernetes.io/master=:PreferNoSchedule
# 删除污点
kubectl taint nodes 190.vpclub.io node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule-
k8s集群备份(迁移)工具velero
-
安装velero
# 参考地址:https://support.huaweicloud.com/bestpractice-cce/cce_bestpractice_0306.html
# 参考地址:https://github.com/vmware-tanzu/velero
# 参考地址:https://velero.io/
# 下载
curl --socks5 ss5.iovhm.com:8080 -OL https://github.com/vmware-tanzu/velero/releases/download/v1.7.0/velero-v1.7.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
## --socks5 ss5.iovhm.com:8080 # 使用 socks5 代理翻墙
## -O 保存文件
## -L 自动重定向
# 解压
tar -xvzf velero-v1.7.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# 复制到 /usr/local/bin/
cp velero /usr/local/bin/
# 配置存储位置 minio,请先自行安装minio,并将minio的 AK/SK填入下面
vi key
[default]
aws_access_key_id=
aws_secret_access_key=
###### 以下命令需要在有kubectl的那台机器执行 ######
# 安装
velero install \
--provider aws \
--image harbor.iovhm.com/hub/velero/velero:v1.7.0 \
--plugins velero/velero-plugin-for-aws:v1.2.1 \
--bucket kube-deployment \
--secret-file ./key \
--use-restic \
--use-volume-snapshots=false \
--backup-location-config region=minio,s3ForcePathStyle="true",s3Url=http://minio-test.abc.com/
## --bucket kube-deployment # minio 中的存储捅的名称,需要提前建好
## --secret-file ./key # minio ak文件路径
## region=minio # 随便填,如果是备份到其他与s3兼容系统(例如云上的对象存储),可能需要地域值。
## s3Url=http://minio-test.abc.com/ # minio的地址,注意,是客户端地址(默认9000那个),不是console地址
# 查看存储库状态,如果显示Available则表示安装成功,否则请根据屏幕提示查找问题
velero backup-location get
# 查看备份记录
velero backup get
# 建立备份
velero backup create huawei-whdev-test.2023.0715.23 --exclude-namespaces cattle-prometheus,cattle-system,fleet-system,ingress-nginx,kube-node-lease,kube-public,kube-system,velero,default
## huawei-whdev-test.2023.0715.23 ,备份名称
## --exclude-namespaces, 不备份的名字空间,多个命名空间用逗号隔开(,),注意,是k8s命名空间,不是rancher的项目名称,不指定则全部备份
## --include-namespaces, 备份这些命名空间,多个命名空间用逗号隔开(,),注意,是k8s命名空间,不是rancher的项目名称,不指定则全部备份
## 强烈建议,首次备份全备,后续不备份 kube-system,kube-public,cattle-system 等系统命名空间,总之,不是你手工建立的都不要备份,因为velero会将kube-system等系统命名空间也进行备份和恢复。可能造成k8s环境系统异常。
## kubectl get ns # 查看集群的命名空间
# 查看备份记录
velero backup get
# 备份恢复(在有kubectl的那台机器执行)
velero restore create --from-backup [备份记录名称] --include-namespaces pk-default
# 恢复并命名空间映射
velero restore create --from-backup [备份记录名称] --include-namespaces pk-default,pk-smart --namespace-mappings src:dest,src2:dest2
## --include-namespaces 需要恢复的名字空间,不指定则全部恢复
## --exclude-namespaces 不进行还原的名字空间 ,不指定则全部恢复
## 强烈建议备份的时候不要备份kube-system等命名空间,恢复的时候不要全部恢复,恢复的时候按名称一个一个恢复,因为velero会将kube-system等系统命名空间也进行备份和恢复。可能造成k8s环境系统系统异常。
minio docker-compose
# vi docker-compose.yaml
version: '3'
services:
velero-minio:
image: minio/minio:latest
restart: always # 自动重启
privileged: true
ports:
- 33900:9000 # client 端口
- 33901:9001 # console 端口
volumes:
- ./data:/data
command: server /data --console-address :9001 --address :9000
environment:
- MINIO_ROOT_USER=
- MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD=!
# 如果你的minio使用容器启动的,不是独立主机、正式使用的端口与部署的端口不一致,可能显示的地址错误
- MINIO_SERVER_URL=http://minio.abc.com
# 如果你的minio使用容器启动的,不是独立主机、正式使用的端口与部署的端口不一致,可能显示的地址错误
- MINIO_BROWSER_REDIRECT_URLhttp://minio-console.abc.com
堡垒机jumpserver使用手册
非必要,不要开放端口
先上一张图。
如图所示,网络上上有无数的人,使用工具扫描,探测默认密码、穷举简单密码。服务器一旦被攻击,轻则中木马挖矿,重则删库丢失数据,造成经济损失。
重要的事情说三遍,非必要,不要开放端口,不要映射端口。
重要的事情说三遍,非必要,不要开放端口,不要映射端口。
重要的事情说三遍,非必要,不要开放端口,不要映射端口。
默认情况下,防火墙仅应该开放80,443端口,其他端口一定要思考是否有开放的必要性
考虑到实际维护,需要进行各种调试,应该使用堡垒机进行维护,本文为自建堡垒机jumpserver使用手册,堡垒机安装管理请参看其他文章
- jumpserver安装手册
- jumpserver管理手册
- jumpserver使用手册
使用
- 登录
登录地址: https://jumpserver.devops.vppark.cn/
如果你还没有用户名,请联系管理员索取用户名密码
- 切换视图
如果你有多重身份角色,可以切换不同的视图使用不同的功能
- 我的资产
可以使用的服务器、数据库等,如果列表没有出现你需要维护的服务器,请联系系统管理员进行授权
- 远程登录
远程登录有两个入口,分别为左的web终端、右上角的图标
- 选择你需要进行连接的的资产,连接方式
左边为资产列表,右边为远程面板。点击对应的资产可以弹出连接窗口,默认使用web cli方式。
如果觉得右边的远程面板太小了,不方便,可以在资产上右键,在新窗口打开。
某些时候需要使用客户端连接、提高效率时,可以选择客户端连接方式。复制相关信息到你的客户端工具,既可以进行连接。
- 安装客户端插件
如果想使用使用客户端连接,需要安装插件
下载对应的操作系统软件版本,进行安装
注意,安装过程非常快,一闪而过,且在桌面不会留下任何图标,安装成功与否,可以参看控制面板内已经安装程序是否出现
- 远程桌面
由于windows无法容器化,使用了ubuntu xface 容器化作为远程桌面。
中文输入法支持,启动fctix
点击键盘图标,如果无法切换到中文输入法,则需要增加中文输入法
添加google pinyin输入法
# 打开终端,运行
ln -sf /usr/local/bin/navicat16 /home/ubuntu/Desktop/navicat16
-
sudo 密码,如果部分命令提示没有权限,需要sudo,请咨询管理员索要 sudo 密码
-
连接到k8s集群内的mysql或redis, 资产名称带有out-k8s的,与主机网络一致,资产名称带有in-k8s的,与k8s网络一致,连接字符串填写服务发现既可
云监控bt-monitor
及时发现问题和预警,在最终用户发现问题前,解决掉问题,是保证业务连续运行的唯一手段。
本文为宝塔出品的bt-monitor安装使用手册,由于宝塔没有提供docker版本,因此自己制作了docker版本
主要功能:主机性能监控、服务器漏洞监控、主机安全监控、URL监控、自定义脚本返回特定字符串监控
官方帮助:https://www.bt.cn/bbs/thread-116143-1-1.html
- 更新日志
2023-10-27:更新版本到v2.2.9
swr.cn-south-1.myhuaweicloud.com/vp-whdev/all-in-devops/bt-monitor:v2.2.9
2023-08-09:更新版本到v2.2.8
swr.cn-south-1.myhuaweicloud.com/vp-whdev/all-in-devops/bt-monitor:20230809
docker-compose文件
version: '3'
services:
bt-monitor:
image: swr.cn-south-1.myhuaweicloud.com/vp-whdev/all-in-devops/bt-monitor:20230708
restart: always # 自动重启
ports:
- 806:806
volumes:
- ./data:/www/server/bt-monitor/data
- ./config:/www/server/bt-monitor/config
environment:
- TZ=Asia/Shanghai
privileged: true
# bt-monitor默认是https访问方式,而k8s默认是http访问后端
# 如果在K8S部署,会提示协议不匹配
# 也由于bt-monitor默认使用的是自签名证书,会提示证书错误,需要根据ingress类型自行解决
# 如果是 traefik ingress则按如下处理
# traefik 增加跳过HTTPS验证
# - --serverstransport.insecureskipverify=true
# 服务发现增加注释,注意,是服务发现,不是POD,提示traefik使用https访问后端
# traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/service.serversscheme: https
# 主控端命令
# btm status
# btm 根据提示
# 被控端命令
# btmonitoragent status
# systemctl status btmonitoragent
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart btmonitoragent
# tail -n200 /usr/local/btmonitoragent/logs/logs.log
# 如果被控老莫名其妙下线,查看服务状态命令 btmonitoragent status 提示服务停止,可以将服务配置改为自动重启
# 本修改不是必须的,需要根据实际情况来
# 2023年7月8日,服务不会自动重连,需要修改
# vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/btmonitoragent.service
# [Service]
# Type=forking
# Restart=always
系统设置
# 进入到容器
docker exec -it d026bd353eab /bin/bash
# 输入btm,根据提示操作
# 查看安全登录地址
btm 2
# 重置管理员密码
btm 6
# 1) 重启主控服务
# 2) 查看登录地址及安全入口
# 3) 停止主控服务
# 4) 查看运行状态
# 5) 查看错误日志
# 6) 修改管理员密码(自动生成随机密码)
# 7) 关闭basic_auth
# 8) 修改管理员密码(手动输入密码)
# 9) 取消域名绑定
# 10) 修改安全入口(手动输入)
# 11) 取消IP绑定限制
# 12) 修改端口(手动输入)
# 13) 修复主控(检查错误并更新云安全监控到最新版)
# 14) 无法访问?(云安全监控故障检测自动修复程序-超强力版)
# 15) 关闭动态口令认证
# 0) 退出或按组合键[ctrl+c]
安装使用手册
根据前面的系统设置提示,得到登录地址,默认用户名为admin , 密码为btm 8 或者 btm 6 设置的密码。
- 用户绑定
根据提示操作,截止发文前,一个账号可以免费使用5台主机。
- 重置访问路径
如果觉得系统自动生成的安全域名不好记忆,可以修改入口路径
- 加入被监控主机
输入正确的主控端IP地址,点击获取命令获取被控端安装命令,到每一台被控端执行
-
对被监控主机授权
bt-monitor为收费软件,截止发文止,每个账号可以免费授权5台主机
- 主机监控信息
- 设置企业微信接收告警
- 创建微信群组
- 添加聊天机器人
将地址填入到告警设置窗口
-
添加业务监控
- URL监控
- 端口监控
- ping
- 自定义监控
如果业务监控提供的三种监控方式都不能满足你。可以使用shell进行自定义监控
- 告警规则设置
将不需要的告警规则去掉,一般只需要:
- 【主机 / 主机状态 / 主机上下线】 匹配 下线
- 【日志 / SSH登录日志 / [所有]用户最近1小时登录失败次数】 大于 5
- 【资源 / 磁盘-[所有] / 磁盘占用率】 大于 90%
- 【资源 / 内存 / 内存占用率】 大于 90%
- 【资源 / CPU / CPU使用率】 大于 90%
k8s-etcdserver-no-space
参考网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/clay-wangzhi/p/17499097.html
etcd默认的空间配额限制为2G,超出空间配额限制就会影响服务,所以需要定期清理
# 设置环境变量
ETCD_CA_CERT="/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt"
ETCD_CERT="/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt"
ETCD_KEY="/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key"
HOST_1=https://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:2379
查看集群状态
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --cacert="${ETCD_CA_CERT}" --cert="${ETCD_CERT}" --key="${ETCD_KEY}" \
--endpoints="${HOST_1}" --write-out=table endpoint status
# 查看ETCD集群报警情况
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --cacert="${ETCD_CA_CERT}" --cert="${ETCD_CERT}" --key="${ETCD_KEY}" \
--endpoints="${HOST_1}" alarm list
# 输出为:
# meberID:XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX alarm:NOSPACE
# 此处 alarm 提示 NOSPACE,需要升级 ETCD 集群的空间(默认为2G的磁盘使用空间),或者压缩老数据,升级空间后,需要使用 etcd命令,取消此报警信息,否则集群依旧无法使用
# 解决方案一:增加etcd的容量
# 修改 etcd.yaml 文件,由2G-->8G,增加以下三个参数
- --auto-compaction-mode=revision
- --auto-compaction-retention=1000
- --quota-backend-bytes=8589934592
# auto-compaction-mode=revision 按版本号压缩
# auto-compaction-retention=1000 保留近1000个revision,每5分钟自动压缩 ”latest revision” - 1000
# quota-backend-bytes 设置etcd最大容量为8G
# 修改后重启
# 解决方案二:压缩老数据清理
# 压缩老数据
# 获取当前etcd数据的修订版本(revision)
rev=$(ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --cacert="${ETCD_CA_CERT}" --cert="${ETCD_CERT}" --key="${ETCD_KEY}" \
--endpoints="${HOST_1}" endpoint status --write-out="json" | egrep -o '"revision":[0-9]*' | egrep -o '[0-9].*')
echo $rev
# 整合压缩旧版本数据
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --cacert="${ETCD_CA_CERT}" --cert="${ETCD_CERT}" --key="${ETCD_KEY}" \
--endpoints="${HOST_1}" compact $rev
# 执行碎片整理
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --cacert="${ETCD_CA_CERT}" --cert="${ETCD_CERT}" --key="${ETCD_KEY}" \
--endpoints="${HOST_1}" defrag
# 解除告警
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --cacert="${ETCD_CA_CERT}" --cert="${ETCD_CERT}" --key="${ETCD_KEY}" \
--endpoints="${HOST_1}" alarm disarm
windows server 2019安装docker
参考网址
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/virtualization/windowscontainers/quick-start/set-up-environment?tabs=dockerce#windows-server-1
安装方法
- 下载安装脚本
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/microsoft/Windows-Containers/Main/helpful_tools/Install-DockerCE/install-docker-ce.ps1
然后再powershell里面执行
.\install-docker-ce.ps1
此时可能因为docker被墙,而无法下载,先使用魔法下载到后放到文件夹内
-
执行脚本,需要在powershell里面执行
-
修改使用linux 容器
C:\ProgramData\docker\config\daemon.json
增加
"experimental":true -
重启docker
打开任务管理器,结束dockerd,在重新启动docker服务
docker-compose
容器编排概述
使用docker run 可以轻松启动一个容器,当容器比较多,又没有条件使用k8s时,可以使用dokcer-compose来编排一组容器
编写docker-compose.yaml
新建你的程序需要运行工作文件件,在此文件夹下新建docker-compose.yaml
# vi docker-compose.yaml
version: "3"
services:
hazlecast: # 服务名,可以用于服务发现
image: vpclub/hazelcast:3.7.1 # 容器镜像
network_mode: host # bridge none # 网络模式, host:直接使用主机网络,bridge:桥接网络(默认),使用桥接网络后需要开发端口
ports: # 端口开放
- 5708:5708
- 5709:5709
- 5710:5710
environment:
JAVA_OPTS: "-Dhazelcast.config=/opt/hazelcast/conf/hazelcast.xml" # 环境变量
volumes:
- ./:/opt/hazelcast/conf/ # 数据挂载
privileged: true # 特权提升,设计到读写主机文件时候需要
# command: [] # 启动命令,覆盖镜像原有命令
# 启动所有容器
docker-compose up -d
# 启动某一个容器
docker-compose up -d <service name>
# 停止所有容器
docker-compose down
nginx-ingress注释解释
官方帮助:https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/user-guide/nginx-configuration/annotations/
官方帮助:https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/user-guide/nginx-configuration/configmap/
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity: 用于指定后端服务的会话亲和性。默认为false。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity-mode: 用于指定会话亲和性的模式,可以是cookie或ip。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/app-root: 用于指定应用程序的根路径。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: 用于指定未经身份验证时的重定向URI。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: 用于指定身份验证服务的URL。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: 用于指定后端服务的协议。默认值为http。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors: 如果设置为true,则允许跨域资源共享。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/from-to-www-redirect: 如果设置为true,则重定向所有从www域名请求的HTTP请求到非www域名的HTTPS。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ingress.class: 用于指定要使用的Ingress Controller类。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/lb-method: 用于指定负载均衡方法。可以是wrr或ip_hash。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/limit-connections: 用于限制连接数。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/limit-rps: 用于限制每秒请求数。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/limit-rpm: 用于限制每分钟请求数。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/limit-whitelist: 用于指定白名单IP地址。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 用于限制客户端请求的大小。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: 用于指定连接超时时间。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: 用于指定读取超时时间。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: 用于指定发送超时时间。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/real-ip-header: 用于指定真实IP地址的HTTP头。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/redirect-to-https: 如果设置为true,则强制将HTTP请求重定向到HTTPS。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: 用于将请求重定向到另一个路径。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/server-snippet: 用于指定要添加到Nginx服务器块的自定义配置。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: 如果设置为true,则所有HTTP请求都将被重定向到HTTPS。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: 如果设置为true,则使用SSL透传。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-protocols: 用于指定允许的SSL协议。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-ciphers: 用于指定允许的SSL密码。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/whitelist-source-range: 用于指定白名单IP地址。
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS" https访问后端
coredns增加全局解析
有时候因为网络设置原因不允许回路,需要对一些域名进行全局解析到内网地址。
# kubectl edit cm coredns -n kube-system
hosts {
172.16.2.250 minio.wvpark.com
fallthrough
}
traefik-ingress注解
# 服务发现使用https访问后端
# traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/service.serversscheme: https
harbor&&docker代理&&docker被墙解决办法
下载安装包
下载地址:https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases
在线安装:配置简单,但是要能直连docker hub下载依赖镜像。
可以根据自己的网络环境选择离线安装或者在线安装,由于docker hub被墙,首选离线安装包
安装与配置
# 解压缩安装包
tar -xvzf harbor-offline-installer-v2.10.3.tgz
# 复制harbor.yml.tmpl并改名为harbor.yml
cp ./harbor.yml.tmpl ./harbor.yml
修改安装配置
# vi ./harbor.yml
# 修改主机名
hostname: harbor.iovhm.com
# 默认情况下不需要改名,如果你的80端口和443端口被占用,请修改
# 如果处于内网环境,没有域名和证书,可以将https节点注释
http:
port: 5000
# 修改harbor持久化路径
data_volume: /data/harbor/data
# 如果你的内网端口(协议)与外网端口不一致
external_url: https://harbor.iovhm.com
执行安装
# 执行安装
./install
# 安装完成后,会在安装目录多出来一个docker-compose.yaml文件
# 后续可以直接使用docker-compose启动
# 默认用户名和密码 admin /Harbor12345
# 首次登录后请更改密码
设置镜像加速代理
- 增加目标仓库
- 选择合适的目标仓库
- 创建项目,并选择为镜像代理,指定需要代理的仓库
- 为安全考虑,应该将关闭镜像仓库的公开访问选项
- 测试拉取
- 同时,在项目里面也可以看到对应的镜像
镜像加速代理之使用镜像复制
出于管理要求,全公开方式镜像代理并不是一个好的选择,使用镜像复制则可以更好的管理
- 设置复制规则
复制模式:
push-based:将本地仓库的镜像复制到目标仓库。harbor并没有仓库概念,取而代之的是项目(命名空间),既你需要将项目(library)之中的某个镜像(image)推送到远端,则本地的资源过滤器填写为 library/image
pull-based:将远程仓库的镜像复制到本地仓库,由于部分镜像的特殊性,既类似nginx,centos等镜像,并没有前缀而导致复制失败,实际上此类镜像也有前缀为library,只不过是docker默认忽略了,既,此类镜像名称应该填写为 library/nginx
目标:同步到那个仓库
扁平化:对较长的路径继续替换,可以点击帮助提示了解更多
- 开始复制
- 查看同步情况
nginx&&nginx-ingress实现灰度发布
一、名词解释
灰度发布:又名金丝雀发布、黑白发布。18世纪时,由于科技落后,矿井没有好的通风条件和瓦斯检测工具,旷工在矿井作业时经常出现瓦斯中毒现象,因此,旷工们在下井时,会携带一只金丝雀,因为金丝雀在状态好的时候,非常喜欢叫唤,通过观察金丝雀的状态,确定矿井的毒气状态。
软件新版本发布后,我们先开放给一部分用户先体验和测试,等系统稳定运行一段时间足够稳定了再逐渐全量上线新版本,最后平滑下线旧版本。称之为灰度发布
- 基于用户体系的灰度发布,针对一些特定的人群,为其写入特定的header或者cookie。
- 根据流量规则,随机抽取部分人群参与灰度测试
二、该选那个呢
- 可以控制
- 基于header可能更便于c/s端,因为b/s无法直接设置header
三、基于nginx-ingress的灰度发布
- 创建2个ingress
不出意外的话,第二个会创建不成功,需要在第二个ingress加入nginx-ingress注释
# 启用灰度发布
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
# 启用基于header的灰度规则,并指定hearder包含指定键(version),客户端传递该hearder键并将值指定为always(总是)或者never(永远不)
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header: "version"
# 指定基于hearder规则时,需要包含的值,不在局限于值为always(总是)或者never(永远不)
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value: "2.0"
# 启用基于cookie的灰度规则,并指定cookie包含指定键(version),客户端传递该cookie键并将值指定为always(总是)或者never(永远不)
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-cookie: "version"
# 网上有部分文章描述说有类似hearder规则的nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-cookie-value注解指定值,实际上没有这个注解
# 基于流量规则,值为0-100之间,既按百分比,0为不接受任何请求,其最大值(100)可以由canary-weight-total定义
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight:10
# 基于流量规则时候的最大值,默认为100,该设置可以忽略
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight-total
# 规则优先级
# canary-by-header -> canary-by-cookie -> canary-weight
# 官方帮助
# https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/blob/main/docs/user-guide/nginx-configuration/annotations.md#canary
三、测试一下基于header的方式的灰度发布
- postmain传入设定的值,查看返回结果
四、测试一下基于cookie的方式灰度发布
- 增加ingress注解
五、基于流量的规则
不推荐使用流量的规则,因为无法精确控制,因此不做测试
六、直接使用nginx灰度发布功能
如果你没有条件使用nginx-ingress,可以直接使用nginx配置文件以支持灰度发布
- 基于权重的灰度发布
upstream backend_by_weight {
server v1.example.com weight=80;
server v2.example.com weight=20;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend_by_weight;
}
}
map $http_cookie $backend_by_cooke {
default v1.example.com;
"~*version=2" v2.example.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$backend_by_cooke;
}
}
- 基于headerd灰度发布
map $http_version $backend_by_hearder {
default v1.example.com;
"2" v2.example.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$backend_by_hearder;
}
}
升级centos7内核
centos7 默认的内核是3.10,最新的k8s要求4.1以上内核,下面是升级方法
# 查看内核版本
uname -r
# 建议内核源文件
mkdir -p /usr/src/kernels
# 导入安装软件包安装公钥
rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
# 下载内核包
wget http://mirrors.coreix.net/elrepo-archive-archive/kernel/el7/x86_64/RPMS/kernel-ml-headers-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
wget http://mirrors.coreix.net/elrepo-archive-archive/kernel/el7/x86_64/RPMS/kernel-ml-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
wget http://mirrors.coreix.net/elrepo-archive-archive/kernel/el7/x86_64/RPMS/kernel-ml-devel-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
# 镜像加速下载
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/kernel/6.9.7/kernel-ml-headers-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/kernel/6.9.7/kernel-ml-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
wget qq829.cn/uploads/software/kernel/6.9.7/kernel-ml-devel-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
# 安装内核包
rpm -ih kernel-ml-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ih kernel-ml-devel-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ih kernel-ml-headers-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
# 查看启动信息
awk -F\' '$1=="menuentry " {print i++ " : " $2}' /etc/grub2.cfg
# 设置默认启动
grub2-set-default 0
# 写入启动信息
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
# 安装 kernel-ml-headers-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm 报错
#
# error: Failed dependencies:
# kernel-headers < 6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo conflicts with kernel-ml-headers-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64
# 先重启到最新的内核,卸载旧内核,再安装
# yum remove kernel-headers
# rpm -ih kernel-ml-headers-6.9.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
centos7 阿里源
CentOS-Base.repo
# 保存位置
# /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
# CentOS-Base
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
# 替换阿里ecs内网环境
sed -i -e '/mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/d' -e '/mirrors.aliyuncs.com/d' /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
# epel.repo
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
# docker源
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
ingress-nginx的几个小技巧
所有注释:https://iovhm.com/book/books/k8s/page/nginx-ingress
一个ingress绑定多个域名
原来我们是直接克隆一个,需要同时修改两个,非常麻烦
# 类似nginx.conf的 server_name
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/server-alias: a.com,b.com
后端路径不与前端路径不一致的时候重写
# ingress的path设置为/xxx/(.*),这是一个正则匹配,请自行gpt
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: $2
使用https访问后端
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS"
增加IP白名单
# 类似deny,allow
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/whitelist-source-range: 10.0.0.0/24,172.10.0.1
设置IP黑名单
# 类似deny
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/denylist-source-range: 10.0.0.0/24,172.10.0.1
增加基础身份验证
# 使用basic认证
# 创建一个键值对(opaque)密钥,
# 键为 auth
# 值为 htpasswd -c auth username 生成
# 在线生成 https://www.bejson.com/encrypt/htpasswd/
# 为ingress增加注解
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-type: basic
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-secret: basic-auth
清除状态不正常的pod&&celanPods.sh
定时清除脚本
#!/bin/bash
export PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
pods_to_delete=$(kubectl get pods --all-namespaces | grep "Terminating\|OutOfpods\|CrashLoopBackOff\|Evicted\|Error\|ContainerStatusUnknown" | awk '{print $2 " -n " $1}')
if [ -z "$pods_to_delete" ]; then
echo "没有需要删除的Pods"
else
echo "$pods_to_delete" | xargs -I {} sh -c 'echo Deleting pod {}; kubectl delete pod {} --force --grace-period=0'
fi
增加到定时任务
# crontab -e
0 */1 * * * /root/cleanPod.sh >> /root/cleanPod.log 2>&1
# 2>&1 , 指示将错误流重定向到输出流
k8s网络无法通讯一例
因为k8s需要使用iptables映射端口和流量,如果缺少模块,可能导致k8s网络不可用
# 查看iptables模块释放加载
lsmod | grep ip_tables
lsmod | grep iptable_nat
# vi /etc/systemd/system/load-iptables-modules.service
[Unit]
Description=Load iptables modules
Before=network-pre.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/sbin/modprobe ip_tables
ExecStart=/sbin/modprobe iptable_nat
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# systemctl enable load-iptables-modules.service